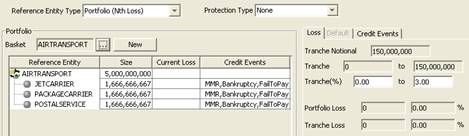
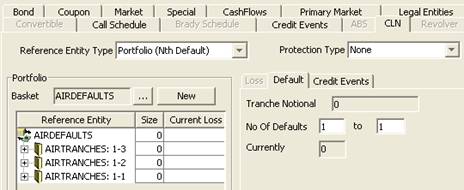
Defining Bond Products
Prior to trading a bond, you need to create the Bond product.
From the Calypso Navigator, navigate to Configuration > Fixed Income > Bond Product Definition to open the Bond window.
When you open the Bond window, the Bond panel is selected by default.
 You can view existing bonds using the Bond Report.
You can view existing bonds using the Bond Report.
|
Contents - Specifying Market Conventions - Specifying Special Characteristics - Specifying Primary Market Information |
Defining Specific Bond and Product Types |
1. Defining a Bond
Select the Bond panel to define a bond.
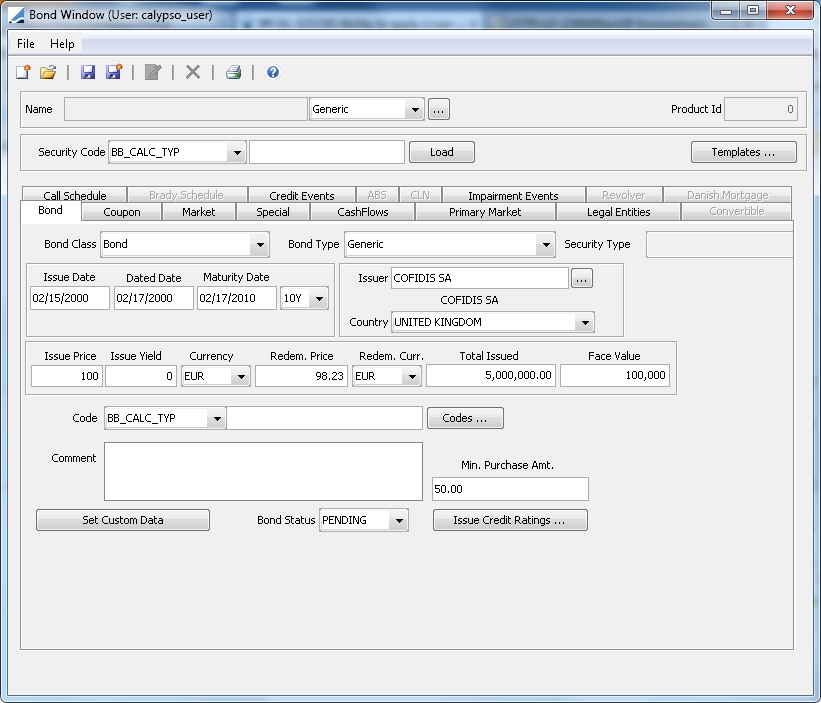
Bond Product Definition Window
1.1 Loading an Existing Bond
You can load an existing bond into the Bond Product window using one of the following methods:
| » | Select a security code from the Security Code list, and enter the actual code value in the adjacent field. |
Then click Load to load the corresponding bond.
| » | You can also click Load at the bottom of the window to open the Product Chooser window. |
Then enter the fields described below.
1.2 Creating a New Bond
You can create a new bond using one of the following methods.
| » | If you have specified bond defaults, select a bond default next to the Name field. It will populate the corresponding fields in the Bond window. You can click ... to create new bond defaults. |
| » | If you have specified bond templates, click Templates and choose “Load Template”. It will populate the corresponding fields in the Bond window. |
| » | Otherwise, click New and enter the fields in the Bond panel and in the other panels as applicable. The fields are described below. |
1.3 Manipulating Bond Templates
You can save the current bond as a bond template, or load an existing bond template to create a new bond.
| » | Click Templates to manipulate bond templates. |
You can convert all bond defaults to bond templates, load a bond template, remove a bond template, and save the current bond as a bond template.
1.4 Modifying a Bond Name
| » | Click Update Name to modify the bond’s name. You will be prompted to enter a new name. |
1.5 Setting Custom Data
| » | Click Set Custom Data to specify custom data as applicable. It invokes a class named apps.product.BondCustomDataWindow that implements com.calypso.apps.product.CustomDataWindow, provided it is implemented and compiled. Refer to the Calypso Developer’s Guide for details. |
1.6 Saving a Bond
| » | Click Save to save your changes. You will be prompted to enter a bond name. |
| – | When a bond is saved, you can save the quote type. By default the proposed quote type is the one specified in the Market panel. |
| – | You will also be prompted to generate the corporate actions for the bond. You can then apply the corporate actions using Trade Lifecycle > Corporate Action > Corporate Action – Apply panel, or the scheduled task CORPORATE_ACTION. |
| » | You can also click Save As New to save the bond as a new bond. You will be prompted to enter a new bond name. |
1.7 Setting Credit Data
| » | Click Issue Credit Ratings to set credit data at the bond level (they can also be set at the issuer level). The Product Credit Rating report will appear. |
| – | Select an agency, a rating type, a value, and a date range then choose ProductCreditRating > Add New Rating (F5) to add the rating value. |
| – | You can also use this report to display existing rating values. |
Ⓘ [NOTE: Access permissions are needed to add, modify or delete a credit rating in the Product Credit Report Rating window. Functions must be configured in the function domain]
1.8 Printing a Bond Ticket
| » | Click Print to print a bond ticket using the default template. |
| – | The default template can be customized as described under Defining a Bond Ticket Template. |
|
Fields |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Name |
Name given by the user when the bond is saved. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Product Id |
Unique id given by the system when the bond is saved. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bond Class |
Select a bond class. The following bond classes are available out-of-the-box:
Ⓘ [NOTE: MBSArm and MBSFixedRate are not currently supported] Bond classes are defined in the productType domain.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bond Type |
Select a bond type. For each bond class, there is a list of bond types in the <bond class>.subtype domain, for example Bond.subtype. The bond type will be used for pricer / curve selection to compute the Yield-to-Price formula. You can create bond types as applicable for reporting purposes. For the “Azeri” bond type, all frequency tenors will be treated as day-based. E.g. Quarterly will be treated as exact 90D and semi-annual will be treated as exact 180D. Ⓘ [NOTE: Domain names are case-sensitive] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Security Type |
You can select a security type provided security types are defined in domain <Bond Class>.extendedType, for example Bond.extendedType. The security type can be used for pricer / curve selection, and reporting purposes. Ⓘ [NOTE: Domain names are case-sensitive] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue Date |
Enter the issue date. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Dated Date |
Enter the accrual calculation start date. Bonds with a Dated Date > Issue Date PricerBondGeneric can compute bonds with a Dated Date > Issue Date. For example, on a Spanish Government bond defined with Issue Date = 07/15/2000 and Dated Date 09/01/2002, it is possible to input trades between the issue date and the dated date in order to obtain the settlement amount, i.e. without any accruals calculation. Similarly, a bond with Dated Date < Issue Date may be purchased on its issue date with accrued interest. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Maturity Date |
You can enter the maturity date, or select a maturity offset. If you select a maturity offset, the maturity date will be calculated as dated date + maturity offset. Date can be left blank for perpetual bonds. You need to set the stub end date however to determine how far to generate the cashflows. Ⓘ [NOTE: The maturity date for a perpetual bond defaults to +60,000 days after the val date. This behavior can be overridden at the API level] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuer |
Click ... to select the issuer. The issuer is a legal entity of role Issuer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Country |
Defaults to the country of the issuer. Modify as applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue Price |
Enter the issue price. Issue Price Base You can specify a different base to use for Issue Price and Redemption Price using the product code "Issue Price Base". If left blank, the default is base 100. Example: Taiwanese bills are entered in base 10,000.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue Yield |
Used in defining Chilean Bond products. Enter the Tasa Efectiva Real Anual (TERA) rate for the bond. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Currency |
Select the issue currency. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Redem. Price |
Enter the redemption price. Issue Price Base You can specify a different base to use for Issue Price and Redemption Price using the product code "Issue Price Base". If left blank, the default is base 100. Example: Taiwanese bills are entered in base 10,000.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Redem. Curr. |
Redemption currency. Defaults to the issue currency. Select another currency as applicable. When the redemption currency differs from the issue currency, you can enter the redemption FX rate in the Market panel.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Total issued |
Enter the total face amount of the issue (original par amount used for generating the cashflows). The amount issued does not necessarily need to be correct but an amount greater than the face amount needs to be populated. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Face Value |
Enter the face value. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Code |
Displays the default code selected in Configuration > User Access Control > User Defaults, and its associated value in the adjacent field. Click Codes to enter the actual code values.
You can create product codes using Configuration > Product > Code. You can add security codes to the domain securityCode.ReprocessTrades that require checking if trades need to be reprocessed if the security codes are modified. You can update security codes in bulk using the Bond report.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Comment |
Enter a free comment as applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Min. Purchase Amt |
Enter a minimum amount required to trade that bond as needed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Bond Status |
Only applies to Bloomberg static data integration. Shows the status of the integration. You can change it as applicable. It is available in the Bond report for filtering bonds and as a column “Bond Status”, and as a static data filter element. |
2. Specifying the Coupon
Select the Coupon panel to specify the coupon.
2.1 Specifying a Fixed Rate
The Fixed Rate label is displayed by default.

| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Rate |
Enter the fixed rate. |
|
Ccy |
Select the coupon currency. |
|
Daycount |
Enter the coupon daycount. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
|
Quoting Ccy |
In the case of an All-In Price Quote, set the quoting currency to be the same as the coupon currency. Otherwise, set it to match the bond currency. If you set the quoting currency to match the coupon currency, it assumes the quote includes the FX rate conversion and inflation adjustment. |
2.2 Specifying a Floating Rate
Double-click the Fixed Rate label to switch to Floating Rate.
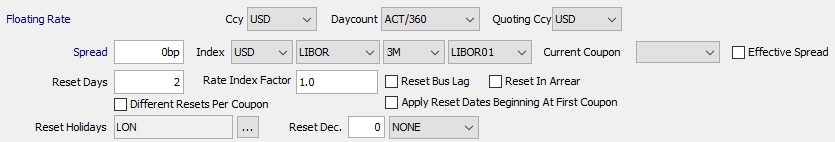
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|||||||||||||||
|
Ccy |
Select the coupon currency. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Daycount |
Enter the coupon daycount. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Quoting Ccy |
In the case of an All-In Price Quote, set the quoting currency to be the same as the coupon currency. Otherwise, set it to match the bond currency. If you set the quoting currency to match the coupon currency, it assumes the quote includes the FX rate conversion and inflation adjustment. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Spread |
Enter a spread value in basis points over the floating rate. Note that this field can be customized to apply a change in spread to the remaining cashflows, in the case of auctioned bonds for example, where the spread changes on the auction date.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Index |
Select the currency, rate index, tenor and source that identify the floating rate. Rate indices are specified using Configuration > Interest Rates > Rate Index Definitions. Note that you can choose an index with a currency different from the coupon currency, in the case where the security is not yet re-denominated but the index is in EUR for example. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Current Coupon |
Used by Colombian DTF and IBR-linked bonds.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Effective Spread |
Used by Colombian DTF-linked bonds.
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Reset Days |
Defaults to the reset lag specified in the Rate Index definition. Modify as applicable. This is the number of days lag for the floating rate’s fixing. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Rate Index Factor |
Enter a factor to apply to the floating rate as applicable. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Reset Bus Lag |
Check the “Reset Bus Lag” checkbox to specify the reset lag as business days, or as calendar days otherwise. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Reset In Arrear |
Check the “Reset In Arrear” checkbox to indicate that the floating rate is known at the end of the interest period, or clear this box otherwise. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Different Rates Per Coupon |
Check “Different Resets Per Coupon” to generate the reset dates based on the coupon payment frequency, or clear it to generate the reset dates based on the index tenor. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Apply Reset Dates Beginning At First Coupon |
When checked, resets will be produced starting from the issue date. Otherwise resets are produced starting at the maturity date. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Reset Holidays |
Click ... to select reset holiday calendars. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Reset Dec. |
Enter the number of decimal places and select the rounding method from the adjacent field. Used for CCT bonds for example. |
|||||||||||||||
|
You can check the "Average Resets" checkbox at the bottom of the window to sample resets at a frequency different from the payment frequency. Otherwise, the resets are sampled at the payment frequency.
Select the sampling frequency. For "WK", you can select the day of the week. When the sampling frequency is more frequent than the payment frequency, you can define the weight of the resets by double-clicking the label next to the reset frequency.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Sample Period Shift |
Only applicable with daily compounding or daily averaging. When checked, the sample weights will be shifted as per the shifted dates of the period. The shifting of observation dates will be visible in the Reset Samples window on the generated cashflows under the "Observation Start Date" and "Observation End Date" columns. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Last Coupon Only |
Only applicable with daily compounding or daily averaging. When checked, the cutoff lag will only be applied to the last interest period. |
|||||||||||||||
|
CutOffLag Holidays |
You can specify an independent holiday calendar for cutoff lag using business days. |
|||||||||||||||
|
Average Days |
Only displayed for Argentine flipper bonds with the "ARS" yield method.
|
2.3 Specifying a Variable Rate
Double-click the Fixed Rate label to switch to Variable.

| » | Click ... to display the Coupon Schedule dialog. |
| – | Select a coupon date rule, or enter a start date, an end date and select a frequency. Then click Generate to generate the corresponding coupon schedule. |
| – | Enter coupon rates (as absolute values) in the coupon schedule as applicable. The coupon rate will apply up to the specified period end date. |
| – | Then click Apply. |
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Ccy |
Select the coupon currency. |
|
Daycount |
Enter the coupon daycount. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
|
Quoting Ccy |
In the case of an All-In Price Quote, set the quoting currency to be the same as the coupon currency. Otherwise, set it to match the bond currency. If you set the quoting currency to match the coupon currency, it assumes the quote includes the FX rate conversion and inflation adjustment. |
2.4 Specifying an Exotic Rate
Double-click the Fixed Rate label to switch to Exotic.
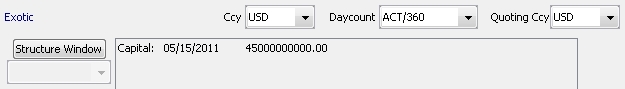
| » | Click Structure Window to display the Structured Dialog. Help is available from that window. When the formula is applied, it is displayed in the formula area. |
You can also select an exotic structure type if you have defined any. See Configuration > Product > Structure Type Creator for details.
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Ccy |
Select the coupon currency. |
|
Daycount |
Enter the coupon daycount. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
|
Quoting Ccy |
In the case of an All-In Price Quote, set the quoting currency to be the same as the coupon currency. Otherwise, set it to match the bond currency. If you set the quoting currency to match the coupon currency, it assumes the quote includes the FX rate conversion and inflation adjustment. |
|
Acc Daycount |
Enter the accrual daycount. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
2.5 Specifying Payment Characteristics
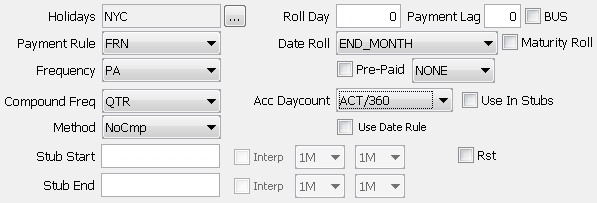
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Holidays |
Click ... to select payment holiday calendars. Note that if you save a bond without a holiday calendar, a warning message will appear. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Roll Day |
Enter the day of the calendar month to be used as each coupon period’s end date day. If this is set to zero, then the maturity date day of the month will automatically be used by default. So, for example, if the issue date is 7/10/04, the maturity date is 7/20/34, the coupon frequency is SA (semi-annual), and a value of 16 is entered in this field, the coupon payment dates will be 7/16 and 1/16 (there will be ‘stub’ periods at both the beginning and the end). |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Payment Lag BUS |
Enter the number of days lag between the coupon date and the actual payment date, as applicable. Check the "BUS" checkbox to specify the payment lag as business days, or as calendar days otherwise. If the payment lag entered exceeds 30 days, the payment day will be calculated with a lag of 1 month for each 30 days, and then the remaining number of days added to the coupon period end date. Example: A payment lag of 44 for a security with coupon period end date on the 12th day of the month would pay on the 26th of the following month. Example: A payment lag of 54 for a security with coupon period end date on the 12th day of the month would pay on the date which is 24 days after the 12th day of the following month. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Payment Rule |
Select the payment rule. The following payment rules are available:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Date Roll |
Payment date roll convention if the coupon period end date is not a business day. Date roll conventions are described under Help > Date Roll Conventions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Maturity Roll |
When checked, the maturity principal payment Pmt Dt is used to calculate the price. If not checked, the maturity principal payment Pmt End is used to calculate the price. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Frequency |
Select the payment frequency. The standard list is: DLY (Daily), WK (Weekly), BIWK(Bi-Weekly), LUN (Lunar), MTH (Monthly), BIM (Bi-Monthly), QTR (Quarterly), SA (Semi-Annually), PA (Annually), ZC (Zero Coupon, End of period). You can check "Use Date Rule" instead to generate the coupon based on a date rule. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Pre-Paid |
Allows you to specify BondMMInterest products for which the coupon is paid at the beginning of the period. The calculation of the Coupon amount is exactly the same as the classic BondMMInterest except that it is paid by the Issuer at the beginning instead of the end of the period. The FX Reset Date for Dual Currency Bonds will be calculated based on the checkbox selection. When checked, the FX reset date will be calculated using the coupon begin date. If unchecked, the reset date is calculated using the coupon end date.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Compound Freq |
Select the reset frequency. By default it is the same as the payment frequency. The weekly frequency "WK(R)" works as follows. For a 3M bond paying MONTHLY compounding WEEKLY, this method splits the 90 days into 3 periods of 30 days each, and then splits the 30 day periods into periods of 7 days thus leaving stubs on each coupon period. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Acc Daycount |
Daycount used for the accrual calculation. By default, it corresponds to the coupon daycount and can be modified. Daycount conventions are described under Help > Day-Count Conventions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Use In Stubs |
Check the “Use in Stubs” checkbox to apply the accrual daycount to stub periods. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Method |
Select the interest calculation method:
On the CashFlow panel, right-click an INTEREST cashflow and choose “Interest History” to see its details. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Use Date Rule |
Check to select a date rule for the coupon generation rather than the frequency.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Cut-Off Lag |
Only appears if Compounding Freq = DLY. The number of days of cutoff lag to be applied every coupon period. You can specify business or calendar days by double-clicking the adjacent label. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Stub Start Stub End Interp |
Stub Start contains the security’s first coupon period end date. If the security’s first coupon period end date is standard, it is not necessary to enter this date here (although it may still be entered). Stub End contains the security’s penultimate coupon period end date. As with Stub Start, it is not necessary to enter this date if the date is standard. It must be set for perpetual bonds to determine how far out to generate the cashflows. If you have a period shorter or longer than the classic periods, you put either the first coupon’s date or the last coupon’s date. When the bond does not have the same Daycount and Accrual Daycount, and a long stub period is detected, then the Accrual Daycount is set on the Coupon, and a CouponPeriodSchedule is created for this Coupon, with two coupon periods having the following characteristics:
Periods can be seen when you right-click a cashflow in the CashFlow panel of the Bond, and choose "Show Paydown Periods" from the popup menu. Interp checkbox Only applies to floating bonds.
Whenever there is a stub on a floating rate, the system automatically calculates the best index tenor for the stub period (provided “No Auto Interp” is unchecked on the rate index definition). If the length of a stub period matches exactly one of the index tenors, there is no interpolation required. If the length of a stub period is between two index tenors, the system defaults the stub index to interpolate between the two index tenors. You can customize these tenors using the "Interp" checkbox and the adjacent tenor fields. If no interpolation is required, select the same tenor in both boxes. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interp Rounding |
The field "Interpolated Rates" is used to determine the rounding, and support rounding for BondFRN Interpolated Rate in Stub. By default, the Interpolated Rates should be set to match the rounding set in the rate index. The drop-down can be set from: Nearest, Up, or Down.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
3. Specifying Market Conventions
Select the Market panel to specify market conventions.
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Settle Days |
Number of days between the trade date and the settlement date. This field is used in the trade window to initialize the settlement date. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accruals Days |
Currently not used. It should be equal to the Settle Days. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Ex-Dividend BUS |
Number of days used to define the ex-dividend date. The following number of days can be specified:
If the coupon date = end of month then the ex-dividend date will also be set at end of month dates. Otherwise, it will follow the calendar month.
Check the "BUS" checkbox to specify the number of days as business days, or as calendar days otherwise. You can specify an ex-dividend schedule instead which will ignore the ex-dividend days and be used to determine the ex-dividend date.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Include ExDate |
When checked, positive accrual will be computed while valuing on ex-div date and accrual measures will be impacted. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Record Days |
Enter the number of record days prior to the coupon payment date. The record date in the cashflows will be displayed as payment end date - record days. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Redeem Days |
Enter the number of redemption record days as needed. In the cashflows, redemption record date = maturity date - redeem days. If "BUS" is checked, business days will be used to determine the record date, otherwise calendar days will be used. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Accrual Dig. |
Number of decimals for the accrual, when expressed in percentage. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NEAREST, DOWN or UP. Rounding methods are described under Help > Rounding Methods. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Price Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the price. If you do not specify the number of decimals, the system will take the value of the environment property BOND_PRICE_DECIMAL. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NEAREST, DOWN or UP. Rounding methods are described under Help > Rounding Methods. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Yield Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the yield. If you do not specify the number of decimals, the system will take the value of the environment property BOND_YIELD_DECIMAL. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NEAREST, DOWN or UP. Rounding methods are described under Help > Rounding Methods. You can specify lower and upper initial yield limits using the MIN_YIELD and MAX_YIELD pricing parameters. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Nominal Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the nominal. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Coupon Rate Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the coupon rate. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NONE, SAME AS ACCRUAL, NEAREST, DOWN or UP.
The other rounding methods are described under Help > Rounding Methods. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Capitalization Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the capitalization factor of PIK (“Payment In Kind”) bonds, such as Brady bonds. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NEAREST, DOWN or UP. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Discount Margin Dec. |
Number of decimal places for the discount margin. You can select the rounding method from the adjacent field: NEAREST, DOWN or UP. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Announce Date |
Date of announcement for a new issue (for Issuance through an issue syndicate, like Corporate Bonds). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Auction Date |
Date of auction for a new issue (for Issuance through an auction, like Government Bonds such as OAT). |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Default Date |
Only applies to Brady bonds. Enter the date at which the bond has defaulted. When a bond has defaulted, all cashflows are set to 0, except for the guaranteed cashflows specified in the Brady schedule. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Withholding Tax |
Click ... next to the Withholding Tax field to bring up the Withholding Tax Config window.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Apply Withholding Tax |
Check to apply the withholding tax to the cashflows, or uncheck otherwise. If you set the environment property SEC_WITHHOLDINGTAX=true, the withholding tax will be automatically withdrawn from the coupons, and reclaim fees will be automatically generated.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
When Issue Bond |
Check to identify a “When-Issue” bond.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
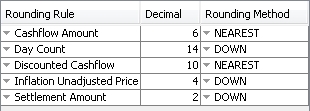
|
Rounding Rule |
You can add rounding rules as needed.
Note that you will also need to set the security code SETTLEMENT_ROUNDING_CONVENTION to total.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Tick Size |
Tick size of the quote. For Repo trades: For securities with tick size other than 100: You can convert Clean Price to decimal format when Dirty Price or Yield are specified on trade screen. For this, you need to set the security product code SECFINANCE_QUOTE_BASE =100. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Yield Method |
Method applied to convert the price to yield and the yield to price.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Quote Type |
Quote type: AOAS (Agency Option Adjusted Spread – Used for European callable bonds), Clean Price, Dirty Price, Discount, Future, Gross Price, Gross Unitary Price, Price, Price32, Price64, Spread, Unitary Price, Yield, Yield To Best, Yield To Custom, Yield To Maturity, Yield To Next, or Yield To Worst. The quote type is automatically displayed in the trade window. For the Spread quote type, you should select a benchmark. See benchmark fields below. For the Yield To Custom quote type, you must have Effective Call = Custom, and a Call Date set in the Call Schedule panel.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
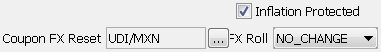
Inflation Protected |
Only applies to Mexican BPA inflation protected bonds (floating rate bond with yield method = MXN). When checked, specify an FX index in the Coupon FX Reset field, and an FX Roll convention.
The rate will be calculated as: Max(Index Rate, FX Index Rate Change) where FX Index Rate Change = (FX End Period / FX Beginning Period - 1) * 360 / Days in Period |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fixed Coupon Rate Coupon FX Reset |
Only appear if the currency of the coupon is different from the currency of the bond. You can enter a fixed FX rate in the Fixed Coupon Rate field, or select an FX Reset from the Coupon FX Reset field. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FX Roll |
Only applies to dual currency bonds. When rolled days will be included in interest calculation, select a date roll convention to determine how to roll the dates for the FX. Note that when using FX Roll, the FX reset date will be computed from the unadjusted coupon period. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fixed Redemption Rate Redem FX Reset |
When the redemption currency is different from the issue currency, you can set the FX rate as follows.
FX Rate Definitions are defined under Configuration > Foreign Exchange > FX Rate Definitions. The FX rates are reset using Trade Lifecycle > Reset > FX Rate Reset. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue Paying Agent |
Name of the Issue Paying Agent for a new issue. The agent should be previously created as a Legal Entity with the role IPA. The Issue Paying Agent will be used for issuance trades. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Calculator Agent |
Name of the calculator agent for a new issue. The agent should be previously created as a Legal Entity with the role Calculator Agent. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Trustee |
Name of the trustee of the issue. The trustee should be previously created as a Legal Entity with the role Trustee. It is used in the Domiciliation process.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Commission Paid |
Automatically checked when the domiciliation commission has been paid.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Benchmark Name |
Click the Benchmark Name radio button, if the bond is quoted in spread over a benchmark bond or bond future that will change over the life of the bond.
Note that the Quote Type should be set to Spread in that case. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Benchmark Sec |
Click the Benchmark Sec radio button, if the bond is quoted in spread over a benchmark bond that will remain the same over the life of the bond.
Note that the Quote Type should be set to Spread in that case. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Future Contract |
Click the Future Contract radio button, if the bond is quoted in spread over a benchmark bond future that will remain the same over the life of the bond.
Note that the future contract will be rolled to the next one for pricing, if the pricing occurs within the number of days specified in the Benchmark panel of the Future contract before the last trading day. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Yield Curve |
Click the Yield Curve radio button, if the bond is quoted in spread using a yield curve. Yield curves are defined using Market Data > Interest Rate Curves > Par Yield Curve from the Calypso Navigator. |
4. Specifying Special Characteristics
Select the Special panel to specify special characteristics.
4.1 Specifying Amortization Characteristics
Bullet
The Bullet label is displayed by default. The entire principal is repaid on the security at maturity.
Amortizing
Some of the principal will be repaid prior to the maturity date. A preset schedule defines the exact repayment dates, and the amount to be repaid on each date (for example, if "Equal" is specified for the Amortizing type, then the par amount will be repaid in equal installments, the final installment being on the security maturity date).
Although the par amount is entered as an original par amount (the concept of paydowns does not apply to this type of security), it does reflect the "current" original par amount.
Double-click the Bullet label to switch to Amortizing.
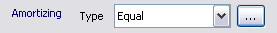
| » | Select the amortization type from the Type field. The following types of amortization are available: |
| – | Annuity: The amount of each payment (interest + principal) remains constant over the life of the bond. The interest payments will be larger at the start and decrease over time, while the principal repayments will be smaller at the start and increase over time. |
| – | Equal: The principal is amortized in equal payments for each interest period. |
| – | Step down: The principal will decrease or increase (as desired) by a specified amount. Enter the step down amount in the Amount field. |
| – | Mortgage: The principal is amortized using the fixed rate and period length of each interest period. You can specify the rounding convention for the constant payment rate in the "Mortgage Payment Rate" rounding rule on the Market panel. The last payment rate is calculated as: |
Amortizationn = Notionaln-1
Paymentn = Amorizationn + Interestn
| – | Schedule: The principal is amortized according to a user-defined schedule. Click ... to define the schedule. In the Principal Schedule window you can select from the drop down whether you want to enter amounts in terms of Quantity, Notional, or Notional Percent, which is the percent remaining of the notional value. |
| – | Custom: The principal is amortized according to the coupon schedule by user-defined amounts specified in the CashFlows panel. |
|
Amortizing Example Take a Security issued on 10/15/94 and maturing on 10/15/24. The Security is set up as "Amortizing", with Amortizing Type "Equal", and payment frequency SA (semi-annual). Total amount issued is 600,000,000. Principal-related cashflows will be: 10/15/94 (600,000,000) 4/15/95 10,000,000 10/15/95 10,000,000 4/15/96 10,000,000 etc., until the maturity date. If a Buy trade is entered for 40,000,000 settling on 11/20/94:
11/20/94 (40,000,000 * price) 4/15/95 666,666.67 10/15/95 666,666.67 4/15/96 666,666.67 etc., until the maturity date (note that there are 60 repayments between the trade settlement date and the security maturity date). If a Buy trade is entered for 40,000,000 settling on 11/20/04:
11/20/04 (40,000,000 * price) 4/15/05 1,000,000.00 10/15/05 1,000,000.00 4/15/06 1,000,000.00 etc., until the maturity date (note that there are 40 repayments between the trade settlement date and the security maturity date). |
Sinking
As with the "Amortizing" Bond, some of the principal will be repaid prior to the maturity date. A preset schedule defines the exact repayment dates and the amount to be repaid on each date (for example, if "Equal" is specified for the Sinking type, then the par amount will be repaid in equal installments, the final installment being on the security maturity date).
The Sinking Bond behaves almost identically to a BondAssetBacked security, in that there is an original par and a current par, and the current par is "paid down". The difference is that the current par is paid down on a BondAssetBacked as a result of a factor being entered, whereas the current par is paid down on a Sinking Bond as a result of a scheduled paydown taking place. Within Calypso, the scheduled paydown is tracked internally at the security level by the automatic creation of an internal factor.
As with a BondAssetBacked, the original par amount is quoted for trades in a Sinking Bond (the current par is determined by using the internal factor).
The price for a Sinking Bond relates to the current par (i.e. the calculation of the principal amount is original par * factor * price).
Unlike BondAssetBacked securities, there is no delay between the paydown effective date and the setting of the paydown amount (caused by the delay in publication of the factor) – This is ALL scheduled in advance for a Sinking Bond.
With a Sinking Bond, the market usually quotes the "original par", so these trades should be entered in Calypso in the same way as for MBS (i.e. enter original par).
With Calypso’s bond trade window, the "Nominal" field on the top left of the screen is the par (original) nominal. For any bonds that have variable notionals (amortizing, sinking, Brady, ABS, MBS, etc.), the "Current Nominal" field shows the current nominal (that is, the current principal bought/sold on the settlement date).
It is not currently possible to enter the "Current Nominal".
Double-click the Bullet label to switch to Sinking.
![]()
| » | Select the sinking type from the Type field. The following types of sinking are available: |
| – | Annuity: The face value will decrease at the fixed rate for each interest period. |
| – | Equal: The face value will decrease in equal amounts for each interest period. |
| – | Step down: The face value will decrease according to a specified amount. Enter the step down amount in the Amount field. |
| – | Mortgage: The face value will decrease at the fixed rate for each interest period. You can specify the rounding convention for the constant payment rate in the "Mortgage Payment Rate" rounding rule on the Market panel. The last payment rate is calculated as: |
Amortizationn = Notionaln-1
Paymentn = Amorizationn + Interestn
| – | Schedule: The face value will decrease according to a user-defined schedule. Click ... to define the schedule. In the Principal Schedule window you can select from the drop down whether you want to enter amounts in terms of Quantity, Notional, or Notional Percent, which is the percent remaining of the notional value. |
| – | Custom: The face value will decrease according to the coupon schedule by user-defined amounts specified in the CashFlows panel. |
|
Sinking Example Take a security issued on 3/15/04 and maturing on 3/15/34, with a Sinking schedule of "equal" payments. The coupon is SA (semi-annual). We buy 10 million par at price of 100 on the issue date. Our principal cashflows will be: 3/15/04 (10,000,000) 9/15/04 166,666.67 3/15/05 166,666.67 9/15/05 166,666.67 etc. until the last principal cashflow: 3/15/34 166,666.67 Original par and current par will be as follows:
|
4.2 Specifying Floater Characteristics
This applies to floating bonds only to set caps and floors on the floating rate.
Simple
The Simple label is displayed by default, indicating that the floating rate is dependent on the floating index rate only.
Floater
| » | Double-click the Simple label to change to Floater. |
![]()
Select the type of limit you want to set from the Type field. The following types are available:
| – | Cap: Enter a cap in the Cap field, in percentage. If you enter for example 5%, this means that if the rate on the coupon date is higher than 5%, the coupon rate will be 5% (the value of the cap). If the rate is less than 5% the rate value is used to calculate the coupon amount. |
| – | Floor: Enter a floor in the Floor field, in percentage. If you enter for example 2%, this means that if the rate on the coupon date is less than 2%, the coupon rate will be 2%. If the rate is higher, the rate value is used to calculate the coupon. Negative floor rates are not supported and if set to a negative value, floor=0 will be applied. |
| – | Collar: Enter a cap and floor in the Cap and Floor fields. |
| – | Straddle: Not currently supported. |
| – | Range: Not currently supported. |
4.3 Specifying Reconvention Characteristics
No Reconvention
The “No Reconvention” label is displayed by default, indicating that the daycount convention will apply over the life of the bond.
Reconventioned
| » | Double-click the “No Reconvention” label to switch to Reconventioned so that you can specify a new daycount convention as of a given reconvention date. |
![]()
Enter the reconvention date in the Date field.
Select the new daycount convention from the DayCount field.
4.4 Specifying Flipper Characteristics
No Flipper
The “No Flipper” label is displayed by default, indicating that the coupon type will apply over the life of the bond. If the bond has a fixed coupon, it will remain fixed, or if the bond has a floating coupon it will remain floating.
Flipper
| » | Double-click the “No Flipper” label to switch to Flipper. |
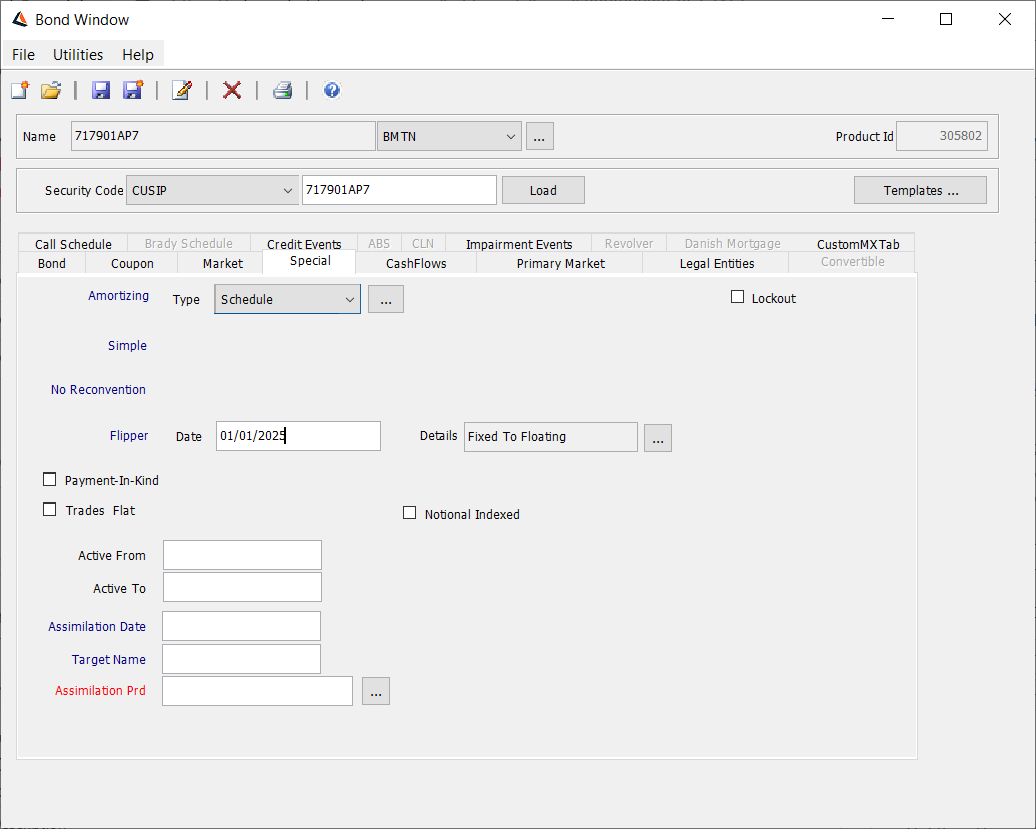
| » | Enter the flipper date in the Date field. |
| » | Click ... next to the Details field to specify the new coupon. The coupon will flip to this coupon as of the flipper date. |
| » | Enter the details related to Reset, Compounding and Average Resets while creating a Bond Flipper at the left side of the window. |
| » | Click on the Add button The details will now be displayed in the 'Flipper History' section at the right side of the window. |
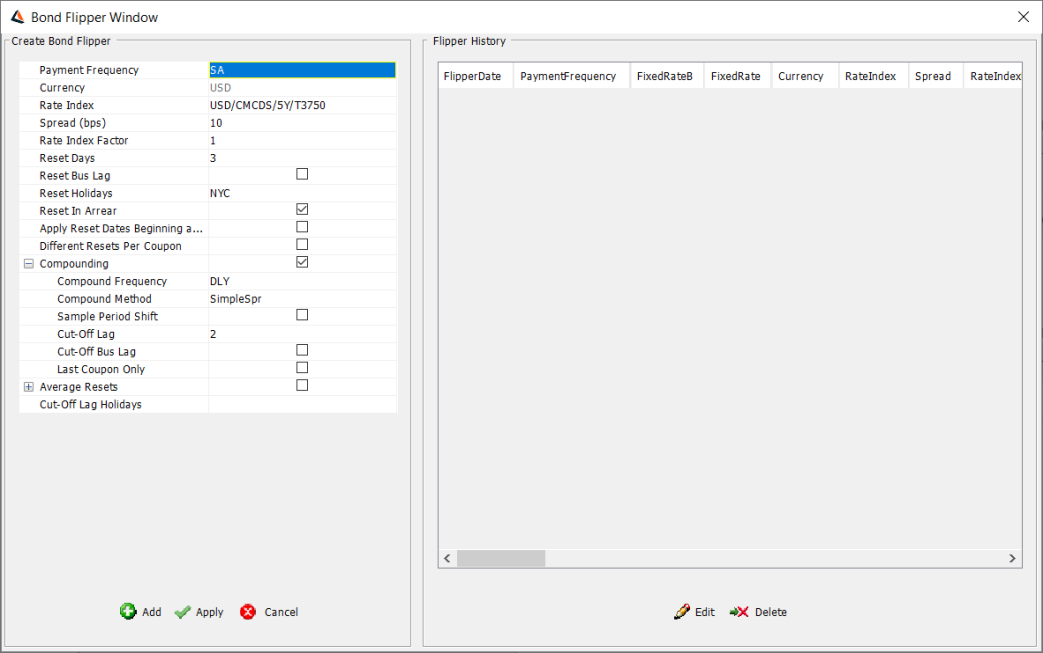
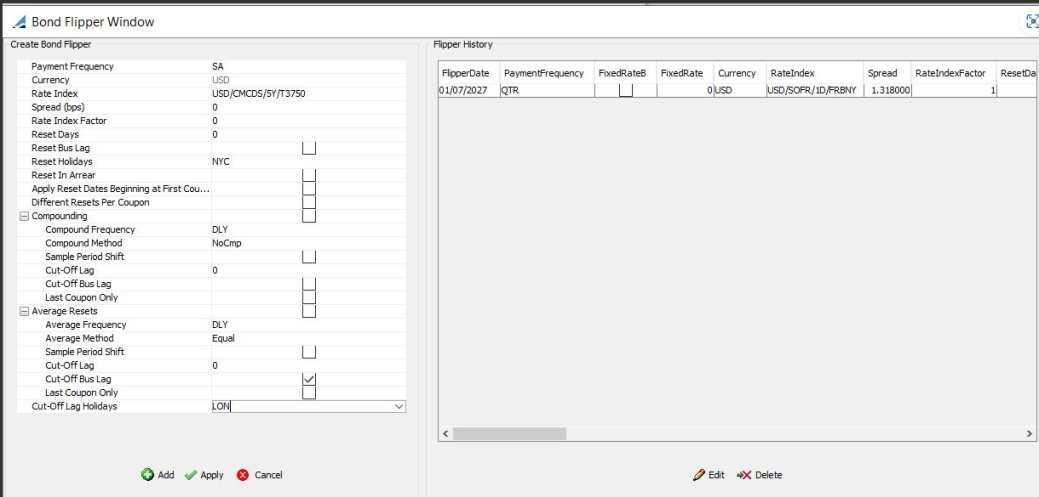
| » | Click on the Apply button - the flipper window will close. |
| » | Save the bond. |
| » | Reopen to verify that the details have been added. |
| • | Floating to fixed: Specify the fixed rate and click Apply. You can select a different coupon frequency as applicable, or select NO CHANGE if the coupon frequency does not change. |
| • | Fixed to floating or variable to floating: Specify the floating rate and click Apply. You can select a different coupon frequency as applicable, or select NO CHANGE if the coupon frequency does not change. You can also modify the fields described below as applicable. |
| • | Support has been provided for Flipper bond to RFR rate index for Fixed to Floating and Floating to Floating. You can change the leg type using the Flipper reconvention. A sample flipper reconvention is shown above. |
| • | If the original trade's leg type is Fixed, the Flipper reconvention flips the leg type to Float. You can then specify the parameters for a Float leg. |
| • | The new Flipper related properties are added to Report Framework: |
| – | For Flipper Type [Fixed to Floating | Floating to Floating | Floating to Fixed] |
| – | Flipper Rate Index: if "…to Floating" |
| – | Flipper Rate Index Tenor: if "…to Floating" |
| – | Flipper Rate Index Spread: if "…to Floating" |
| – | Flipper Coupon: if "…to Fixed" |
| • | Currently only the flipper date is available for selection in criteria. |
| • | Users are request to add only 1 line in the Flipper window. |
| • | The system can handle max of 2 lines of flipper details. This is allowed only when the old flipper data is a Non-RFR index and the security has later on changed the flipper details to have an RFR index. |
Ⓘ Note - On Config Workbench, if you export a Flipper Bond prior to upgrading to 17 June MR, you will not be able to import it after upgrade. You first need to upgrade to 17 June MR and export / import Flippers Bonds after upgrade.
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Spread |
Enter a spread value in basis points over the floating rate. |
|
Rate Index |
Select the rate index, tenor and source that identify the floating rate. Rate indices are specified using Configuration > Interest Rates > Rate Index Definitions. |
|
Rate Index Factor |
Enter a factor to apply to the floating rate as applicable. |
|
Apply Reset Dates Beginning At First Coupon |
When checked, the reset dates will be produced starting from the first coupon from the flipper date onward. Otherwise resets are produced started at the maturity date. |
|
Reset Days |
Defaults to the reset lag specified in the Rate Index definition. Modify as applicable. This is the number of days lag for the floating rate’s fixing. |
|
Reset Bus Lag |
Check the “Reset Bus Lag” checkbox to specify the reset lag as business days, or as calendar days otherwise. |
|
Reset In Arrear |
Check the “Reset In Arrear” checkbox to indicate that the floating rate is known at the end of the interest period, or clear this box otherwise. |
|
Reset Holidays |
Click ... to select reset holiday calendars. |
|
Compounding |
This includes Compound Frequency, Compound Method, Sample Period Shift, Cut-Off Lag, Cut-Off Bus Lag, Cut-Off Lag Holidays, Last Coupon Only. |
|
Average Resets |
This includes Averaging Frequency, Averaging Method, Sample Period Shift, Cut-Off Lag, Cut-Off Bus Lag, Last Coupon Only. |
|
Cut-Off Lag Holidays |
Drop-down widget for Holidays. |
4.5 Specifying Additional Characteristics
| » | Enter the fields described below as applicable. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Payment-In-Kind |
Check the "Payment-In-Kind" checkbox for specifying payment-in-kind bonds.
|
|
Trades Flat |
Check the “Trade Flat” checkbox for handling distressed bonds. You will be prompted to enter a distress date in the As Of field. The bond does not receive any coupon as of the distress date. |
|
Notional Indexed |
Check the “Notional Indexed” checkbox to specify an inflation bond.
|
|
Active From / Active To |
Range of dates when the product can be used in the system. |
|
Assimilation Date |
Input the date of the assimilation as applicable (bonds merger, for example process of French Government Bonds, with new issues’ slices). A corporate action can be generated on the assimilation date using the selected assimilation product. See the Assimilation Prd field below. |
|
Target Name |
Double-click the Target Name label to select the ISIN code of the assimilation product. |
|
Assimilation Prd |
Click ... to select the actual assimilation product. Ⓘ [NOTE: In the case of issuance assimilation, the assimilation product is set by the scheduled task ISSUANCE_CONSOLIDATION - See Capturing Bond Trades for details] |
|
Link to Basket |
Only applies to Bond, BondFRN and BondAssetBacked. When checked, the bond is eligible to belong to a basket. You can select the basket from the adjacent field. Note that this is for information purposes only.
You can click Show Basket to view the basket, and New Basket to create a new basket. Help is available from that window. |
|
Lockout |
Check the "Lockout" checkbox to specify lockout details for a UST FRN.
|
5. Generating the Cashflows
Select the CashFlows panel to generate the cashflows.
5.1 Manipulating Cashflows
Generating Cashflows
| » | Select a valuation date from the Val Date field and select a pricing environment from the Pricing Env field. |
Then click Generate. The cashflows are displayed.
Note that if you have customized the cashflows, you should not click Generate if you have not locked the columns that contain modified values, because those columns will be overridden. You should instead right-click any cell and choose 'Recalc' from the popup menu.
See also the “Customize Flows” checkbox below.
| » | Select the type of cashflows you want to display from the Display field: all cashflows, interest cashflows only, or principal cashflows only. |
| » | Check the “Forecast Unknown Flows” checkbox to forecast floating flows. |
For AusCPI bonds, it is possible to display the “p-Factor” and “K-Factor” columns provided “Forecast Unknown Flows” is checked.
Editing Cashflows
| » | Check the “Customize Flows” checkbox to modify the cashflows as applicable. A star will appear next to the label of the CashFlows panel. |
| – | To modify a value, double-click a cell and modify its value as applicable. |
A column that contains modified values will show a star to the right of the column heading.
Note that if you don’t want modified values to be overridden when the cashflows are generated, you need to lock the corresponding columns. Right-click a modified value and choose “Lock Column” or “Lock All Modified Columns” from the popup menu.
A locked column will show a star to the left of the column heading.
| – | The Manual Amt column is automatically checked when the Pmt Amt is manually modified. It indicates that changing parameters that would normally be used in the calculation (fixed rate, interest start and end dates) will have no affect since the payment amount has been manually set. |
| – | Note that when you customize any column of the bond flows, even if the Daycount column has not been customized, the accrual will be computed using the coupon daycount. If the bond flows are not customized, then the coupon amount will be computed via the coupon daycount and the accrual will be computed via the accrual daycount. |
5.2 CashFlow Menu
| » | Right-click any cell in the cashflows to display the Cash Flow Menu. |
| – | The menu items of the Cash Flow menu are described below. |
|
Menu Items |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Copy Ctl-C Paste Ctl-V |
Allows copying and pasting into values. Select a cell, type Ctrl+C, then select another cell and type Ctrl+V. The content of the first cell will be pasted into the second cell. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Add |
Right-click a row and choose Add. The selected row will be split between two rows. The first one will be one day long, and the second one will fill the remaining term of the original period. You can edit the periods as applicable. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Remove |
Right-click a row and choose Remove. The selected row will be removed. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Scheduler |
Only applies to the Notional, Spread, and Rate columns. Opens the Scheduler dialog. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Sample Values |
Not applicable to bonds. For averaging and compounding bonds, please use the Bond Trade window instead to verify sample rates as the Bond window uses curves as of the current date, and not as of the valuation date. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Check Resets |
Checks the reset rates. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Configure Columns |
Allows selecting and organizing the displayed columns. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Rename Columns |
Allows customizing the column names. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Save Configure Columns |
Allows saving the column configuration. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lock Column |
Right-click a modified value and choose “Lock Column” so that the value will not be overridden when the cashflows are generated. A locked column will show a star to the left of the column heading. Note that cashflows columns which are locked but not modified will cause the corresponding fields to be outlined in blue in the trade worksheet. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Lock All Modified Columns |
Allows locking all columns that contain modified values. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unlock Column |
Right-click a locked column and choose “Unlock Column” to unlock it. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Unlock All Columns |
Allows unlocking all locked columns. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Show Paydown Periods |
Applies to Asset Backed bonds with variable pool factors changes occurring more frequently than coupon payments. Right-click a row and choose “Show Paydown Periods” to show any paydown. This also applies to bonds with long stub periods, when the bond daycount and the accrual daycount are different. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Interest History |
Applies to floating compounding bonds. Right-click a row and choose “Interest History”. The Interest History window will be displayed. The columns are the following:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Show External Flows |
External cashflows are defaulted to Calypso-generated cashflows unless they have been imported from Bloomberg. You can paste cashflows copied from an Excel spreadsheet into the external cashflows. External cashflows are only saved once they have been modified. Right-click any cashflow to invoke a popup menu for additional capabilities. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Recalc |
When cashflows have been customized, choose Recalc to display the cashflows without overriding unlocked columns. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Generate |
To generate the cashflows. Note that if you have customized the cashflows, you should not choose Generate if you have not locked the columns that contain modified values, because those columns will be overridden. You should instead choose Recalc. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Export to Excel |
Allows exporting the cashflows to an Excel spreadsheet. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Export to HTML |
Allows exporting the cashflows to an HTML page. |
6. Specifying Primary Market Information
Select the Primary Market panel to specify issuance information. Issuance trades can be entered using Trade > Fixed Income > Issuance.
| » | Select a role from the Role field. It should be Lead_Manager or Syndicate_Member. |
| » | Click ... next to the Legal Entity field to select a legal entity for that role. |
| » | Enter a percentage in the % field. This is the percentage of the issue that the selected legal entity should purchase. |
| » | Then click Add. Repeat as needed for other members of the issuance. |
7. Specifying Product Codes by Legal Entity
Select the Legal Entities panel to specify product codes by legal entity.
You can use this panel to specify for example domiciliation codes, or specific product codes by market place.
| » | Click Insert to insert a row. |
| » | Then select a role, a legal entity, a product code, and enter a product code value. Repeat as needed. |
8. Specifying a Call Schedule
Select the Call Schedule – Calls/Redemptions panel to specify a call schedule for callable bonds and perpetual bonds. The schedule is used by the Corporate Action process to perform early redemptions as applicable.
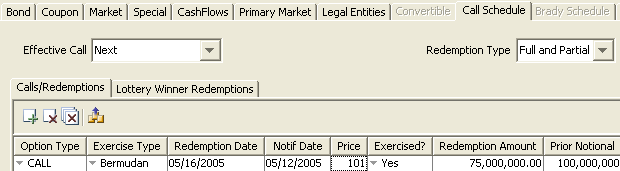
| » | Select the effective call method as applicable. |
All pricer measures are computed based on the effective call.
The system computes the effective call by first looking at the pricing parameter EFFECTIVE_CALL_METHOD to see what the effective method should be (Worst, Best, Next, Maturity, or Custom). If it is not specified in the pricing parameter, it uses the effective call method defined here.
| – | Worst: The call that would occur on the worst option, where worst is defined as the yield to that date. When the val date is past the last call date, the yield is equal to yield-to-maturity. |
| – | Best: The call that would occur on the best option, where best is defined as the yield to that date. When the val date is past the last call date, the yield is equal to yield-to-maturity. |
| – | Next: The call that would occur after the current val date. When the val date is past the last call date, the yield is equal to yield-to-maturity. |
| – | Maturity: The bond is not callable. |
| – | Custom: The call that would occur if you called on the entered call date, but using the redemption price from the call that occurs after that date. If the val date is past the custom date, then the yield behaves as yield-to-worst. |
Note that you must have Effective Call = Custom and a call date set here in order for the Yield To Custom quote type, the YIELD_TO_CUSTOM pricer measure, and the bond trade "Custom" Yield price to work.
| » | Select the redemption type as applicable: “Full and Partial” or “Full”. |
When you select “Full and Partial”, you can perform partial redemptions. In the redemption row, you can define the amount of redemption, and the outstanding notional amount will be recomputed accordingly. In order for the corporate action process to generate the corresponding corporate action, you need to set the “Exercised?” column to Yes.

You can also check “Interest Clean Up” to perform interest cleanup on the redemption date.
| » | To generate the call schedule, click |
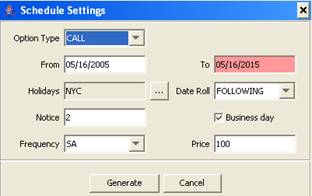
Enter the fields as needed and click Generate. The fields of the call schedule are described below.
The Notice days allow determining the notification date. Check “Business day” if the notice days are business days.
| » | You can also click |
| » | You can right-click a row to bring up the Redemption menu. It allows configuring the columns and saving the column configuration. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Option Type |
Choose between CALL and PUT. |
|
Exercise Type |
Select European, American, or Bermudan. For European Callable bonds, you need to set the quote type to AOAS, and the effective call method to Maturity to price using AOAS curves.
|
|
Redemption Date |
Enter the redemption date for European callable bonds. |
|
First Exercise Date |
Enter the first exercise date for American and Bermudan callable bonds. |
|
Notif date |
Enter the redemption notification date. |
|
Price |
Enter the redemption price. |
|
Exercised? |
Choose Yes to allow the generation of corporate actions for partial redemptions. For callable flipper bonds, when flipper date > stub end date and Exercise flag of Bond Call Schedule is checked, the cashflows ignore the flipper date and the stub end date is set to the exercise date. When flipper date > stub end date and Exercise flag is not checked, an error is generated. The Exercise flag must be set manually. |
|
Redemption Amount Prior Notional Outstanding Notional |
Only applies to redemption type “Full and Partial”. Enter the amount of notional that is redeemed. It will re-compute the outstanding notional accordingly. Note that to perform a partial redemption, you need to set the “Exercised?” column to Yes. |
|
Interest Clean Up |
Check to perform interest cleanup on the redemption date. |
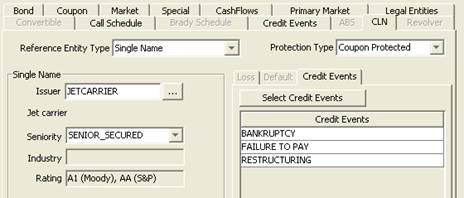
9. Loading Credit Events
Select the Credit Events panel to load credit events that apply to the selected product.
Credit events are created using Trade Lifecycle > Corporate Action > Credit Events.
| » | Click Load to load credit events that apply to the selected bond. |
10. Loading Impairment Events
Select the Impairment Events panel to load impairment events that apply to the selected product.
Impairment events are created using Trade Lifecycle > Corporate Action > Corporate Action in the context of asset impairment for the JGAAP and USGAAP accounting requirements.
A full example is given in the Calypso Positions Management User Guide.
| » | Click Load to load impairment events that apply to the selected bond. |
11. Defining a Bond Ticket Template
You can create a bond ticket template under $CALYPSO_HOME/custom/resources/<custom package>/templates/BondDealTicket.html. If this template is not found, the system will use the default template provided by Calypso.
Refer to the Calypso Developer’s Guide for information on creating custom code and custom packages.
11.1 Ticket Generation Rules
BondDealTicket.html contains rules to fetch the actual HTML templates that you want to use based on any bond criteria.
You can copy resources/calypsox/BondDealTicket.html to $CALYPSO_HOME/custom/resources/<custom package>/templates and edit it as applicable.
For example,
<!--calypso>
if ( |BOND_SUBTYPE| == "UST" )
include "BondDealTicket_Tmpl1.html";
else if ( |BOND_SUBTYPE|== "When-Issued" )
include "BondDealTicket_Tmpl2.html";
else
include "BondDealTicket_Tmpl1.html";
</calypso-->
Then BondDealTicket_Tmpl1.html and BondDealTicket_Tmpl2.html for example contain the actual ticket templates.
So, only BondDealTicket.html is a mandatory file name, then any file name can be used to define the ticket templates. Also BondDealTicket.html is NOT the actual HTML template but just a placeholder to define what ticket templates will be used.
Note that BondDealTicket.html and the ticket templates must be located in the same directory, i.e. $CALYPSO_HOME/custom/resources/<custom package>/templates.
11.2 HTML Ticket Templates
The actual ticket templates are created as standard Calypso message templates using bond-related keywords.
You have two samples under resources/calypsox/BondDealTicket_Tmpl1.html and resources/calypsox/BondDealTicket_Tmpl1.html.
For information on creating HTML templates, see Help > Message Template Keywords. The keywords specific to bond tickets are described in the Bond section.
12. Specifying Argentine Bonds
Argentine floating rate bonds include the following:
| • | BonacS4 |
| • | LedesmaC3 |
| • | TarshopC17 |
12.1 Yield Method
The yield method "ARS" has specific calculations for Argentine bonds.
 Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
12.2 Average Days
The "Average Resets" field "Average Days" is only displayed for Argentine flipper bonds with the "ARS" yield method.
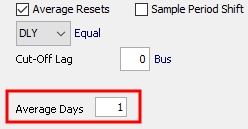
For these bonds, the averaging ignores unknown rates and averages only the known rates.
When Average Days = 1, RateCurrent = rate on Val Date or last known rate before
When Average Days = N where N is an integer > 1, RateCurrent = average of N business days, with the last day of the range being Val Date - 2 business days
 See Average Resets for details on using this field.
See Average Resets for details on using this field.
12.3 Sample Days
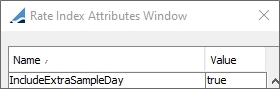
For Argentine bonds, it is a special case that the samples should go to Coupon End Date. This behavior is controlled by the index attribute IncludeExtraSampleDay.
12.4 Multiple Quote Sources
In Argentina, a bond can be traded in multiple markets, generating different quotes for the same bond.
 See Multi Quote Mapping for details.
See Multi Quote Mapping for details.
13. Specifying Asset Backed Bonds
Asset Backed Securities are securities which "pay down" based on a factor.
You can select the ABS (Asset Backed Securities) panel, provided the bond class is BondAssetBacked.
ABS bonds can be imported from Intex – Refer to the Calypso Intex Integration User Guide for details.
| » | Select the bond type as applicable. The following bond types are available: |
| – | ABS: ARM bonds are supported through the Structured Finance module – Refer to the Calypso Structured Finance User Guide for details on ARM bonds. |
| – | AUDMBS: For AUD MBS bonds. It allows saving "<quote name>.TM" quotes required by PricerBondAssetBackedAUD. |
| – | IO (Interest Only): An interest only security is essentially a stream of cashflows that represent interest on outstanding principal. Note that factors need to be captured for these securities, even though no principal paydowns apply. |
| – | PO (Principal Only): PO securities only receive principal repayments. Principal only securities are similar to zero coupon bonds since they are priced at a discount to par, but (unlike zero coupon bonds) they are typically priced with a dollar price (clean price). |
| – | Pass Through: A security which “passes through” payments of interest and principal on the underlying loans to the investor shortly after receipt from borrowers. |
| – | Principal + Interest: A mix of IO and PO. |
| – | Stripped: Stripped paydown ABS securities are created by separating the interest and principal payments from the pool of assets in order to create two new securities: PO securities and IO securities. Some paydown ABS securities may also be partially stripped so that each investor class receives some interest and some principal. |
| » | In the Special panel, you can only choose the Bullet amortization type for an ABS bond. The logic of scheduled payment is built into the pricer. |
| » | Then select the ABS panel to define the details of the ABS. The ABS panel is described below. |
| » | Once the ABS panel is defined, select the CashFlows panel to generate the cashflows. |
13.1 Coupon Panel
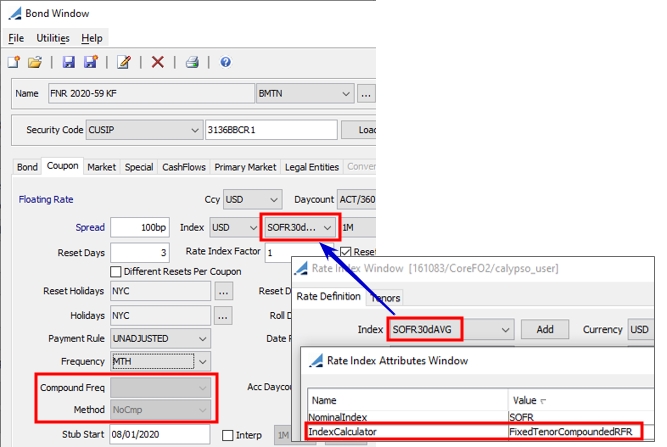
By default, the "Compound Freq" and "Method" fields in the Coupon panel are hidden for BondAssetBacked products.
You can enable them by adding the domain BondAssetBacked.showCompounding with the value "true".
When using a floating rate index with the FixedTenorCompoundedRFR index calculator to support fixed tenor deals, for example US 30 Day Average SOFR, the "Compound Freq" and "Method" fields are not available.
13.2 ABS Panel
If the principal percentage on the ABS panel is less than 100, then the system automatically reduces the principal percentage by that amount, regardless of the type. If that rate is set to 100, the system does not reduce the principal percentage.
If the bond is set up as a zero coupon bond (frequency = ZC, rate = 0, and compounding frequency = NON), then no interest payments are made, turning the bond into a principal only bond. Note that factor schedule changes still apply and cause principal paydowns. Also note that you need to set the ABS type to VARIABLE, since there is no schedule of coupons for the fixed or variable schedule to mimic.
If the ABS is set to Interest Only and your principal percentage is not less than 100, a warning is issued. If the ABS is set to Principal Only and the bond is not set up as a zero coupon bond, a warning is issued. These warnings however, do not prevent from saving the bond.
| » | Enter the ABS details as applicable. The fields are described below. |
| » | Click Add/Edit in the Factor Schedule section to add a factor. The Factor Entry dialog will be displayed. |
| – | Enter an effective date: The first date should be the issue date with a factor of 1. |
| – | Enter a factor: The value should be decreasing between 1 and 0. The factor may be > 1. |
An empty factor is an indication that the factor is not yet known, hence it will not be factored into the cashflows.
If the factor has not changed since the security issuance, it should be set to 1 (it should not be empty) so that if there is a coupon change, the coupon change will be applied.
| – | Enter a coupon rate that will be used to calculate the interest of the next period. |
| – | Enter the weighted average coupon, weighted average maturity, and weighted average loan age. |
| – | Enter shortfall and recovery amounts if any, for interest, principal and writedown. |
| » | If you modify past factors, you will be prompted to check the trades that could be impacted (i.e. trades settling in the blackout period). The list of impacted trades will appear in the Process Trades window so that you can re-process the trades to take into account the modified factors. |
ABS Identification
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Series |
Enter the series. |
|
Class |
Enter the class in the series. |
|
Groups |
Enter the group of collaterals supporting the ABS. |
|
Collateral |
Select a collateral type from the Collateral field. You can add collaterals to the BondAssetBacked.collateralType domain. |
Principal Payments
|
Fields |
Description |
|||||||||
|
Schedule Type |
Select the type of factor structure. The following types are available:
Note that for an ABS using the prepayment type PSA or CPR, the schedule type should be either Fixed Schedule or Variable Schedule. |
|||||||||
|
Factor Delay Days |
Enter the number of days between the factor’s effective date and the factor’s known date. |
|||||||||
|
Business Day |
Check the “Business Day” checkbox to indicate that the specified delay corresponds to business days, or calendar days otherwise. |
|||||||||
|
Principal Fraction |
Enter the percentage of principal that will be received at the early redemption date as applicable. |
|||||||||
|
Payment Lag |
Applies to the Variable type of factor only. Enter the number of days between the application of the paydown and its payment. If the payment lag entered exceeds 30 days, the payment day will be calculated with a lag of 1 month for each 30 days, and then the remaining number of days added to the coupon period end date. Example: A payment lag of 44 for a security with coupon period end date on the 12th day of the month would pay on the 26th of the following month. Example: A payment lag of 54 for a security with coupon period end date on the 12th day of the month would pay on the date which is 24 days after the 12th day of the following month. |
|||||||||
|
Business Day |
Applies to the Variable type of factor only. Check the “Business Day” checkbox to indicate that the specified payment lag corresponds to business days, or calendar days otherwise. |
|||||||||
|
Early Redemption Date |
Enter an early redemption date only when known. Entry of a zero factor will automatically set this field to the Effective Date of the zero factor. |
|||||||||
|
Date Roll |
Applies to the Variable type of pool factor only. Select the date roll convention to apply if the payment date falls on a non business day. |
Quotes
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Prepayment Type |
Enter the value for the Bloomberg code MTG_PREPAY_TYP: PSA, CPR, etc. |
|
Speed Assumption |
Displays the quotes of the selected prepayment type. Click Edit to enter the quote. |
|
Weighted Average Life |
Displays the weighted average life of the issue as it is published by external data feed. Click Edit to enter the WAL. This is used for calculating premium accrual, discount accrual and amortization values. A WAL of 4.5 must be interpreted as 4.5 years, not 4 years and 5 months. Double-click the “Weighted Average Life” label to bring up the Quote window showing all of the WAL quotes for the bond between the issue date and today. |
13.3 CashFlows Panel
You can display the pool factor at coupon date. Right-click any cell and choose “Configure Columns” from the popup menu to configure the display columns.
| » | Right-click an Interest cashflow and choose “Show Paydown Periods” to display the details of the paydowns of the period. |
This only applies for variable pool factors changes occurring more frequently than coupon payments.
Also the following columns are specific to asset backed bonds.
|
Columns |
Description |
|
Scheduled Payment |
Value of the Scheduled Payment (Interest + Principal) only populated for PSA bonds. |
|
Scheduled Interest |
Value of the Scheduled Interest (based on the Outstanding Principal). |
|
Scheduled Principal |
Value of the Scheduled Principal Payment (= Scheduled Payment - Scheduled Interest). |
|
CPR |
Prepay annual rate %. |
|
Estimate Principal PrePayment |
Scheduled Principal * CPR. |
|
Estimate Total Payment |
Scheduled Payment + Estimate Principal PrePayment. |
|
Estimate Pool Factor |
Pool Factor included Principal PrePayment Estimation. |
|
Estimate Face Value |
Face Value included Principal PrePayment Estimation. |
Ⓘ [NOTE: For Asset Backed bonds, the Bond Trade window should be used for verifying rates and cashflows]
13.4 External Cashflows
Asset Backed Securities require forecasts to try to predict the future cashflows (principal and interest) based on prepayment models. The external cashflows feature allows importing cashflows from Bloomberg based on a variety of forecast models.
Ⓘ [NOTE: Special license requirements may be required for some models]
To enable external cashflows, follow the steps below.
| » | Add the value “true” to the BondAssetBacked.USE_EXTERNAL_FLOWS_FOR_PRICING domain. |
| » | Add the values “BAM”, “CPY”, “CPJ”, “CPR” and any other desired prepayment model to the ABS.PrepayTypes domain. |
| » | Add the values “BAM”, “CPY”, “CPJ”, “CPR” and any other desired prepayment model to Bloomberg.PrepaymentType domain. |
Once this is enabled, all bond definitions imported from Bloomberg will use the cashflows (forecasted and historical) as specified from Bloomberg based on the chosen prepayment model. Trade cashflows will use the same cashflows defined in the bond definition.
 Please refer to the Calypso Bloomberg Data License Integration Guide for more details on importing ABS bonds from Bloomberg.
Please refer to the Calypso Bloomberg Data License Integration Guide for more details on importing ABS bonds from Bloomberg.
13.5 Special Discounting for 30/360 Daycount
For ABS bonds settling on the 31st day of the month and with 30/360 daycount convention, you need to set the domain BondAssetBacked.DC30_360_SpecialDiscountingFor31 with value "true" in order to calculate the yield based on discounting to the 1st of the next month.
13.6 REPROCESS_AFFECTED_TRADES Scheduled Task
The REPROCESS_AFFECTED_TRADES scheduled task checks if there are any pool factor changes to the bonds within 1 business day. If there is, it reprocesses the trades related to the modified bonds (pool factors only).
You need to add REPROCESS_AFFECTED_TRADES to the scheduledTask domain.
You can set a static data filter to filter trades, and select the trade action to be applied. It applies the AMEND action by default.
Whatever workflow action is used should include the workflow rule CheckBondCalculations.
14. Specifying BondMMInterest Products
Instruments with short or mid-term maturities will be entered in the system as BondMMInterest products.
Coupon Panel
| » | If the coupon is paid at the beginning of the period, check the "Pre-Paid" checkbox and select the discounting method from the adjacent field. The default is NONE. |
15. Specifying Brady Bonds
You can select the Brady Schedule panel provided the bond class is BondBrady.
| » | Select the Special panel to specify the amortization type. |
| » | Select the Brady Schedule panel to specify the principal and interest guarantee schedules. |
| » | Then select the CashFlows panel to specify the pay-in-kind rate. |
15.1 Special Panel
Brady Bonds are amortizing or sinking bonds.
| » | Double-click the Bullet label to switch to Amortizing. You can double-click one more time to change to Sinking as applicable. Then, you can select the bond amortization type or sinking type. |
 See Specifying Amortization Characteristics.
See Specifying Amortization Characteristics.
15.2 Brady Schedule Panel
| » | Click Add in the Principal Guarantee section. Then enter a guarantee period start date and end date, and a percentage of outstanding principal guaranteed for the given period. |
| » | Click Add in the Rolling Interest Guarantee section. Then enter a guarantee period start date and end date, and a percentage of interest and a number of coupons guaranteed for the given period. |
15.3 CashFlows Panel
You can display the pay-in-kind rate (Capitalization Rate). Right-click any cell and choose “Configure Columns” from the popup menu to configure the display columns.
| » | Check the “Customize Flows” checkbox, and enter the pay-in-kind rate in the Capitalization Rate field as applicable. The pay-in-kind rate is the coupon cap that accrues on the outstanding principal. |
| – | Setting the capitalization rate will compute the capitalization factor, which will in turn compute the face value, notional amount, and amortization amount. |
| – | The payment amount is computed as Rate - Capitalization Rate. |
16. Specifying Brazilian Bonds
Brazilian bonds are Brazilian government bond products issued by Tesouro Nacional. These bonds have a specific pricer associated with calculation, and each has its own sub-type.
| • | LTN – Letra do Tesouro Nacional, zero coupon national treasury bill. |
| • | LFT – Letra Financeiras do Tesouro, zero coupon financial treasury bill indexed to the SELIC rate. |
| • | NTN-F – Nota do Tesouro Nacional Serie F, fixed coupon national treasury note (series F), carries a 10% coupon paid semi-annually. |
| • | NTN-B – Nota do Tesouro Nacional Serie B, fixed coupon national treasury note (series B), indexed to the IPCA inflation index and carries a 6% coupon paid semi-annually. |
| • | NTN-C – Nota do Tesouro Nacional Serie C, fixed coupon national treasury note (series C), indexed to the IGPM inflation index and carries a 6% coupon (except for NTN-C 2031 with a 12% coupon) paid semi-annually. |
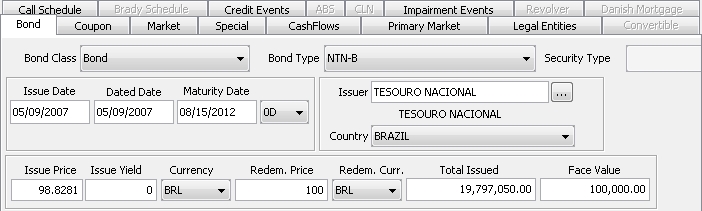
| » | Select 'Bond' for the Bond Class. |
| » | Select a Brazilian product for the Bond Type as appropriate: LTN, LFT, NTN-F, NTN-B, or NTN-C. |
| » | Enter all necessary details. |
| » | Save and name your bond. |
16.1 Daycount
Brazilian bonds typically use the daycount BU/252 with EXP. BU/252 requires that the holidays you want to exclude be set in the environment property BU252_HOLIDAYS.
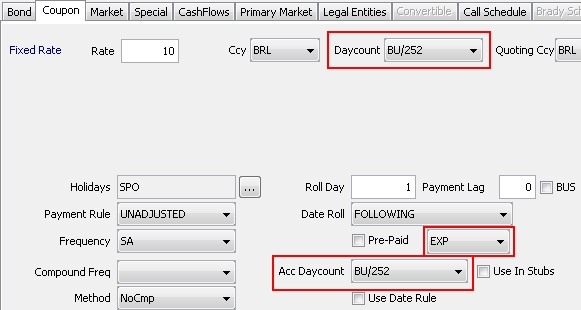
16.2 Yield Method
Brazilian bonds typically use the yield method Exponential.
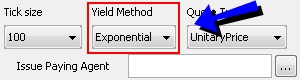
16.3 Quote Types
Two quote types support the pricing of Brazilian fixed income products.
- UnitaryPrice = Price + accrued interest (non-inflation bonds)
- GrossUnitaryPrice = UnitaryPrice + inflation price (inflation bonds)
16.4 Cashflows
For the Brazilian sub-types, cashflows are automatically calculated using the daycount convention: Daycount Fraction = Number of Months in Period / 12
16.5 Pricing
These bonds use the pricer PricerBondBrazilian. In addition to specific pricing logic, this pricer is also designed to use the following Pricer Configuration parameters.
Model Parameters panel:
| • | BOND_FROM_QUOTE – Set to false if you wish to price from curves. In this case, the discount curve will contain implicitly or explicitly both the zero curve and the market spread over the zero curve. |
| • | COMPUTE_NOTIONAL_FACTOR – Set to true to enable the projection of notional factors for T+n trades. |
| • | ZD_PRICING – When set to true, pricer measures will perform the ZD_PRICING discounting using the curve specified in the DI_CURVE parameter in the Product Specific panel. In addition, CA_COST will be discounted by PricerBondBrazilian. |
Product Specific panel:
| • | DI_CURVE – It should be set for each of the Brazilian product types. This represents the risk-free curve, and will be used for ZD_PRICING. |
|
Pricer Measures |
Description |
|---|---|
|
NOTIONAL_FACTOR01 |
The PV unadjusted by the Notional Factor. It represents the sensitivity to a change in the Notional Factor. It should only be used on bonds that are notional indexed. |
|
QUOTE_TYPE_PRICE |
Displays the price based on the appropriate formatting for the bond quote type. For example, if the quote type is UnitaryPrice or GrossUnitaryPrice, the QUOTE_TYPE_PRICE will be based on the face value like those quote types. |
16.6 LFT
For an LFT bond, you can only select a Notional Factor index.
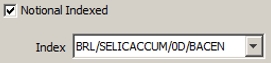
This index type uses the attribute UNDERLYING_RATE_INDEX in scenarios where the Notional Factor quote is unavailable and one needs to be projected.
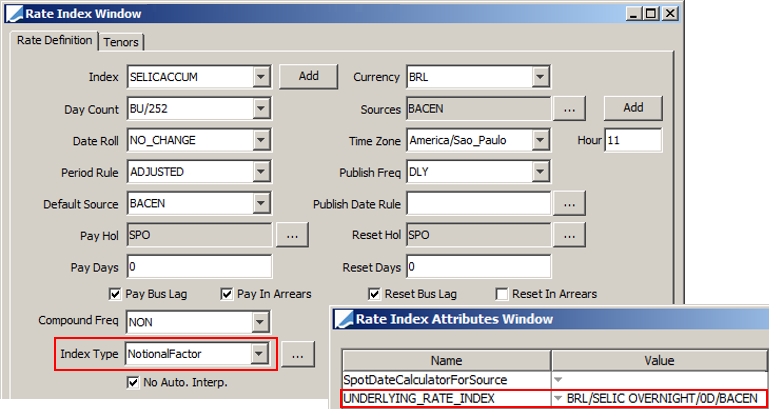
In order to properly use the Notional Factor index for LFT, you need to set the Model Parameter COMPUTE_NOTIONAL_FACTOR to true.
Reprocessing LFTs on Settle Day
When an LFT trade is settled in the future, it is based on a projected Notional Factor. It is market practice for the price and settlement of the LFT trade to be updated on the settle day, when the Notional Factor is known.
The scheduled task REPROCESS_SETTLING_TRADES can be used to recompute the Notional Factor, price, and settlement for LFT bonds. The trade filter can be configured to specify which trades should be reprocessed, for example only the LFT bond sub-type and trades settling on the Val Date.
16.7 NTN-B and NTN-C
NTN-B bonds are indexed to the IPCA inflation index. NTN-C bonds are indexed to the IGPM inflation index. They use the following attributes:
| • | IndexCalculator – Set to BrazilInflationIndex. |
| • | VariationIndex – Select an index for daily projection rates. |
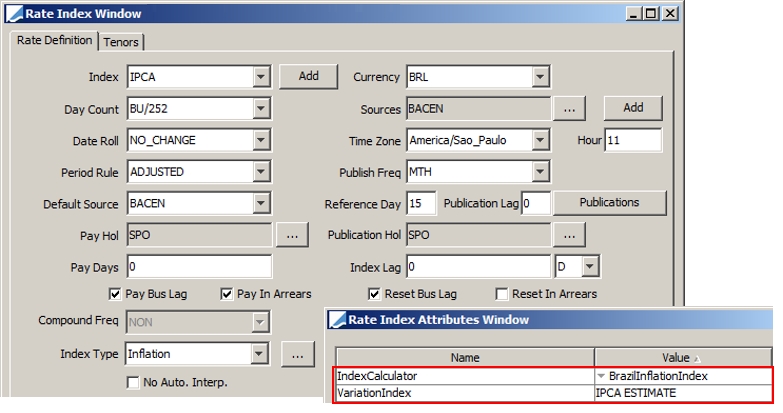
The index is typically published monthly, which is compounded by the variation index to get a value for each day.
Rate = Index Quote * (1 + Variation Index Quote / 100) ^ (Days from Last Reset to Valuation Day / Days from Last Reset to Next Reset)
16.8 Sample Trade
In the Bond Trade window, for the quote types UnitaryPrice and GrossUnitaryPrice, the quantity appears by default in place of the nominal. You can however double-click the Quantity label to switch to Nominal.
If the bond definition is associated with a legal entity of role MarketPlace in the Legal Entities panel, the MarketPlace field in the Details panel of the Bond Trade window will be automatically populated.
17. Specifying Chilean Bonds
Chilean bonds are products issued by Chilean entities or government. These bonds have a specific yield method and pricer associated with calculation. Bonds are denominated in pesos (CLP), though some bonds are denominated in UF.
UF is a non-deliverable currency with a daily spot rate that is known up to the 9th of the following month. For front and middle office purposes, it is treated as a currency, but as an index in the back office. You cannot select this currency type when creating a bond.
| » | Select 'Bond' for the Bond Class. |
| » | Select a Chilean product for the Bond Type as appropriate: PDBC, BCP, BCU, BTP, or BTU. They are described below. |
| » | Select Chile as the issuer and the country. |
| » | Select CLP as the currency. |
| » | Specify the Issue Yield (see below). |
| » | Save. |
Note that on the Coupon panel, CAMARA is set as the default index when specifying a floating rate.
17.1 Chilean Types and Pricer Measures
The following bond types and pricer measures are specified for the 'PricerBondChilean' valuation routine. Specify them in the Results panel of the Market Data window. Calypso supports the following types of Chilean bonds:
| • | PDBC (Pagares Descontables del Banco Central) – Peso denominated, short term discount issue. |
| • | BCP – Peso denominated bullet bond, semi-annual coupon. |
| • | BCU – UF denominated bullet bond, semi-annual coupon. |
| • | BTP – Peso denominated Treasury bond. |
| • | BTU – UF denominated Treasury bond. |
| • | Bonos de Reconocimiento – Bonos de Reconocimiento does not have a designated Bond Type. |
 See Bonos de Reconocimiento for details on these bonds.
See Bonos de Reconocimiento for details on these bonds.
|
Pricer Measures |
Description |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
VALOR_PAR |
K(1+yt)ACT/365
You can use a different daycount by specifying it in the security code VALOR_PAR_DAYCOUNT. Otherwise ACT/365 is used.
Bonos de Reconocimiento Bonos de Reconocimiento use a different formula for VALOR_PAR.
|
|||||||||
|
PRECIO |
100Pd / ValorPar
|
|||||||||
|
VALOR_ACTUAL |
Actual Price for Chilean bonds. 100 * (ValorPar / Precio) |
|||||||||
|
VALOR |
Value of the trade (NPV) for Chilean bonds. (Trade Nominal * ValorActual) / 100 |
|||||||||
|
VALOR_MERCADO |
Market value of a Chilean bond, displayed in CLP. If the bond is denominated in CLP, then identical calculation as VALOR. If the bond is issued in CLF or UF, then calculated as: Round(VALOR) * FX Rate The rounding precision can be set in the “Pre FX Settlement Amount” rounding rule in the bond definition Market panel.
Note that this rounding is not applied to the VALOR pricer measure itself. |
17.2 TERA
Chilean bonds have a special Issue Yield, TERA. This value is entered in the bond product definition.
| » | Enter the Issue Yield for the bond. |
Example issue yield:
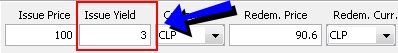
Chilean daycount conventions can be added on the Market panel in the Yield Method drop down. Chilean bonds should use Exp_ACT360 or Exp_ACT365 as a yield method. These yield methods use the ACT/360 or ACT/365 daycount conventions irrespective of the bond’s daycount. Amortizing bonds will have the 1 day payment lag suppressed when computing the yield.
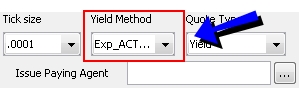
17.3 Bonos de Reconocimiento
Bonos de Reconocimiento (Recognition Bonus) is a representative document of a worker's contributions into Chile's old pension system.
Setup
Use the following setup for Bonos de Reconocimiento:
| • | Yield Method = Exp_ACT365 |
| • | Sec code COMPLETE_YEAR_MONTH_DAYCOUNT= true |
| • | Check "Notional Indexed" and specify the IPC index |
 See Specifying Inflation Bonds for details.
See Specifying Inflation Bonds for details.
| • | Pricer = PricerBondChilean |
VALOR_PAR
Bonos de Reconocimiento use a different formula for VALOR_PAR.
Where
| • | IPC1 is the last Consumer Price Index known |
| • | IPC2 is the Consumer Price Index for the previous month of the issuing date of the Bonos de Reconocimiento |
| • | R is the coupon rate, which you should set to 4% |
| • | AC is the number of complete years (round down) from issuing date to valuation date, always an integer |
| • | M is the number of complete months (round down) that remain in the fraction of the year after calculating the variable AC, always an integer |
Payment
Bonos de Reconocimiento have a single payment at maturity. The payment calculation compounds annually for full years and a monthly portion for the remainder. In Calypso, this can be broken up into a coupon and principal component.
Where
| • | IPC1 is the last Consumer Price Index known |
| • | IPC2 is the Consumer Price Index for the previous month of the issuing date of the Bonos de Reconocimiento |
| • | R is the coupon rate, which you should set to 4% |
| • | ac is the number of complete years (round down) from issuing date to maturity date, always an integer |
| • | m is the number of complete months (round down) that remain in the fraction of the year after calculating the variable ac, always an integer |
To calculate ac and m:
1. If the month for the maturity date is greater than or equal to the month of the issuing date:
ac = year of val date - year of issuing date
m = month of val date - month of issuing date
2. Else, if the month for the maturity date is less than the month of the issuing date:
ac = year of val date - year of issuing date - 1
m = month of val date + 12 - month of issuing date - 1
18. Specifying Chinese Bonds
Chinese Discount Notes are issued under par and pay accrued interest at maturity. The notes are issued at a short period and a special daycount has been modified to accommodate coupons in a leap year.
Chinese Discount Notes (defined as BondMMDiscountWithAI in Calypso) trade on clean price and accrued interest is explicitly stated in the settlement calculation.
| » | Select 'BondMMDiscountWithAI' for the Bond Class. |
| » | Select 'Discount' for the Bond Type. |
| » | Enter all necessary details. |
| » | Save and name your bond. |
18.1 Pricing
These bonds are priced using PricerBondMMDiscount.
For explanatory purposes, original issue discount (OID) is used to calculate NPV.
| – | OID = 100 - Issue Price |
| – | OID_FRACTION = OID / 100 |
| – | OID_VALUE = OID_FRACTION * Nominal |
| – | Days in Period = Maturity Date - Issue Date |
|
Pricer Measures |
Description |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ACCRUAL |
Accrued interest from issue to value plus 1 day.
|
||||||
|
ACCRUAL_BO |
If FIRST_ACCRUAL is set to 'true' in the pricing parameter, accrued interest is from issue to valuation plus 1 day.
If FIRST_ACCRUAL is set to 'false' or null, Accrual days is the same except without the extra day added. |
||||||
|
ACCRUAL_FIRST |
Calculated the same as ACCRUAL_BO, but will be subject to the FIRST_ACCRUAL pricing parameter. |
||||||
|
ACCRUAL_SETTLE_DAY |
If FIRST_ACCRUAL is set to 'true' in the pricing parameter, accrued interest is from trade settlement to valuation plus 1 day.
If FIRST_ACCRUAL is set to 'false' or null, Accrual days is the same except without the extra day added. |
||||||
|
PREM_DISC |
Chinese notes accrete to the final value of the issue price rather than par because of implicit accrued interest.
|
||||||
|
PREM_DISC_YIELD |
Yield amortizes or accretes to issue price rather than par. If trade price is lower than issue price, yield calculates down to issue price at maturity. If price is higher, yield calculates up. |
||||||
|
NPV |
The change in market value plus the accrued interest. Accrued interest is derived from the original issue discount.
|
||||||
|
NPV_NET |
Equal to the change in market value without accrued interest, accretion or amortization.
|
||||||
|
NPV_DISC |
Equal to the change in the market value with either accretion of the discount subtracted or the amortization of the premium added.
or
|
18.2 Chinese Discount Note Accounting Events
The following accounting events allow generating the proper postings for Chinese discount notes.
|
Accounting Event |
Trigger Event |
Pricer Measure |
|---|---|---|
|
COUPON_CLIP |
LIQUIDATED_POSITION from REDEMPTION corporate action. |
ACCRUAL_FIRST |
|
ACCRUAL_INC_REAL |
LIQUIDATED_POSITION from REDEMPTION corporate action. |
ACCRUAL_SETTLE_DATE |
|
PREM_DISC_YIELD_REAL |
LIQUIDATED_POSITION from REDEMPTION corporate action. |
PREM_DISC_YIELD |
|
REALIZED_CLEAN_PL |
LIQUIDATED_POSITION from REDEMPTION corporate action. |
Redemption nominal * (Issue price - trade price) |
|
ACCRUAL_REAL |
LIQUIDATED_POSITION from buy/sells. |
ACCRUAL_SETTLE_DATE |
|
ACCRUAL |
TRADE_VALUATION |
ACCRUAL_SETTLE_DATE |
|
PREM_DISC_YIELD |
TRADE_VALUATION |
PREM_DISC_YIELD |
|
MTM_DISC_YIELD |
TRADE_VALUATION |
NPV_DISC |
 See Capturing BondMMInterest and BondMMDiscount Trades for additional details.
See Capturing BondMMInterest and BondMMDiscount Trades for additional details.
19. Specifying CMTB Bonds
CMTB bonds can be used only as curve underlying instruments.
They do not have a maturity date. The coupon is fixed and the quote type is Yield.
In the Curve Underlying window, you can assign specific tenors to these bonds (or benchmark of these bonds).
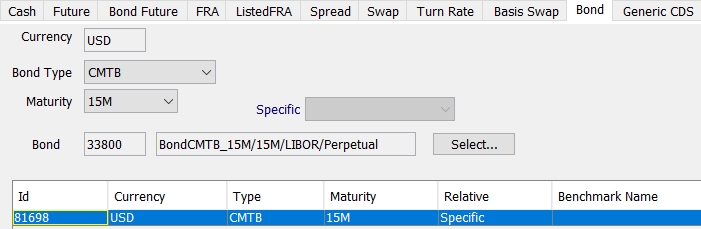
When used in a curve, the maturity date is calculated from the curve date by applying the specified tenor.
These are synthetic bonds that cannot be opened from the curve.
20. Specifying Colombian Bonds
20.1 Pricing
The Colombian bonds described below use PricerBondColombian to handle the various rate conversions and rounding requirements.
 Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
20.2 Exponential Interest Cashflow
Some Colombian bonds require that the interest cashflow be based on an exponential formula. This is specified on the Coupon panel.
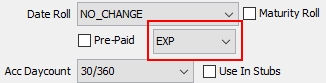
20.3 Local Corporate Bonds
Colombian non-government floating rate securities linked to the DTF, IBR, or IPC indices have various characteristics relating to the use of nominal and effective rates when issuing securities.
Current Coupon and Effective Spread
The Current Coupon and Effective Spread fields on the bond definition Coupon panel are only used by specific Colombian bonds.
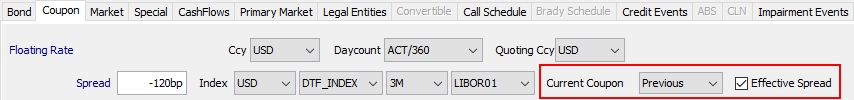
| • | Current Coupon – Only used by Colombian DTF and IBR-linked bonds, where from the settlement date to the next coupon date, the cashflows are calculated using either the "previous" rate or "current" rate. |
| – | Previous rate: Rate valid on coupon start date. |
| – | Current rate: Rate calculated using latest DTF rate on valuation date. |
Whether "previous" or "current" rate is used is determined at the time of issuance for a given bond. For future coupons, the "current" rate is always used.
| • | Effective Spread – Only used by Colombian DTF-linked bonds, where both the DTF rate and the spread are quoted in effective terms, however, the coupon rate must be in nominal terms. |
Check "Effective Spread" to convert from an effective rate to a nominal rate.
Yield Method
Colombian local corporate bonds linked to the DTF, IBR, and IPC indices use the Exp_ACT365 yield method.
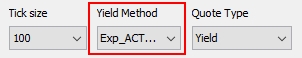
Rate Index Attributes
The following Rate Index Attributes are required to specify the Index Type and Index Convention.
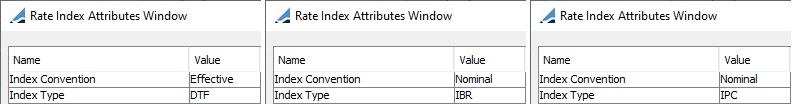
20.4 Bonos Pensionales
Colombian pension bonds, or Bonos Pensionales, are linked to the IPC inflation index.
IPC_RATE Index
The IPC_RATE index is used to store the percentage change of IPC_INDEX in the quotes.
The IPC_RATE rate index should be configured as a regular index as shown with Quote Type = Yield.
The IPC_RATE is applicable for one month rather than a year. This rate represents a month-on-month inflation rate. The quotes are published daily by the price vendor. This quote is saved daily in the quote set. The quote will be updated on the 5th of every month (or previous business day if the 5th is a holiday), so the quote will be same for the rest of the month.
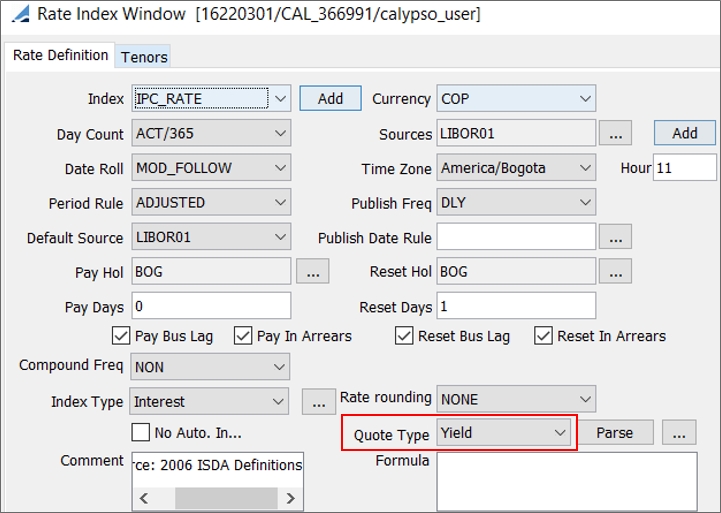
IPC_INDEX Index
The IPC_INDEX rate index should be configured as a regular monthly inflation type rate index as shown with Quote Type = Price and Calc Mtd = Interpolated.
The monthly IPC_INDEX quotes store the monthly Colombia CPI quotes.
Rate rounding will be used while calculating the IPC_INDEX from the IPC_RATE. By default it is 5 for inflation rate index.
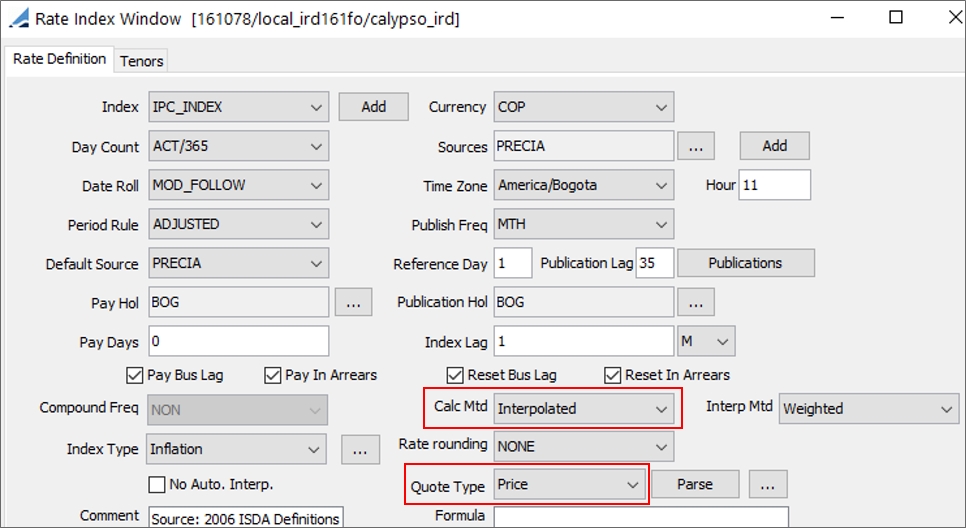
Index Calculator
Bonos Pensionales use the InflationIndexIPC index calculator to forecast by projecting the IPC rates with known IPC values.
InflationLevelCalculator Scheduled Task
The scheduled task InflationLevelCalculator should be run daily. When a new IPC_RATE quote is published, the new quote will be used to convert the IPC Real to IPC_INDEX.
 Refer to Calypso Scheduled Tasks documentation for details.
Refer to Calypso Scheduled Tasks documentation for details.
Yield Method
Bonos Pensionales use the Exp_NL365 yield method.
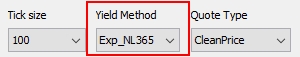
20.5 UVR Bond Forwards
Only one specific type of Colombian UVR bond forward is supported in Calypso, where the bond currency is UVR and the redemption currency and coupon currency are COP. The bond forward settlement currency can never be UVR. This type of cross currency bond is only supported for UVR bond forwards; cross currency bonds are otherwise not supported for bond forwards.
The UVR to COP FX forward rate is calculated using an FX curve. On the exercise date, the UVR to COP conversion is done using that date's spot price between UVR and COP. No FX reset is needed. Upon exercise, the known date is set to the fixing date.
Pricer
Unlike Colombian bond trades which use PricerBondColombian, Colombian UVR bond forward trades use PricerBondForward.
In the bond definition Bond panel, set the UVR product code to TRUE so PricerBondForward can identify the bond as a UVR bond forward.

 Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details on bond forward pricing calculations.
Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details on bond forward pricing calculations.
Trade Capture
Bond forward trades can be captured using the Bond Forward Trade window.
 See Capturing Bond Forward Trades for details.
See Capturing Bond Forward Trades for details.
21. Specifying Convertible Bonds
You can select the Convertible panel, provided the bond class is BondConvertible.
Select the Convertible panel to define the convertible features, and the Conversion Schedule panel to define the conversion schedule.
You can enter the price in monetary units in trade screens for convertible bonds quoted in Price.
21.1 Convertible Panel
| » | Enter the Convertible Details. The fields are described below. |
| » | Click Add to add a conversion price reset row. Then enter the fields as applicable. The fields are described below. |
Convertible Details
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Target Product |
Click ... to select the target equity. The bond will be converted to the selected equity. |
|
Target Code |
Select the target code from the Target Code field. |
|
Issue Strike |
Enter the equity price on conversion date. |
|
Start |
Enter the start date of the conversion process. |
|
End |
Enter the end date of the conversion process. |
Conversion Price Reset Schedule
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Type |
Choose between DOWN or UP to define the type of option. |
|
Date |
Enter the option date. |
|
Cap |
Enter the cap value (for a DOWN option). |
|
Floor |
Enter the floor value (for an UP option). |
|
Multiplier |
Enter the multiplier (bond / equity) that will apply if the cap or the floor is reached. It will override the multiplier specified in the Conversion Schedule panel. |
|
Price Set? |
Check the “Price Set?” checkbox if the option is exercised. In that case, enter the new equity price in the Historical Price field. |
|
Historical Price |
Enter the new equity price if the option is exercised. |
21.2 Conversion Schedule Panel
The Effective Call and Redemption Type fields do not apply to convertible bonds.
| » | Click |

Enter the fields as needed and click Generate. The fields of the conversion schedule are described below.
| » | You can also click |
|
Fields |
Description |
|
Redemption Date |
Enter the effective conversion date. |
|
Option Type |
Select the option type. |
|
Percentage |
Enter the percentage of securities that is converted. |
|
Type |
Select mandatory or optional. If mandatory, this means that the conversion will definitely occur and that the bond will no longer exist after the effective conversion date. There is no processing based on that field. It is for information purposes only. |
|
Settlement |
Select the type of exercise: Physical. Ⓘ [NOTE: Cash settlement is not currently supported] |
|
Price |
Enter the exercise price. |
|
Bond Unit |
Enter the unit of bond that will be converted. |
|
Target Unit |
Enter the unit of equity after the conversion. |
|
Exercised? |
Select Yes or No to indicate if the conversion has been exercised (Yes/No). The system generates the Convertible Corporate Action only if it is flagged as "Exercised". At Maturity, the system does not generate the REDEMPTION Corporate Action if it is flagged as "Exercised". |
22. Specifying Credit Linked Notes
A Credit Linked Note (CNL) is a debt instrument bundled with an imbedded credit derivative. In exchange for a higher yield on the note, investors accept exposure to a specified credit event. For example, a note might provide for principal repayment to be reduced below par in the event that a reference asset defaults prior to the maturity of the note.
A Credit Linked Note is a bond whose coupon and principal payments depend on a credit event. Unlike a corporate bond, where the credit event is on the issuer, a CLN can have a credit event in any reference name.
In a simple case, an investor will buy a CLN (Reference name Ford) from an Issuer (Citigroup) and receive a coupon of Libor + x. He will lose the remaining coupons and the principal amount if there is a credit event on Ford or Citigroup. With Risk Aggregation, the exposure is reported as the exposure for the CDS, not the issuer of CLN.
22.1 Types of CLN
| • | Principal-protected notes – The principal is guaranteed by the issuer. The coupons are risky and they disappear if there is a default on a reference credit. |
| • | Boosted coupon notes – The coupons are guaranteed by the issuer, but the principal payment is linked to the default event of a reference credit. |
| • | Reduced coupon notes – Principal repayment is the face amount. If the reference credit event occurs, the termination payment is enhanced by the loss in the event of default of a reference asset. |
| • | Credit Sensitive notes – The coupon changes with the credit rating of the reference entity. If the reference entity is downgraded, the coupon steps up. If the credit goes below a certain level, the investor can put the bond to the issuer. |
| • | Index Linked notes – The coupon and redemption is linked to an index. As an example, the coupon can be zero and the principal can be linked to the level of the iBoxx credit derivative index. |
| • | Counterparty-funded structures or SPV-funded structures. |
| • | Reference Pool – Static or managed. |
| • | Settlement – Cash or physical. |
22.2 Bond CLN Product
The Bond CLN product is a bond of class BondCLN.
Select the CLN panel and enter the fields described below, then click Save to save the bond.
|
Fields |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Reference Entity Type |
Select the reference entity type: Single Name, Portfolio (Nth Loss), or Portfolio (Nth Default). A CLN is composed of the following: Risky Bond + CDS (Single Name or Nth Loss Basket) + Risk Free Bond (Charged asset). The pricers used are: PricerBondCorporate, PricerCreditDefaultSwap, PricerNthDefaultBasket and PricerBond to value the individual sub components. A single name is valued as a Single Name CDS + Risky Bond + Risk Free Bond. If there are multiple names, these are valued as Nth Loss basket using the same valuation model used to value the CDS NthDefault. Single Name
Portfolio (Nth Loss)
In the Loss panel, the Tranche Notional is set to the Total Issued of the bond. Enter the from and to percentages of the tranche to calculate the size of the basket.
You can also right-click an item of the basket and select Set Credit Events. Portfolio (Nth Default)
In the Default panel, the Tranche Notional is set to the Total Issued of the bond. Enter the number of defaults to calculate the size of the basket.
You can also right-click an item and select Set Credit Events. |
||||||||||||||||||
|
Protection Type |
Select the protection type: Coupon Protected, Principal Protected or None. When credit events are applied, the processing is based on the type of protection.
|
22.3 CLN Trades
It is recommended to capture trades for Credit Linked Notes using a BondCLN product in the Bond Trade window.
23. Specifying Danish Mortgage Bonds
Danish mortgage banks publish a range of data for bond investors in order to obtain a more effective pricing of callable mortgage bonds with focus on debtor’s prepayment behavior in callable bonds, hence for Danish Mortgage Bonds, you can define a drawing schedule in the system.
Negative interest rates on Danish Mortgage Bonds imply that the investor has to pay the issuer interest, however this is not physically done. Therefore the custodian compensates the issuer for the loss of cash with redemption of the security. The negative interest redemption is handled through the use of a PINK rate on the drawing schedule, and the PINK corporate action.
Danish Mortgage Bonds are defined with the bond class BondDanishMortgage, and the bond type "Standard". The drawing schedule must be defined in the Danish Mortgage panel. The actual drawing is performed using the Corporate Action process.
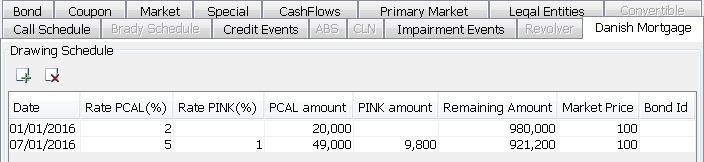
| » | Click |
For the first entry:
| • | PCAL Amount = PCAL Rate * Issue Amount |
| • | PINK Amount = PINK Rate * Issue Amount |
| • | Remaining Amount = Issue Amount - PCAL Amount - PINK Amount |
Subsequent entries are computed based on the previous entry's Remaining Amount, rather than the Issue Amount.
The PCAL drawing rate creates CA products of type REDEMPTION.DRAWING.
The PINK rate allows a redemption of principal without a cash payment to offset the value of negative coupon payments, if any. It creates CA products of type REDEMPTION.PINK.
23.1 Legacy Danish Bonds
When saving the bond, you are prompted to create a drawn bond automatically or not (bond with bond class BondDanishMortgage and sub-type "Drawn").
| • | If you choose Yes, the Drawn Bond Id will be automatically populated in the drawing schedule. |
| • | If you choose No, you can manually update the drawn bond Id. |
The cashflow schedule is then updated with the information of the drawing.
You can also use the scheduled task BOND_DRAWING to generate the Drawn Bonds on drawing date, prior to generating the corporate actions.
The Drawn Bond is created with the same characteristics as the master bond.
The following security codes are set:
| • | ISIN: Same as master bond (provided it is not defined as "Unique") |
| • | FromBondProduct: Id of master bond |
| • | DMB Serie: Maturity date |
Additional security codes can be propagated to the Drawn Bond provided they are not defined as "Unique" – They have to be added to domain BondDanishMortgage.SecCodes.
A Drawn Bond is created for each entry in the drawing schedule
On the Drawn Bond, the Danish Mortgage panel provides information about the master bond.
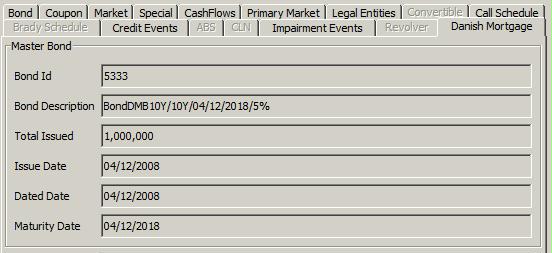
At drawing date, the position on the master bond is amortized by the prepaid amount, and a drawn position is generated on the Drawn bond. Both bonds can be traded.
23.2 TARGET2 Compliant Danish Bonds
In order to enable this feature, set the environment property UseNewDMBRedemption=true.
There is no creation of a "drawn" bond.
In this case, two corporate actions are generated for Danish Mortgage Bonds on the same payment date: REDEMPTION/DRAWING in order to amortize the bond by the drawn amount, and CASH/INTEREST in order to generate the coupon amount.
The corporate actions should be applied by payment date so that they can be created together.
The Record Days on the bond should be set to 1, so that on the CA the Record Date is one day before the Payment date.
24. Specifying Floating Rate Notes
24.1 Principles
| • | Some floating rate bonds, indexed on a particular floating rate, may pay interest coupons at different periods than the reset frequency they are referring to calculate full coupon. The reset frequency can be greater than the payment frequency, allowing the system to calculate the full coupon based on the different reset rates. |
| • | Also, the payment of the coupon can be more frequent than the rate at which it has been calculated. In that case, the payment cashflows will refer to the same rate. |
| • | All these reset and payment frequencies will be defined in the coupon panel of the bond product and used by the system to generate the appropriate cashflow schedule. |
Note that the cashflow schedule will display only payment flows. If one coupon payment is composed of several resets, a utility tool “Interest History” has been set up to show the internal periods used to calculate the coupon.
| • | The internal periods are not customizable, resulting from the frequency method configured in the coupon definition. Only the payment periods can be modified in the cashflow schedule, updating consequently the internal periods. |
| • | Lastly, in the option that the reset frequency is greater than the payment frequency, a compounding method can be applied to the coupon amount calculation. |
Floating rate notes can be defined as Bond or BondFRN. BondFRN should be reserved for actual FRNs (short term floating rate notes) and not for all floating rate bonds.
24.2 Coupon Panel
In the Coupon panel, select Floating Rate, and configure the following.
| » | The compound frequency specifies the frequency of reset. By default, field is the same as the payment frequency. |
| » | The method is the Interest calculation method: |
| – | NoCmp means that the coupon amount to be paid is the sum of the individual reset interest amounts. |
| – | Flat means that the reset interest amounts will compound to calculate the coupon to be paid. Note that this method is not used when the payment frequency is greater than the reset frequency. |
24.3 CashFlows Panel
In the CashFlows panel, generate the cashflows.
You can see the details of an interest cashflow by choosing “Interest History” from the Cash Flow menu. This will display the individual periods with the respective reset rates based on the dates configured in the floating rates definition of the Coupon panel.
The columns are described below.
|
Columns |
Description |
|
Start Date |
Starting date of the reset period. If it is the first reset period of the cashflow, this date is the same as the Pmt Begin date. |
|
End Date |
Ending date of the reset period. |
|
Days |
Number of days included in the reset period. |
|
Period |
Ratio of number of days in the reset period by the daycount. |
|
Rate |
Rate used for interest calculation, populated into the quote. |
|
Accrual |
Total amount of accruals for that period. |
|
Total |
Sum of the accruals. Equal to the Accrual for the first period and then cumulated for the next periods. |
|
Reset Date |
Date at which the rate is selected. Date initialized according to the set up of the floating rate definition in the coupon panel. |
|
Base Interest |
Is the accrual interest amount. |
|
Compound Interest |
Show only the compounded interest on that period. Field that remains blank when the method = NoComp. |
24.4 DISC_MARGIN Pricer Measure
DISC_MARGIN calculates the discount margin of a floating rate bond, which is the spread added to current rates to equal the bond yield. Ref: Stigum and Robinson, “Money Market and Bond Calculations” (1996), Ch. 17. For the average rate needed for that formula, the Calypso implementation uses the index rate as of the valuation date.
24.5 FRN Pricing
The following algorithms can be used to price FRN bonds:
| • | PricerBondGeneric – Standard bond pricing. When solving for the dirty price from a yield to maturity, all future coupons are taken into account. |
| • | PricerBondFRN – When solving for the dirty price from a yield to maturity, we assume that the bond matures on the next coupon date when computing the dirty price from the yield. |
| • | PricerBondFRNMargin – It handles PV01 calculation based on discount margin instead of yield. So PV01 is essentially an analysis in the effect of a one basis point shift in the discount margin. |
This affects PV01 only when the pricing parameter BOND_FROM_QUOTE is set to true, also the pricing parameter FORECAST_FROM_CURVE must be set to false.
Note that you also need to make sure that the Compound Frequency is set on the reference index, even if it is set to NON because by default it is not set.
| • | PricerBondFRNAUD – Pricing for BondFRN product with sub-type AUDFRN. It uses the AFMA formula to calculate the dirty price, given a cash rate, swap rate, and a trading margin. |
Note that the sub-type must be set to AUDFRN in order for the trading margin quotes ("<bond quote name>.TM") to be saved.
CASH_RATE_01 pricer measure is available for FRN AUD Bonds (BondAUDFRN / PricerBondFRNAUD) for reporting to represent the Cash_Rate sensitivity. The SWAP_RATE and CASH_RATE are derived from the forecast curve and not the discount curve.
CASH_RATE_01 is the sensitivity to a 1 bp increase of the CASH_RATE.
CASH_RATE_01 = PV_AFMA (〖Cash_Rate〗+1bp)-PV_AFMA (〖Cash_Rate〗)
25. Specifying Inflation Bonds
Follow the steps below to define inflation bonds.
25.1 Creation of the Rate Index
Make sure that the CPI value (or RPI, TIPS, etc.) is available in the rate_index domain.
Then specify the CPI rate index (or RPI rate index, etc.) using Configuration > Interest Rates > Rate Index Definitions.
| » | Enter the fields described below. |
| – | Set the index type to Inflation. |
| – | Set the quote type to Price. |
| – | Select a publication frequency, enter a reference day and a publication lag. |

The reference day is the day of the month when the inflation is effective, and the publication lag is the time lag between the effective date of an inflation level and its actual publication.
You can click Publications and generate the dates to make any modification if needed. Otherwise the reference day and publication lag are used to determine the publication dates.
Ⓘ [NOTE: The system does not support end-of-month reference days 29, 30, and 31. This restriction also pertains to the Publications Dates window when modifying the Reference Date fields]
| – | Click Attributes, and set the IndexCalculator to InflationIndex. |
If the IndexCalculator attribute does not appear, click ... to add it.
| » | Save. |
| » | Select the Tenors panel and add tenors as needed. Then save the rate index. |
You can click Rebase in the Rate Index Definition window to rebase the index level as needed.
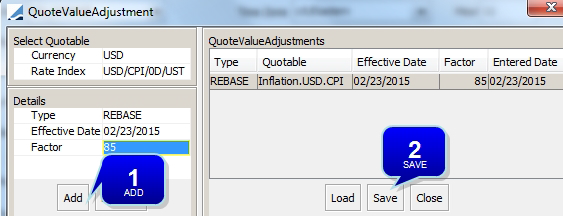
| » | Enter an effective date and a rebase factor in percentage, then click Add. |
| » | Click Save. |
25.2 Creation of the Inflation Bond
You can create a bond sub-type IndexedInflation in the Bond.subtype domain as applicable. This is optional.
For RPI indexed bonds, select the Gilt sub-type.
Select the Market panel.
| » | For English (issued in or after July 2005), French, American, and South African inflation bonds, the quote type must be defined as CleanPrice. For English indexed bonds issued before July 2005, the quote type must be defined as GrossPrice. |
Select the Special panel.
| » | Check the “Notional Indexed” checkbox. |
| » | Select a reference index from the Index field. Only reference indices of type Inflation can be selected. |
| » | Check the “Guaranteed Notional” checkbox to indicate that the notional redemption is guaranteed at maturity. |
| » | Select an Inflation Floor option as needed: |
| – | NONE: Default. |
| – | Guaranteed Principal: Inflation indexation on final principal payment is floored. |
| – | Guaranteed Principal and Coupons: Inflation indexation on all coupon payments, and final principal payment is floored. |
| » | Enter the index date in the “Index date” field. |
| » | Enter the rate index value on the issue date in the "Idx Value" field. |
| » | Enter a number of decimal places in the "Rounding" field and select the rounding method from the adjacent field. If you do not set these values, the default behavior is to round NEAREST to 5 decimals. |
| » | Check the "Round Gross Price Before Adjustment" checkbox as applicable. This will round the prices before the inflation adjustment and not after. |
Peruvian inflation bonds generally use this convention.
25.3 Rounding the Corporate Actions
To specify rounding on the associated corporate actions, follow the steps below.
| » | Add the value “ROUND_CA_AMOUNT” to the rateIndexAttributes and domainName domains. |
| » | Add the values “true” and “false” to the ROUND_CA_AMOUNT domain. |
| » | In the rate index defaults, click Attributes and set the ROUND_CA_AMOUNT attribute to True. |
| » | In the Coupon panel of the Bond product, set the Coupon Digits field to the number of decimal places that you want. |
25.4 Index Override Panel
You can customize index values on an inflation bond. Fields will default to values set in Rate Index Defaults for the selected index.
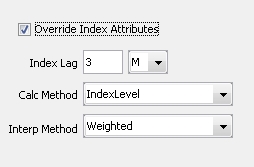
Select the Special panel in the Bond Product Definition window.
| » | Click the "Override Index Attribute" checkbox to activate the feature. |
|
Fields |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Index Lag |
Reset lag for the index, Select a numerical value along with day, month, etc. from a drop down menu. |
|
Calc Method |
Indexlevel – Create a single rate index and save quotes. or Interpolated – Create a single forecast curve for obtaining inflations prices to calculate bond payouts based on a product definition. |
|
Interp Method |
'Weighted'. |
25.5 Pricing
TIPS should use PricerBondUST. Set USE_REAL_YIELD in the pricing parameter set if you would like to use PricerBondGeneric for valuation. Otherwise, defaults to False.
26. Specifying Islamic Bonds
Islamic bonds are identified with the following security codes:
| • | Sukuk=True |
| • | IslamicContract=Musharaka, Mudaraba, or Ijara. |
You need to add <calypso home>/client/resources/samples/dbscripts/SchemaData_islamic.xml to ExecuteSQL in order to populate Islamic static data.
The only difference from standard bonds is the corporate action process, where INTEREST corporate actions are replaced with DISTRIBUTION corporate actions.
27. Specifying Lottery Winner Redemptions
Select the Call Schedule – Lottery Winner Redemptions panel to specify lottery redemptions for bonds redeemed by lottery.
There is no processing based on these redemptions. This is for information purposes only.
The Effective Call and Redemption Type fields do not apply to lottery redemptions.
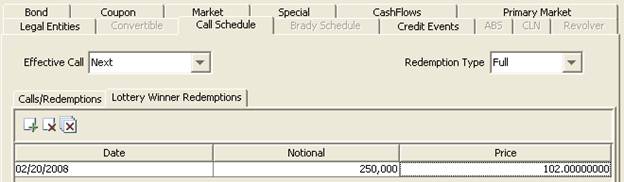
| » | Click |
28. Specifying Mexican CETES Bonds
Mexican CETES (Mexican Government T-bills) can be captured as BondMMDiscount with the Quote Type “Yield”, and the Yield Method “MXN”.
BondMMDiscount and BondMMInterest use the pricing parameter MMKT_FROM_QUOTE.
The pricer measure YIELD_BEY uses the Stigum formula.
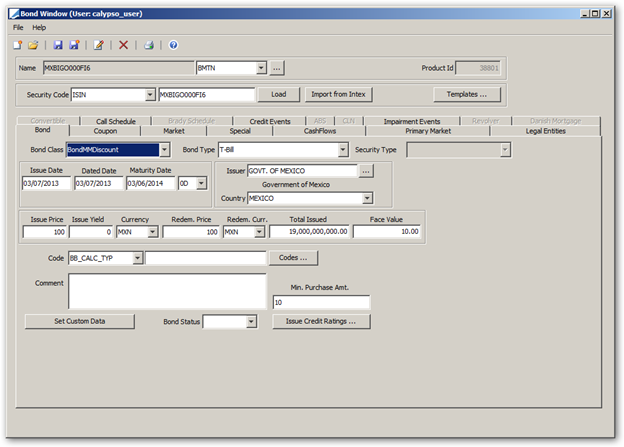
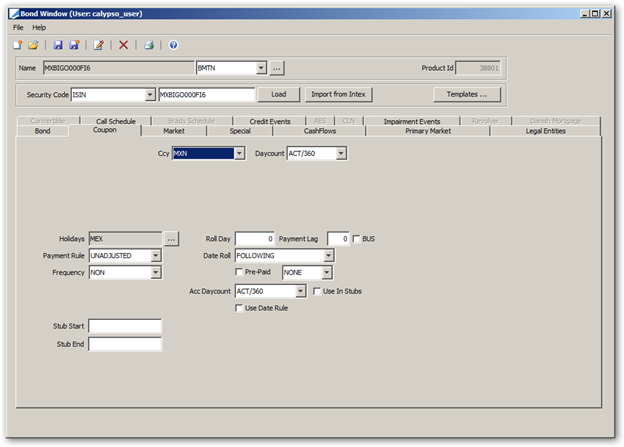
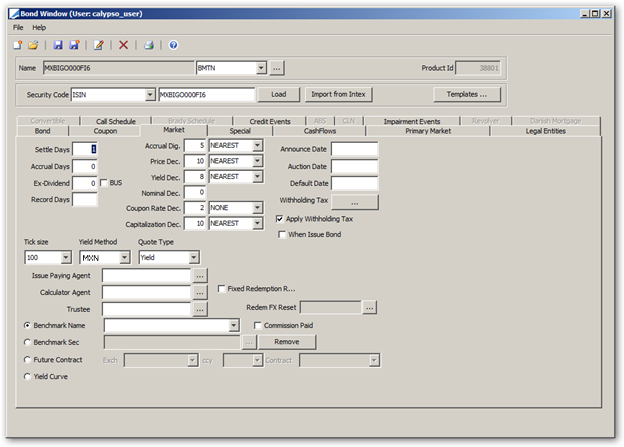
28.1 Zero Coupon Risky Bond
To address the case when Principal Recovery must be considered in the PRICE calculations (when INCL_RECOVERY_PRINCIPAL is true) and there have been no Coupon flows (and hence no prior principal recovery adjustments), in this case the final Principal payment is adjusted for the Recovery amount. The Recovery Amount is included in the 'Credit Principal' Column of the Last Principal flow, the 'Probable PV' Column and the 'PRICE' pricer measure reflects this adjustment.
Setup
| • | Product Code – Create product code IS_RISKY of type "string". On the bond level the value of this code must be set to "YES". |
| • | Pricer Configuration – Select the Model Parameters panel. For PricerBondGeneric add Pricing Param Name: INCL_RECOVERY_PRINCIPAL to true. |
| • | Probability Curve – Create the probability curve and add it in the Credit panel of the Pricer Configuration window. |
29. Specifying Moroccan Bonds
The Moroccan bond market is one of the most important components of the Moroccan financial market. Support for Moroccan Bonds (new yield method and day count logic) is provided impacting yield method computations for the Moroccan bonds when configured with Yield method = 'Moroccan'.
29.1 Day Count
Created a new Day Count that is to be used with bonds with maturity longer than one year.
-
Name: Moroccan/ACTB
This day count will not appear in the daycount drop-down field in the bond definition, but it is embedded in the pricer pricerBondMoroccan.
First Cash-Flow is First Long Coupon Period
A = Stub Start – virtual regular start date
M= Stub Start – Dated Date
Coupon=Notional*period interest*(Stub Start-Dated Date)/A
Accrual=Notional*period interest*(Settle Date-Dated Date)/A
Subsequent Cash-Flows
All subsequent cash-flows are generated based on a Day Count fraction like ACTB/ACTB.
29.2 Yield Method
Uses the new daycount Moroccan/ACTB.
Notation
y = Yield to maturity
A = Stub Start - virtual regular start date
Maturity > 364 Days
If the time to maturity (maturity date – spot date) is <= 364, the Moroccan yield uses the following discount formula:
1/(1+y*(maturity date – spot date)/360)
If the spot date is in a First Long coupon period, the Moroccan yield uses the following discount formula:
1/(1+y)^((Spot Date-Dated Date)/A +i-1)
i >= 1. Here, i represents the number of periods.
29.3 Configuration
-
Configure your bond using ACTB/ACTB as the default daycount, the pricer overrides the default daycoount
-
Use the new yield method Moroccan
-
Quote type: yield
-
Only supports pricing from quotes.
-
Must use the pricer BondMoroccan
30. Specifying Payment-In-Kind Bonds
Payment-in-kind bonds pay a predetermined coupon rate as of a predetermined date: Full coupon rate - PIK rate, i.e a predetermined portion of the payment is capitalized back to the principal. Specific rules in the bond definition will outline how the rates are repaid. The PIK start date and rate can be entered on the Special panel of the bond window.
The PIK definition can be added to any payment schedule.
30.1 PIK Bond Example
PIK dates and rates are tied to a predefined bond, so the definition of the bond product will be necessary.
1. Set up the bond in the bond window.
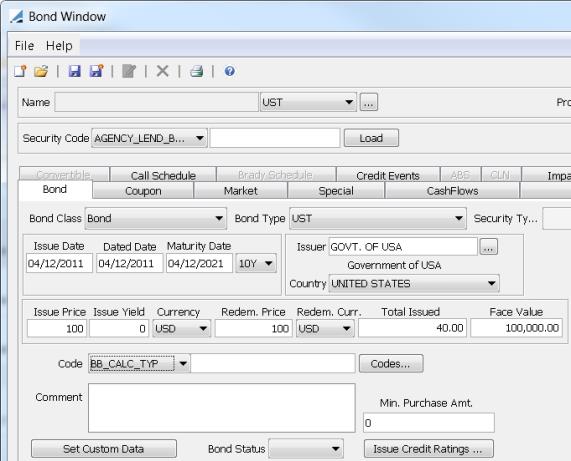
2. Set up the bond coupon rate.
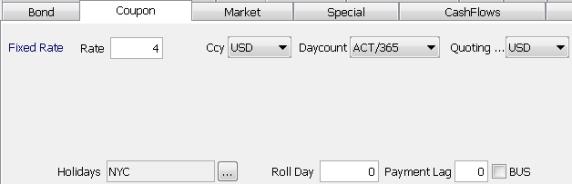
3. Navigate to the Special panel.
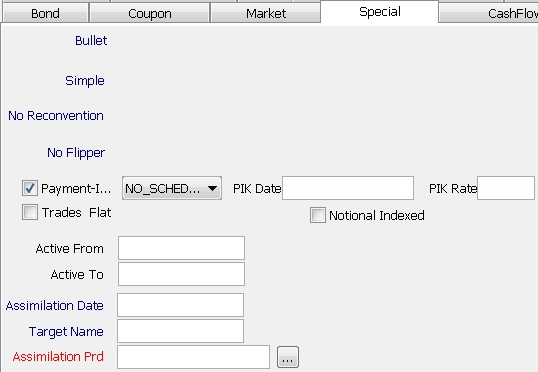
In the Special panel of the bond window:
| » | Specify payment-in-kind by checking the "Payment-In-Kind" checkbox. |
| » | You can specify a single payment-in-kind date and rate, or you can specify a PIK schedule. |
| – | For a single PIK date and rate, select NO_SCHEDULE from the drop down and specify the PIK date and rate in the adjacent fields. |

Example: Of the specified 4% bond coupon rate, 1% will be capitalized to the principal beginning 4/12/2012, paying on a bullet schedule.
| – | For a PIK schedule, select PIK_SCHEDULE from the drop down and click ... to define a PIK schedule. |
The PIK schedule is based on the coupon dates, and the generated dates cannot be edited. Enter a PIK rate for each period.
| » | Save. |
In the CashFlows panel of the bond definition window, generate cashflows and set the columns to display PIK capitalization rate, capitalization factor, etc. by right-clicking on the flows data and selecting Configure Columns. A window will be displayed and allow customize of data to view.
The Capitalization rate and factor can be viewed against existing cashflow data.
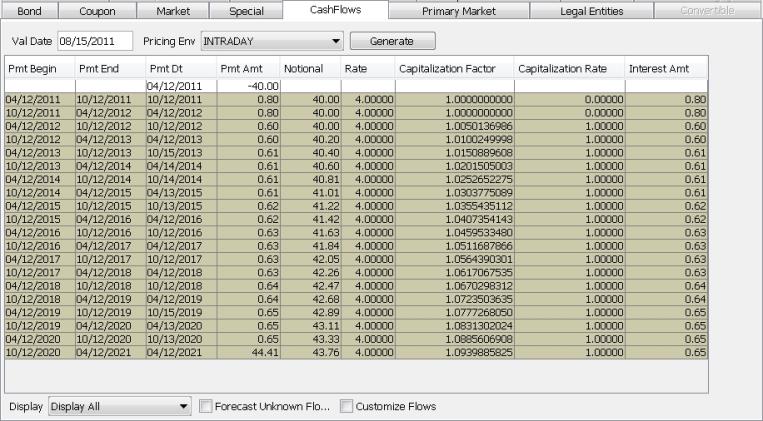
30.2 Payment-In-Kind Accounting Events
|
Accounting Event |
Description |
|---|---|
|
ACCRUAL_BS |
The component of the bought interest related to cash interest, i.e. coupon rate on the bond less any PIK interest. |
|
ACCRUAL_BS_PIK |
The bought interest that is related to the PIK interest. |
|
ACCRUAL_PIK |
Represents accrual of PIK interest. |
|
ACCRUAL_REAL_PIK |
For use in buy/sell trading in a PIK security. Liquidation results from accrued interest being realized. |
|
ACCRUAL_INC_REAL_PIK |
Coupon payment occurrence for an non-liquidated security. |
31. Specifying Re-Issue Bonds
From time to time, securities may be re-issued. This is normal in the case of Treasury Bills, where the 12-month issue is usually re-issued when it is getting close to 6 months to maturity – the re-issue will be for a 6-month T-bill. T-bills are often re-issued again when they are 3 months to maturity. Coupon securities can also be re-issued at one or more points during their life.
When a security is re-issued, the re-issue is traded as a separate security (having all the same attributes as the original security, but with a separate CUSIP) during the period from the re-issue announcement up to the date when the "regular" settlement date for the original security is the same as the re-issue date. At that time, the two securities are merged, and all trades in the re-issued security are modified to specify the original security.
Ⓘ [NOTE: Currently, Calypso assumes that this merge (often referred to as "assimilation") will take place at start of the business day PRIOR to the re-issue security's Issue date]
The characteristics of the re-issuance security are always identical to the original security, except for the issue date (and dated date) and CUSIP.
First, here is a typical configuration for a 12 month Tbill.
Suppose that this security is to be re-issued on 12/07/09. A NEW security must be created for the re-issuance.
Here is the setup for the re-issuance security:
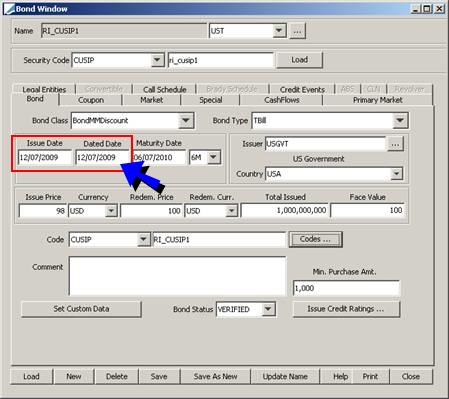
Note the new CUSIP.
| » | Set the Issue Date and Dated Date to re-issuance date. |
In the Market panel, set the Announce Date to the re-issuance announcement date.
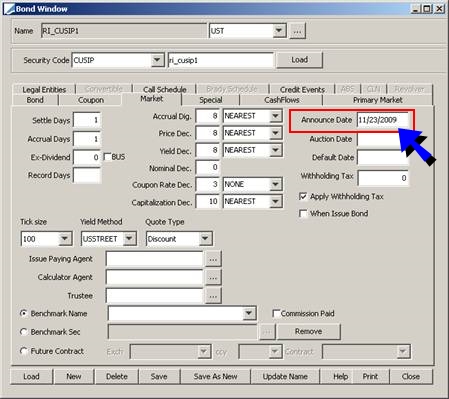
In the Special, panel, set the Assimilation Date to the re-issuance date.
Ⓘ [NOTE: The assimilation will actually take place at start of business ONE DAY PRIOR to the specified Assimilation Date]
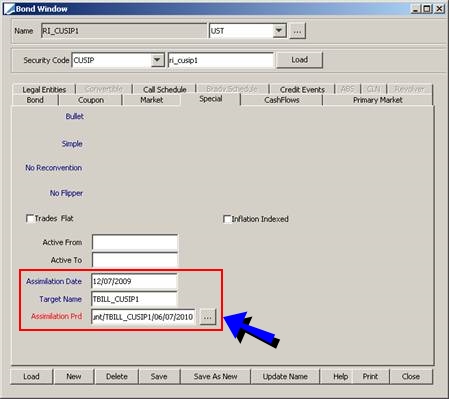
| » | Select the security into which this re-issuance security will eventually be merged from the Assimilation Prd field. |
Upon saving, the re-issuance security will have the value ‘Re-Issue’ in the Product Code field "When-Issued".
32. Specifying Revolver Bonds
32.1 Bond Panel
| » | The face value and total issue amount are set to 0. The drawns will generate cash transfers. |
32.2 Revolver Panel
Select the Revolver panel to define the drawns.
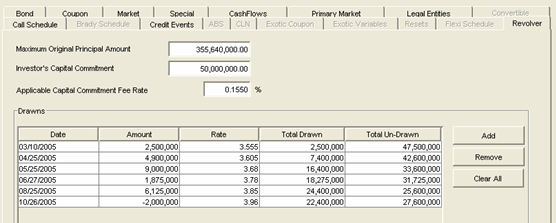
| » | Enter the maximum principal amount, investor’s commitment amount (trade amount), and fee rate. |
| » | Then click Add to add a drawn row: date, drawn amount, and rate. |
The rate on each drawn is the rate used to calculate the interest on the drawn amount. The bonds’s coupon rate is only used when there is no drawn during a coupon period.
The drawns generate cash transfers through corporate actions. Note that the environment property USE_NEW_CA_LOGIC should be set to true. The corporate actions are automatically generated from revolver characteristics using the Generate panel in the Corporate Action window. Then they must be applied to the positions from the Apply panel. Note that two corporate action (CA) trades will be created: a CA trade between the book and the processing org to update the PL, and a CA trade between the book and the agent (nostro/custodian) to reflect the cashflows.
Ⓘ [NOTE: You need settlements instructions for the agent – The following engines need to be running: Transfer engine, Inventory engine, and Liquidation engine. You can check engine status from the Engine Manager of Web Admin: event subscription and engine parameters. Refer to Calypso Web Admin documentation for complete details]
32.3 Pricer Measures
The following pricer measures are specific to revolver bonds:
| • | ACCRUAL_DRAWN – The value of the drawn part of the coupon on val date. |
| • | ACCRUAL_UNDRAWN – The value of the undrawn part of the coupon on val date. |
| • | FACILITY_AMOUNT – Investor’s capital commitment (must be added using Configuration > System > Add Pricer Measure with the class tk.pricer.PricerMeasureBondRevolver). |
| • | DRAWN_AMOUNT – Total drawn amount available at value date (must be added using Configuration > System > Add Pricer Measure with the class tk.pricer.PricerMeasureBondRevolver). |
| • | UNDRAWN_AMOUNT – Total undrawn amount available at value date (must be added using Configuration > System > Add Pricer Measure with the class tk.pricer.PricerMeasureBondRevolver). |
Also, the following pricer measures are calculated differently for revolver bonds:
| • | ACCRUAL_FIRST = ACCRUAL_DRAWN + ACCRUAL_UNDRAWN (with or without an additional day based on pricing parameter ACCRUAL_FIRST) |
| • | ACCRUAL = ACCRUAL_DRAWN + ACCRUAL_UNDRAWN |
The following pricing parameters must be set to true: BOND_FROM_QUOTE and BV_ALTERNATE.
33. Specifying Risky Bonds
Risky bonds are usually any corporate bonds set up as a benchmark over a reference bond, and quoted in spread. You can price risky bonds off credit curves. The default probability implied by the CDS spreads is taken into account for this.
In the Bond panel, click Codes and select the bond’s seniority in the DebtSeniority code.
In the Market panel, set up the bond as a benchmark over another bond.
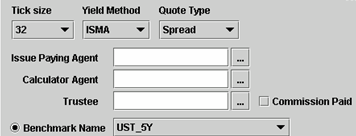
When capturing a trade on this bond, the probability curve for the bond’s issuer will be loaded from the pricing environment if any.
The following pricer measures can be computed for a risky bond:
| • | Z_SPREAD – The static spread over the Zero curve which makes the Theoretical Price equal to the Market Price (Price from Quotes). In the above example, if 117.515 bp are added to the Zero curve, the Theoretical price 100.59306 will become 98.027. |
| • | PV01_CREDIT – The spread sensitivity. The spread is increased by 1bp and the change in NPV is calculated. |
If BOND_FROM_QUOTE = Yes. The spread quote is bumped by 1bp, and the difference in NPV is the PV01_CREDIT.
If BOND_FROM_QUOTE = No. The discount curve is shifted 1bp and the difference in NPV is the PV01_CREDIT.
For a fixed rate bond, the PV01 will be the same as PV01_CREDIT. For a floating rate bond, the PV01 will be close to 0 (no interest rate sensitivity for a FRN).
| • | Theoretical Price – The Price using the curve. |
| • | Notional Equivalent – This is defined as Notional * Modified Duration / Modified Duration (Benchmark). The modified duration of benchmark is set up using the Global Parameters. |
| • | Default Exposure – This is relevant for Risky Bonds (Corporate Bonds) and CDS. It measures the amount of money we lose in case of default. A positive number indicates a Loss and a negative number indicates a profit. The definition of Default Exposure is for Bonds: NPV (Market Value), and for CDS: NPV (Market Value) + Notional. |
| • | CDS_SPREAD – This used to calculate the CDS level if the Bond is to be hedged with a CDS. If the bond uses a probability curve generated from CDS spreads, it calculates the break-even spread for the (hypothetical) CDS underlying the curve with the same maturity date as the bond. The CDS is priced using the probability curve in the PricerConfig associated with that CDS, which is usually (but not forced to be) the same as the probability curve of this bond. |
34. Specifying Russian Bonds
Russian bonds use specific rounding rules for calculating accrued interest. Two methods, "Pro-Rata" and "MICEX", are used with PricerBondGeneric to calculate this requirement properly.
The "Pro-Rata" method for calculating is accrued interest is:
1. CPN_Rate/100 * Face_Amt * Factor * Num_Total_Period_Days/365(or 366) = CPN_Amt_Full_Period
2. Round CPN_Amt_Full_Period to 2 decimals to produce RD_CPN_Amt_Full_Period
3. RD_CPN_Amt_Full_Period * Num_Days_Accrual/Num_Days_in_Full_Period = Raw_Accrual
4. Round Raw_Accrual to 2 decimals to produce RD_Accrual
5. RD_Accrual * Quantity = Accrued Interest
6. Round Accrued Interest to 2 decimals to produce the final result.
The "MICEX" method for calculating the accrued interest is:
1. CPN_Rate/100 * Face_Amt * Factor * Num_Days_Accrual /365(or 366) = Raw_Accrual
2. Round Raw_Accrual to 2 decimals to produce RD_Accrual
3. RD_Accrual * Quantity = Accrued Interest
4. Round Accrued Interest to 2 decimals to produce the final result.
Either method is set on the bond product using the security code "ComputeCouponPerQty". When the sec code is set to false or left blank, the special coupon per face rounding for Russian bonds will not be applied to the coupon amount of the accrued interest.
For correct calculation with the appropriate rounding and precision, set the Coupon Rate Decimals to 2 and NEAREST on the Market panel of the bond product. Accrual digits should be set to 2 more than the number of digits in the total issued amount of the bond or any lager number.
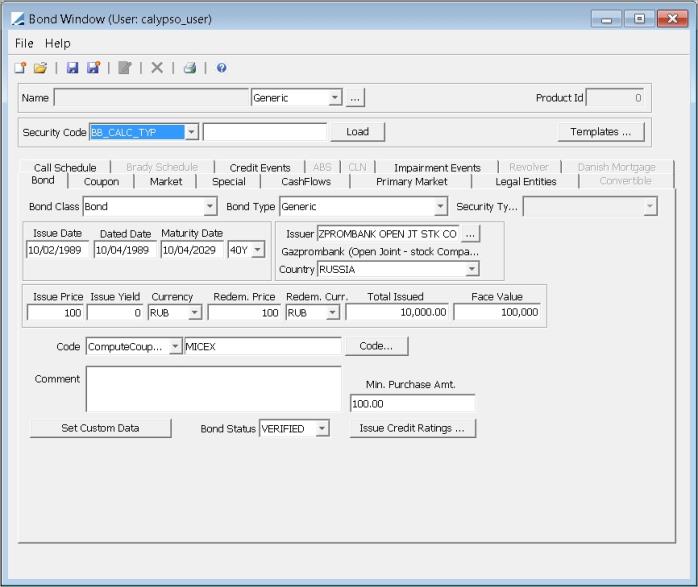
Sample Russian Bond definition
| » | Select 'Bond' for the Bond Class. |
| » | Select 'Generic' for the Bond Type. |
| » | Select 'ComputeCouponPerQty' in the Code drop down. |
| » | Enter 'Pro-Rata' or 'MICEX' for the Code value OR |
Click the Code... button and enter the value for 'ComputeCouponPerQty' in the Code Window, then click Apply.
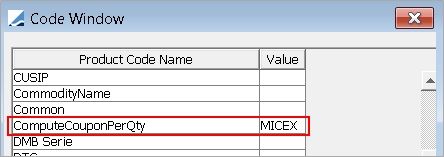
Russian Inflation Bond Accrued Interest
PricerBondRussian is used for Russian inflation bonds. It has a specific calculation method for accrued interest.
 Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
Refer to the Calypso Bond Analytics Guide for details.
35. Specifying Taiwanese Bonds
Some Taiwanese TCB bills are set to mature on non-business days, in which case the principal payment rolls forward to the next business day. These bills must be priced using the principal payment date, not the maturity date. A dedicated pricer and security code allow for this calculation.
Taiwanese money market bond trades can be captured using the Bond (Custom) Trade window.
 See Capturing Taiwanese Money Market Bond Trades for details.
See Capturing Taiwanese Money Market Bond Trades for details.
35.1 Security Codes
In the bond definition Bond panel, you can set several product codes that are specific to Taiwanese bonds.
BOND_CATEGORY
Set the BOND_CATEGORY product code to "TCB" to identify the bond as a TCB bond.

Issue Price Base
You can specify a different base to use for Issue Price and Redemption Price using the product code "Issue Price Base". If left blank, the default is base 100.
Example: Taiwanese bills are entered in base 10,000.

TAIWAN
You can set the product code TAIWAN to true to enable the "Dirty Price (<base>)" field in the Bond (Custom) Trade window.

The "Dirty Price (<base>)" field displays the Dirty Price in the base specified in the Issue Price Base product code.
Example: If Issue Price Base = 10,000, the field will display "Dirty Price (10K)". If Issue Price Base = 100,000, the field will display "Dirty Price (100K)".
Disabling Round-trip Pricing
For Taiwanese bonds, if desired, you can set the product code DisableRoundtripPricing to TRUE to disable the Dirty Price field and prevent round-trip pricing.

Ⓘ [NOTE: DisableRoundtripPricing was designed for the Taiwanese market and it is not recommended for use on other bonds]
35.2 Pricer
Ensure that the pricer PricerBondTCB is used for TCB bonds. When the maturity date falls on a non-business date, the principal payment date will be considered when doing the day difference. As a result, price to yield or discount, or yield to discount or price will change accordingly.
35.3 Pricer Measures
The pricer measures DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED and TRADE_DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED allow displaying these prices in a different base as they are controlled by the Issue Price Base product code.
 See " Issue Price Base" above for details.
See " Issue Price Base" above for details.
|
Pricer Measures |
Description |
|---|---|
|
DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED |
Class Per local market practice, the face value for a TWN bill should set up with 100,000, while the price base for the same bill should be in 10,000. The base is controlled by the Issue Price Base product code. If Issue Price Base = 10,000, then: DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED = DIRTY_PRICE * 100 |
|
TRADE_DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED |
Class Per local market practice, the face value for a TWN bill should set up with 100,000, while the price base for the same bill should be in 10,000. The base is controlled by the Issue Price Base product code. While DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED is the market price, i.e. the market quote on valuation date, TRADE_DIRTY_PRICE_SCALED is the price of the original trade, i.e. what you paid for the bond. It does not change over time. |
35.4 Maturity Roll
The "Maturity Roll" flag allows specifying which date is used to calculate the price. When checked, the maturity principal payment Pmt Dt is used to calculate the price. If not checked, the maturity principal payment Pmt End is used to calculate the price.
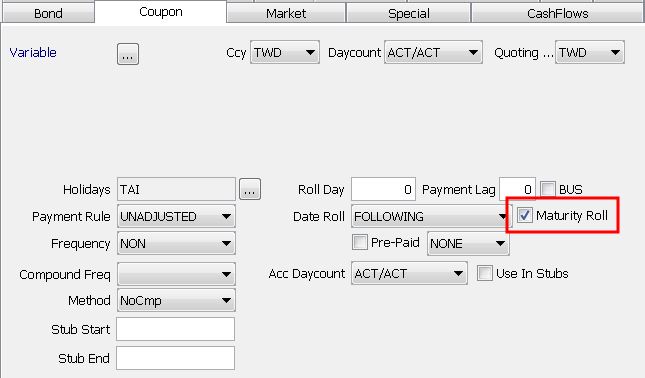
35.5 Withholding Tax
 See Withholding Tax Generation.
See Withholding Tax Generation.
36. Specifying US Treasury Floating Rate Notes
United States Treasury floating rate notes (UST FRNs) are issued for a term of two years and pay varying amounts of interest quarterly until maturity. Interest payments rise and fall based on discount rates in auctions of 13-week Treasury bills.
36.1 Rate Index Definition
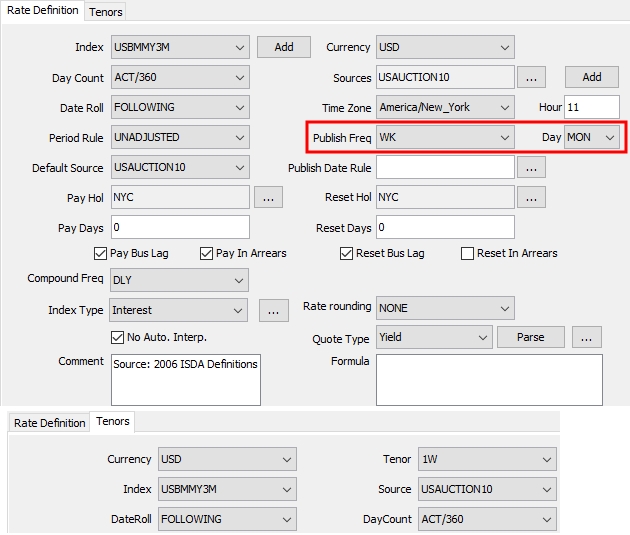
Ⓘ [NOTE: No index calculator is needed]
36.2 Quotes
Quotes are published weekly on Mondays, effective the following business day. The quote published on Monday must be populated on the next business day through the following Monday.
In the example below, the quote of 0.1100305950 published on Monday, May 4 is populated in Calypso from Tuesday, May 5 through Monday, May 11.
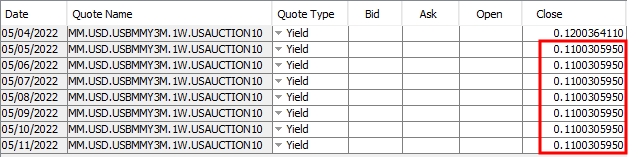
36.3 Coupon Panel
Select the Coupon panel.
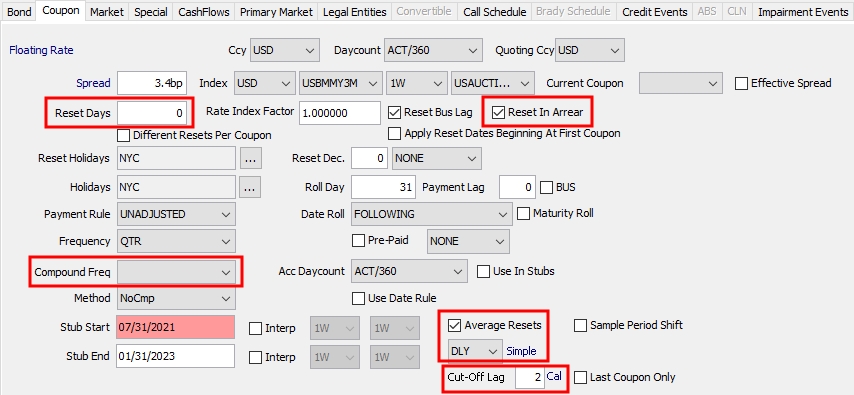
| » | Set Reset Days to 0 if the quotes published on Mondays are entered on Tuesdays (as described above), or set to 1 if the quotes published on Mondays are entered on Mondays (the same day). In the latter case, setting Reset Days = 1 tells the system to pick the observed index value one day before for any given day. |
| » | Check the "Reset In Arrear" checkbox as the final coupon rate for the period is not known in advance. |
| » | Check the "Average Resets" checkbox and specify the reset sampling frequency details as shown above. Averaging and compounding cannot be used together on UST FRNs. |
| » | In the Cut-Off Lag field, enter the number of lockout days. |
36.4 Market Panel
Select the Market panel.
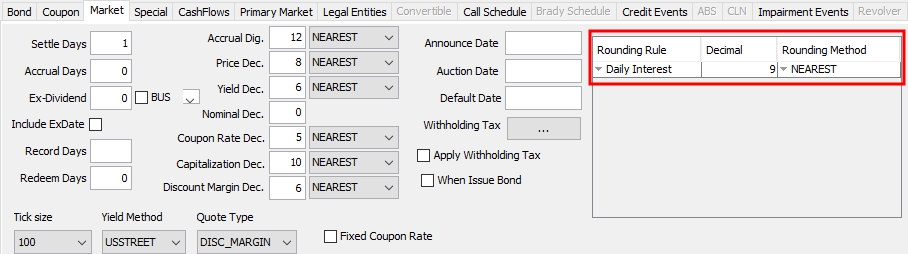
| » | Configure the Daily Interest rounding rule as shown above. The rounding is applied to each calendar day. Note that the samples table will continue to show aggregated numbers on non-business days but the rounding will be applied to each calendar day behind the scenes. |
36.5 Special Panel
The Floor feature is not supported on UST FRNs.
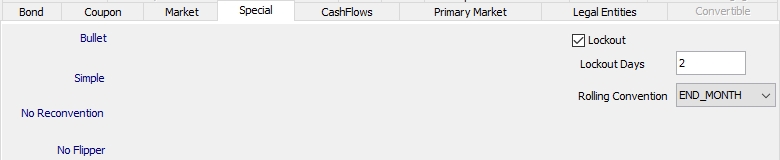
36.6 Pricing
These bonds have a specific pricer, PricerBondUSTFRN, which supports the lockout and reopening functionality. All price and accrual calculations are based on the valuation date.
The pricing parameter FORECAST_FROM_CURVE must be set to false.
Added flooring functionality to UST FRN Bonds to floor the negative rates and extended the support to cash flow interest calculation.
37. Specifying When-Issue Bonds
The lifecycle of every Treasury coupon security begins with the announcement of the security (announcement date), the subsequent auction of the security (auction date), and the subsequent issuance of the security (issue date). During the period between the announcement date and the auction date, Treasury Coupon securities are considered to be in ‘when-issued’ (WI) status. At that time, no coupon rate is defined for the security and the Yield to Price calculation will be done using an "expected coupon rate".
You need to add “When-Issued” to the available product codes as a string using Configuration > Product > Code.
You can create Bond products as well as BondMMInterest products that you will trade as WI.
The system will recognize that the Bond is WI if the issue date is after the Announce Date and the Auction Date. Note that the Auction Date must be before the current date.
In the Coupon panel, leave the Coupon rate field empty as shown below.
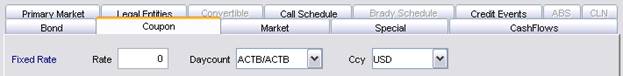
Select the Market panel, and set the following information:
| » | Enter the Announce Date and the Auction date as shown below. |
| » | Specify "Quote Type" as Yield. |
| » | Check the "When Issue Bond" checkbox. |
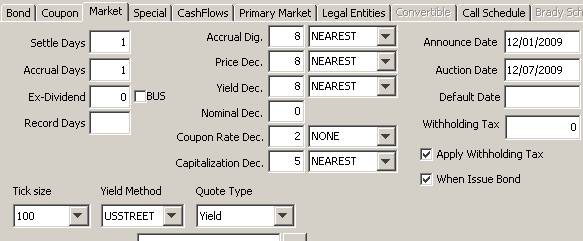
When you save the Bond, the system automatically set the product code "When-Issued" = "When-Issued".
Upon saving, the system also creates the Bond name with "When-Issued" attached to it, and creates a special quote for the Expected Coupon rate. This quote should be entered for each date from the Announcement Date up to (and including) the Auction date, or this can be propagated automatically each day using the PROP_RATE_1BUSDAY scheduled task.
 See Capturing When-Issue Bond Trades for details.
See Capturing When-Issue Bond Trades for details.
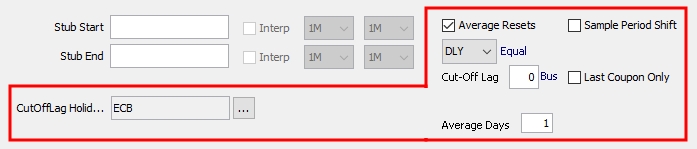



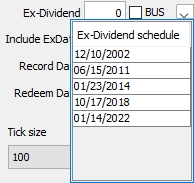
 next to the "BUS" checkbox.
next to the "BUS" checkbox.