Capturing Commodity Forward Trades
 See Commodity Forwards Migration for details on Commodity Forwards to Spot Migration.
See Commodity Forwards Migration for details on Commodity Forwards to Spot Migration.
To capture Commodity Forward Trades, it is recommended to use the Pricing Sheet - Commodity Forward.
You can also choose Trade > Commodities > Forward to open the Commodity Forward worksheet, from the Calypso Navigator. The commodity forward trade is based on the commodity reset, not the commodity itself. You must define a commodity reset to construct a commodity forward trade.
Commodity forward trades without certificates do not update the position by default. You need to run the scheduled task CMD_FWD_SETTLE on the settlement date to terminate the commodity forward trade and create a commodity spot trade. If you want to update positions for commodity forward trades without certificates, you need to set the environment property NEW_CMD_FWD_NO_POSITION = false.
Ⓘ [NOTE: For transactions involving future physical deliveries of commodities, the Commodity Forward product is best suited.]
|
Commodity Forward Quick Reference
When you open a Commodity Forward worksheet, the Trade panel is selected by default. Configuration
Entering Trade Details
Or you can enter the trade fields directly. They are described below, see Field Description. Note that the Trade Date is entered in the Details panel.
Saving a Trade
You can also hit F3 to save the current trade as a new trade, or choose Trade > Save As New. A description will appear in the title bar of the trade worksheet, a trade id will be assigned to the trade, and the status of the trade will be modified according to the workflow configuration. Pricing a Trade
Note that a cross-currency commodity forward also requires an FX curve, an FX rate, and an FX reset.
Trade Lifecycle
|
Deal units are in reference units in trade window.
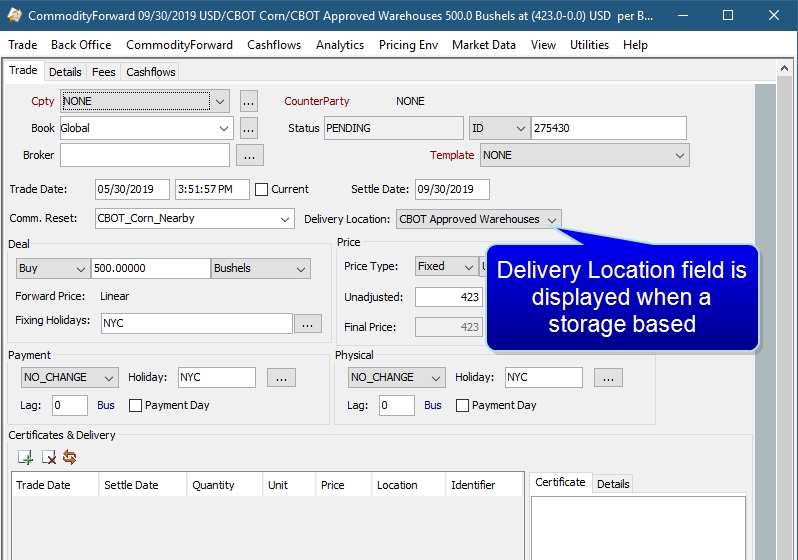
1. Field Descriptions
| Fields | Description |
|
Role/Cpty |
The first two fields of the worksheet identify the trade counterparty. The first field identifies the trade counterparty's role. The default role is specified using Utilities > Set Default Role. However, you can change it as applicable. You can select a legal entity of specified role from the second field provided you have setup favorite counterparties. You can also type in a character to display the favorite counterparties that start with that character. Favorite counterparties are specified using Utilities > Configure Favorite Counterparties. Otherwise click ... to select a legal entity of specified role from the Legal Entity Chooser. You can also type [Ctrl-F] to invoke the Legal Entity Chooser, or directly enter a Legal Entity short name. |
|
Book |
Trading book to which the trade belongs. Defualts to the book selected in the User Defaults. You can modify as applicable. You can select a book provided you have setup favorite books Favorite books are specified using Utilities > Configure Favorite Books. Otherwise, click ... to select a book. The owner of the book (a processing organization) identifies your side of the trade. |
|
Id |
Unique identification number of the trade. The trade id is automatically assigned by the system when the trade is saved. You can load an existing trade by typing the trade id into this field and press [Enter]. |
|
Ext Ref |
You can also display the internal reference or external reference. The default trade reference to be displayed can be selected in the User Defaults. |
|
Int Ref |
The internal reference and external reference can be set in the Details panel of the trade worksheet. |
|
Status |
Current status of the trade. The status is automatically assigned by the system based on the workflow configuration. The status will change over the lifetime of the trade according to the workflow configuration and he actions performed on the trade. |
|
Broker |
Displays the broker if a broker fee is captured in the Fees panel. |
|
Template |
You can select a template from the Template field to populate the worksheet with default values. Then modify the fields as applicable. |
Dates Details
| Fields | Description |
|
Trade Date and Time |
Enter the start date and time of the trade. The trade date defaults to the current date. Check Current to use the current system time. |
|
Settle Date |
Enter the maturity date for the trade. (For most emissions trades, the settle date is equal to the allowance delivery date.) |
Commodity Details
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
|
Comm. Reset |
Select the commodity reset which will drive the forward. When the reset is selected, fields specific to the reset pre-fill with the appropriate information. |
|
Delivery Location |
This is the delivery location for storage based commodities. It is populated from the CommodityLocation domain value. The pricer recognizes the delivery location and prices the forward according to the relevant location differentials. NOTE: The location spread of the location indicated is used to adjust the projected forward price of the commodity taken from the forward curve and will have a valuation impact on the trade. Changing the delivery location has a pricing impact but does not have an impact on the fixed price of the forward, which is a saved trade attribute. |
Deal Details
| Fields | Description | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
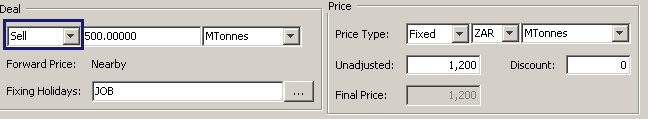
Buy / Sell |
Select the direction of the trade. |
|||||||||
|
Quantity |
The quantity of the certificate in commodity units. |
|||||||||
|
Quantity Unit |
Unit of measure that the quantity represents. You can use a different unit type than the unit in the product definition. The quantity unit defaults to the unit defined in the commodity definition. If a unit other than the default unit is chosen, the application requires a conversion definition to correctly convert the units for the cashflows. Commodity positions are always kept in the default unit in the Position Keeper. To define the conversion definition, from Calypso Navigator, choose Configuration > Commodities > Commodity Conversion. |
|||||||||
|
Forward Price |
The Forward Price is automatically displayed based on the commodity reset that has been chosen. Calypso out-of-the-box provides the following forward price methods: Nearby — The Nearby (aka Prompt) future is the future in a given contract listing which is closest to expiration on a specified date. This future is typically the most liquid and contains the highest open interest, making it the primary choice for a derivative reference price. In Calypso, the projected price returned by the Nearby method is equal to the the price of the first sequentially available curve point on or after the fixing date. Lme3M — The LME 3 Month price is similar in concept to the Cash price. In Calypso, the projected price returned by the LME3M method is equal to the value on the curve which corresponds to the date 3 calendar months after the fixing date according to the Fixing Holiday Calendar subject to the Forward Price Holiday Calendar. Note: this value may correspond to an actual curve point, or may be interpolated using the interpolation method specified in the forward curve. LmeCash — Futures listed on the London Metals Exchange (LME) have daily expiries, whereas most other commonly traded commodity futures have monthly listings. Because of this, LME products tend to be quoted in terms of tenor-based futures such as Copper Cash Buyer's Price or Lead 3 Month Buyer's Price. In keeping with this convention, derivatives settled using the LME Cash reference price require a method which can project the price of the official cash settlement price on a given fixing date. In Calypso, the projected price returned by the LMECash method is equal to the value on the curve which corresponds to the date 2 business days after the fixing date according to the Fixing Holiday Calendar subject to the Forward Price Holiday Calendar. Note: this value may correspond to an actual curve point, or may be interpolated using the interpolation method specified in the forward curve. SecondNearby — The Second Nearby future on a given date is the future which is next to expire after the prompt. In Calypso, the projected price returned by the Second Nearby method is equal to the price of the second sequentially available curve point on or after the fixing date. NearbyNonDelivered — The projected price for a fixing date will be equal to the value of the chronologically closest point on the forward curve which is equal to or greater than the fixing date subject to the restriction that the fixing date is not after that underlying's first delivery date, or for commodity forward points, the pillar date. If the fixing date falls after the nearby underlying's first delivery (or pillar) date, but before the underlying's last trading date, the value of the next (chronologically) curve point will be used. Many agriculture future contracts have first delivery dates which fall BEFORE the last trading day, meaning that if you hold a short position in one of these contracts, even if the future is still trading, you may be notified by the exchange that you are required to deliver the physical commodity. Therefore, financial players in the agriculture markets always make sure that they exit future positions before the first delivery date to avoid that scenario. Likewise, financial derivatives, such as swaps and options, take a similar approach and will typically fix off of the nearest future which has not already passed its first delivery date. For example, look at 2 consecutive CBOT Wheat futures:
For a commodity fixing on March 1, you would expect the NEARBY forward price method to use the LTD of 3/14/08 from the curve to project the price, and for a commodity fixing on March 5, you would STILL expect the NEARBY forward price method to use March 14, as the fixing has not passed the last trade date (aka the MAR08 curve date on the forward curve). In terms of the above example, for a commodity fixing on March 1, you would expect the NearbyNonDelivered forward price method to use the LTD of 3/14/08 from the curve to project the price since it is before the MAR08 future's first delivery date. For a commodity fixing on March 5, you would expect the NearbyNonDelivered forward price method to use May 14 as the curve date from which to project the price as it is after the first delivery date of the nearby curve point. Linear — The linear method is not a commonly used method. The projected price that it returns is the price from the curve for the date which is equal to the fixing date. For a curve which uses no interpolation between points, the Linear method will resemble the Nearby method. Fixed — In some cases, derivatives are traded which agree upon a specific future as the reference price, regardless if that future is prompt, second prompt, etc. For these situations, we offer the Fixed forward price method. Using this method, the user must specify a date which corresponds to the date on the forward curve whose price will be used for all fixing dates for any derivative which uses that Commodity Reset. Any example would be a 3 month averaging swap over the months of Jan - Mar 2008 which references the Dec 2008 future. Each day of this swap will settle off of the price of the Dec 2008 future, therefore the projected price of all future fixing dates will be the same, based on the curve date chosen in the reset definition. IceNearby — The convention of many swaps traded on the The Intercontinental Exchange (ICE) is to fix off of the prompt future up to, but not including, that future's last trading day. On that day, the price will fix off of the second prompt contract. The theory behind this is that there is uncharacteristic volatility associated with a future on it's last trading day due to market forces trying to reconcile positions before the future ceases trading. In Calypso, the projected price returned by the ICENearby method is equal to the price of the first available curve point after, but not equal to, the fixing date. InterpolatedPrice — The forward price calculation is delegated to the interpolation method set on the underlying Market Data item, of which only curves are currently supported. If there is no interpolator set on the underlying market data item, "Nearby" forward price lookup method is used. Note: You cvan add custom methods by creating a class named |
|||||||||
|
Fixing Holidays |
Click ... to select the holiday calendar for the fixing method. It defaults to the holiday calendar defined for the deliverable reset. |
Price Details
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
|
Unadjusted |
Enter the unadjusted price. |
|
Discount |
Enter any discount. The discount may be calculated in the case of storage-based commodities. Complete the certificate details as described below, and click Compute Certificate Discount. Note: The Final price is the only price used in the valuation of the commodity forward. Adding a discount only impacts the NPV of the trade if the discount is allowed to alter the final price. |
|
Final |
The Final field displays the final price. |
|
Price Type |
Select either a Fixed or Floating price, the currency and the units. The Price currency and unit default to the currency and unit of the selected commodity. However, you can set these independently. The Commodity Forward supports cross commodity unit conversion of the price units, deal units, and units for the certificates. The valuation is supported. For example, the trade capture, valuation, and risk support entering physically delivered commodity Forwards where the price is quoted in reference currency and reference units, but the quantity is entered in terms of the number of future contract equivalents. This is standard in the LME Base Metal OTC market, where OTC Forwards and Listed Futures are interchangeable. The conversion details should be configured in the commodity conversion table. |
|
Comm. Reset |
Select a commodity reset. You are able to select a different reset than the one that is being used to book the Forward. |
|
Spread |
Enter a Floating price spread. |
|
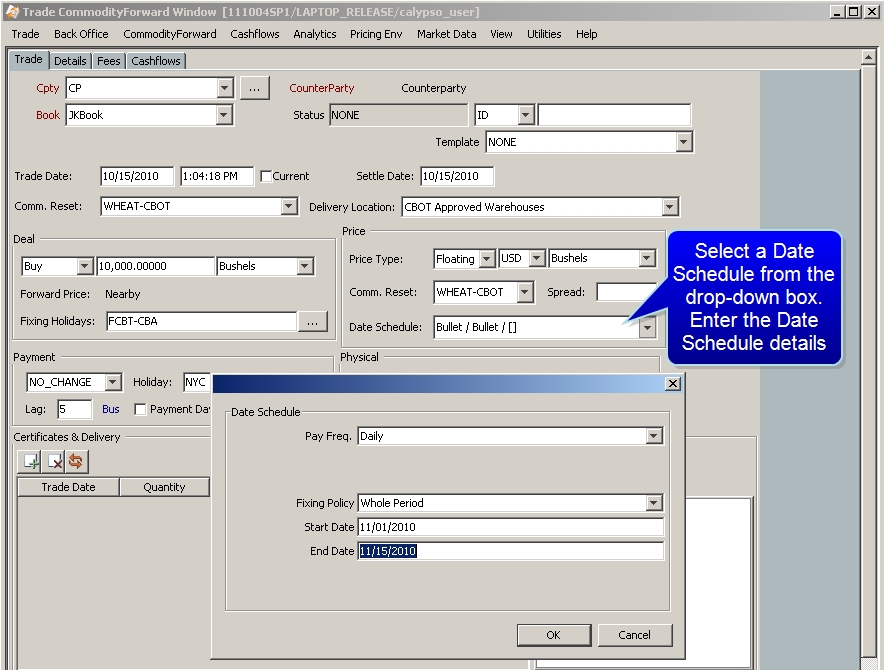
Date Schedule |
Click the drop down box to display and select a desired date schedule for the float side of the forward.
The summary of what is chosen in the Date Schedule window is then displayed.
|
Payment Details
Define the payment lag details for the cash payments (the COMMODITY flows).
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
|
Date Roll |
Select the date roll convention to roll the payment dates when they fall on non-business days. The payment calendar is used to determine business days. From Calypso Navigator, chooseHelp > Date Roll Conventions for a description of date roll conventions. |
|
Holidays |
Click ... to select the calendar(s) the application uses to determine the business days. |
|
Lag |
Specify lag days from the end date of the payment period (in business or calendar days) for the actual payment to take place. By default, business days are used to calculate the payment date. To specify calendar days, double-click the Bus label to toggle to Cal. |
|
Payment Day |
Select to enter a specific payment date. |
Physical Details
Define the payment lag details for the security transfer (the SECURITY flows).
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
|
Date Roll |
Select the date roll convention to roll the payment dates when they fall on non-business days. The payment calendar is used to determine business days. From Calypso Navigator, chooseHelp > Date Roll Conventions for a description of date roll conventions. |
|
Holidays |
Click ... to select the calendar(s) the application uses to determine the business days. |
|
Lag |
Specify lag days from the end date of the payment period (in business or calendar days) for the actual payment to take place. By default, business days are used to calculate the payment date. To specify calendar days, double-click the Bus label to toggle to Cal. |
|
Payment Day |
Select to enter a specific payment date. |
Certificates & Delivery
checkValidCertificate Workflow Rule
The checkValidCertificate workflow rule can be used for validation on commodity certificates for buying and selling on Commodity Forward trades.
For a Buy deal, this workflow rule checks:
| • | If there is an existing inventory with the same Identifier. If so, then: |
| – | if there is an open quantity on the existing inventory, the certificate is not valid and is rejected with a message, "Cannot amend inventory with the same certificate identifier on trade window." |
| – | if there is no open quantity, the trade is allowed if the buyingSameCmdCertificate keywoard is set to true. |
| • | If there is no inventory with this existing name, then the new certificate is allowed. |
For a Sell deal:
| • | When the certificate is selected to sell using the Certificate Selector window, all of the fields on the certificate are non.-editable except for the Price field. The price is automatically set as the contract/trade price when the certificate is selected. |
| • | The checkValidCertificate workflow rule verifies the following for the sell deal: |
| – | if the quantity on the Commodity Forward trade matches the quantity on selected certificate. If it does not match, it is rejected with an error message. |
| – | if the price on the Commodity Forward trade matches the price on the selected certificate. If it does not match it is rejected with an error message. |
| – | if there is an existing inventory of the same identifier name. If not, it is rejected with an error message. |
Additionally:
| » | When using this workflow rule for a Buy/Sell Commodity trade, if the Commodity Forward trade settle date plus the lag is not equal to the certificate settle date, an error message is received and the trade cannot be saved. |
| » | The Delivery Location on the Commodity Forward trade should be the same as the location on the certificate attached to the Buy and Sell trade. This validation is part of this workflow rule. |
Buying/Defining a Certificate - Storage Based
- Use with storage-based commodities.
- Buy trades require the user to create a new certificate. Sell trades require the user to select a certificate from the current certificate inventory.
- To add a certificate to the trade, the direction of the trade should be set to Buy.
- The valuation currency of the certificate is always the currency of the underlying commodity.
-
You can save a trade without a certificate, and add the certificate later, as needed.
-
When you save the trade without a certificate, the trade and associated transfers are promoted to the next status based on the workflow configuration. However, the transfers should not be authorized until the certificate is actually set on the trade. To prevent the authorization of the transfers, you can add the rule CheckRealCommodityCertificate to the transfer workflow transition PENDING – AUTHORIZED – VERIFIED.
Ⓘ NOTE: The Certificate & Delivery panel is not required for Emission commodities
The following is an example for storage-based commodities.
| » | Click  to add a certificate. to add a certificate. |
| » | Enter the certificate quantity, units, price, select the location, and enter the certificate details. Certificate details are: |
Storage Date - The date through which storage has been paid.
Maturity Date - The end date of the storage contract.
Grade - The quality rating of the commodity. Lower quality indicates lower value. This list is populated from the CommodityGrade domain value.
Handling Fee - This is a fee in the commodity currency, associated with the physical movement of the commodity.
Future Delivery Set - The future against which the certificate is eligible to be valued, for certificates hedged against a specific future delivery period.
| » | Additional details may be recorded in the Details panel by selecting a custom-built template. See Certificate Templates for details. |
NOTE: The Location field in the Certificates and Delivery panel is populated from the CommodityLocation domain value. (From Calypso Navigator, choose Configuration > System > Domain Values)
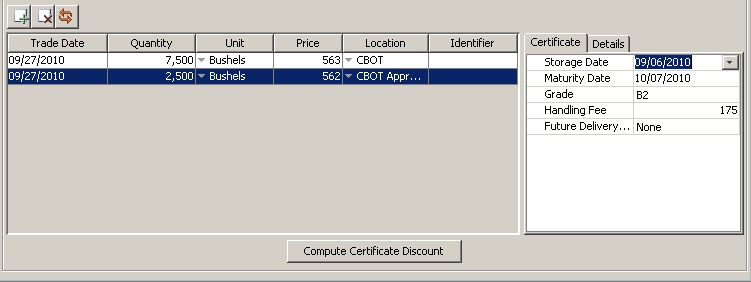
| » | Quote names for the location differential, storage cost and grade differential needed for the certificate are created in the Quote Creator. |
| » | Choose Market Data > Market Quotes > Quotes or Pricing Env > Check and click Get Quotes to view or edit the quotes for the grade differential, location differential, and storage cost. |
| » | In the forward trade, click Compute Certificate Discount to calculate the actual price that the bank is paying for the certificate. NPVY = Q * [(F – SC– LD – GD- Handling)*df – SD], where |
| – | NPVY = The present value of the Certificate in Currency Y, which is the Trade Currency of the Certificate |
| • | Q = Quantity of the commodity in unit X, which represents the unit of the Certificate |
| • | F = Market price of the specified future in currency Y and commodity unit X |
| – | If the future quote is not in unit X, it should be converted using the value in the Commodity Conversion table. |
| – | If the future quote is not in currency Y, it should be converted to currency Y using the Forward FX Rate on the First Delivery Date of the future, unless the value date is between the first delivery date and the last trade date of the future, in which case the future price should be converted to currency Y using the spot rate. |
| • | SC = Cost to store commodity from value date until first delivery date of F in Currency X and commodity unit Y |
| – | SC = 0, if no future is specified, AND there is no future contract which is defined as the "IsDefaultDeliverableFutureContract" (To define a default deliverable contract, set the IsDefaultDeliverableFutureContract attribute to Yes in the Future Contract window of the desired contract, accessible from Calypso Navigator by selecting Configuration > Listed Derivatives > Future Contracts), |
or
| – | SC = 0, if no future is specified, AND the value date is between the First Delivery Date and the Expiry Date of the Nearby Future, otherwise, |
| – | SC = (TF – TD) * S, where |
| – | TF = First Delivery Date of F, or the First Delivery Date of the Nearby Future if no future is specified, otherwise |
| – | TF = TV if TV is after the first delivery date and before the last trading date of F, otherwise |
| – | TF = TV if there is no future specified and no future is define as "IsDefaultDeliverableFutureContract" |
| – | TD = Value Date or Certificate Storage Date, whichever is greater |
| – | S = Storage rate in currency Y per commodity unit X |
If the storage rate is not in currency Y, then it needs to be converted at the forward FX Rate at TF
If the storage rate is not in commodity unit X, then it needs to be converted using the factor available in the commodity conversion table
| • | LD = Location Differential in currency Y per commodity unit X |
| – | If the Location Differential is not in currency Y, then it needs to be converted at the forward FX Rate at TF (using definition of TF above) |
| – | If the Location Differential is not in commodity unit X, then it needs to be converted using the factor available in the commodity conversion table |
| • | GD = Grade Differential in currency Y per commodity unit X |
| – | If the Location Differential is not in currency Y, then it needs to be converted at the forward FX Rate at TF (using definition of TF above) |
| – | If the Location Differential is not in commodity unit X, then it needs to be converted using the factor available in the commodity conversion table |
| • | Handling = Handling fee as defined above |
| • | df = 1 if no future is specified, AND there is no future contract which is defined as the "IsDefaultDeliverableFutureContract", or |
| • | df = 1, if no future is specified but there is a future defined as "IsDefaultDeliverableFutureContract", AND the value date is between the First Delivery Date and the Expiry Date of the Nearby Future, otherwise |
| • | df = Discount factor from Tv to TF from the zero curve of currency Y |
| • | SD = Accrued storage cost in currency Y |
| – | SD = S * (Tv – Ts), if TS < TV |
| – | SD = 0 if Ts > Tv |
| – | TV = Value date |
| – | TS = Storage Date on the Certificate |
| – | S = Storage rate in currency Y per commodity unit X |
If the storage rate is not in currency Y, then it needs to be converted at the forward FX Rate at TF
If the storage rate is not in commodity unit X, then it needs to be converted using the factor available in the commodity conversion table
| » | Hit F5 to resave the trade with the certificate. |
Ⓘ [IMPORTANT NOTE: If you want to remove a Certificate from a Commodity Forward trade, you need to cancel the trade and capture a new trade without the Certificate - It is not supported to remove a Certificate from an existing trade]
2. Defining an Emission Certificate
When an Emission commodity reset is chosen in the Comm Reset field, the Certificates and Delivery area reflects this type of trade. The pricer automatically calculates the cheapest allowance to deliver which becomes the default allowance type for delivery. This is displayed in the Cheapest to deliver field. When the time for delivery comes or when the actual delivery specifications are known, the user selects the Set delivery check box and is able to designate the actual number and allowances for delivery.

Selling a Certificate
Certificates may be sold when the direction of the deal is set to Sell. When a certificate is sold, it must be chosen from a list of certificates that are currently available.
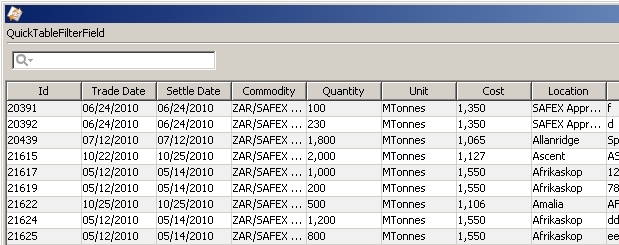
| » | Load a forward trade in the worksheet. |
| » | Set the deal direction to Sell, and click  to open the certificate selection window. to open the certificate selection window. |
| » | Use the filter field at the top of the window to quickly find certificates that meet your desired criteria. |
| » | Highlight a certificate and click Select. |
The certificate loads in the certificate panel.
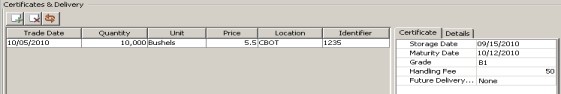
Only the Price field is editable when selected and is automatically set as the contract/trade price.
| » | Save the trade. |
You can amend, split and merge certificates from the Certificate Management window.
3. Floating Rate Forward
The Commodity Forward trade can be configured to use a floating price at which to purchase or sell the underlying commodity. This can be achieved by changing the Price Type from “fixed” to “floating”. The user can then choose a commodity reset as well as the date or dates over which that reset will be observed. If more than one date is chosen, the floating price will be calculated as an arithmetic average of the observed rates. Once all of the observations have occurred, the calculated price will now act as the fixed price for the transaction. The user has the ability to apply a fixed spread to the floating price if they desire.
|
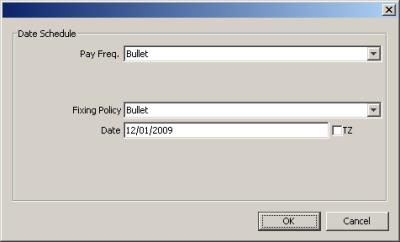
Date Schedule |
|
|
Pay Freq. |
See Payment Frequencies for details. |
|
Fixing Policy |
See Fixing Policies for details. |
|
Intraday Policy |
See Intraday Policies for details. This field is displayed for swaps with Electricity resets. You need to enter an intraday policy for this type of swap, because resets can be at various times of the day, depending on the peak hour schedule. |
4. FX Triangulation
It is possible to price cross currency Commodity Forwards when the reset and the settlement / payment currency differ. For example, when FX rates for A/B and C/B are known, the FX rate for C/A can be solved for. Using the discount curve for each currency, the FX Forward rate for C/A is derived using triangulation.
Commodity Forward FX Triangulation is enabled by setting the FX_POINTS pricing parameter to False. (Market Data > Pricing Environment > Pricing Parameters Set)
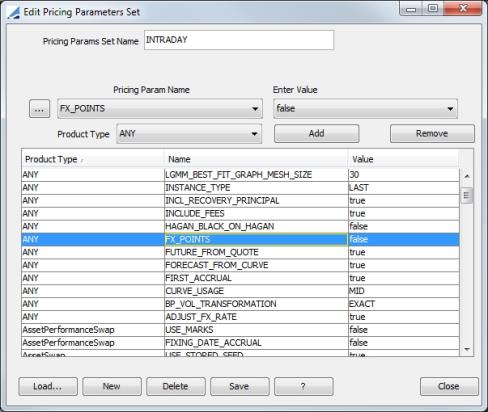
| » | Future FX cashflows for Commodity Forward trades are discounted using a zero curve for each currency. The result is converted to a single currency. |
| » | When FX_POINTS is False, the discount curves for both the traded / deal currency and the settlement currency need to be configured. |
5. Sample Trade
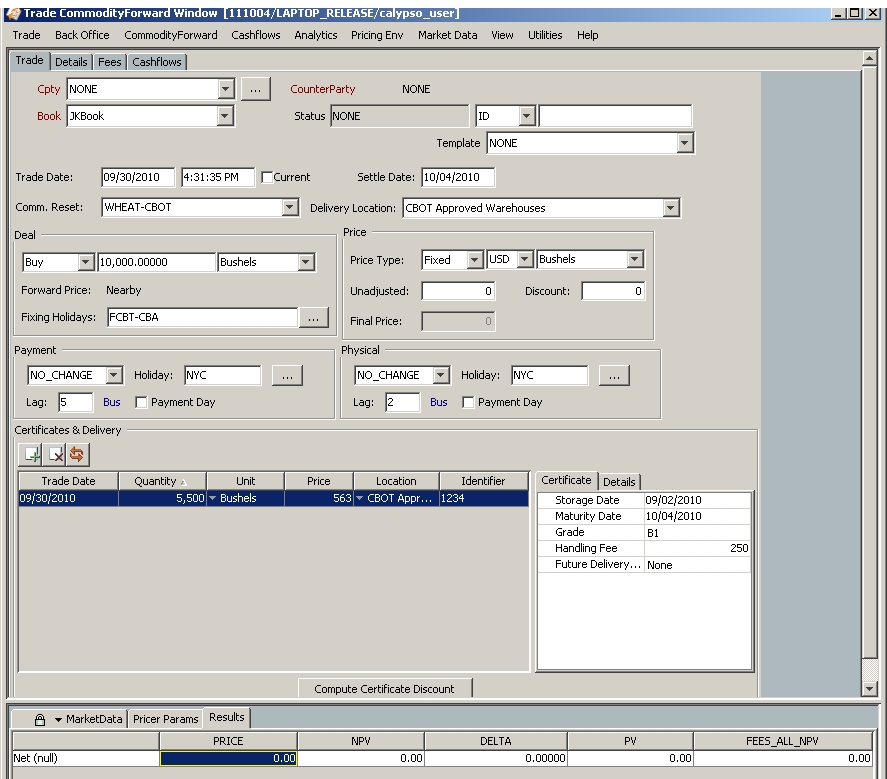
The certificate and trade units do not have to match. For example, you can have a trade in tonnes and a certificate in contracts.
 See also -
See also -