Collateral Optimization
The collateral optimization function of Calypso allows you to allocate collateral payment by making the best use of the global collateral inventory. The Optimization tool can be tailored to adhere to various business or relationship constraints that may need to be taken into account.
|
Collateral Optimization Quick Reference Optimization Panels
The allocation panel shows how the contract will be or has been allocated (depending on whether the margin call trades have already been saved or not). This is true whether the user allocates the margin using an optimizer or not. In Cover Distribution Manager, the allocation panel shows how the collateral in the deposit account has been allocated to cover the liabilities, as well as necessary margin calls. Graphs can be create based on this panel
Like the panel described above, this panel shows the allocation. The difference is that in this panel, the allocation can be viewed for one, multiple or all the contracts loaded in the collateral manager. The point of this panel is to have a more global view at multi-contract level, unlike the ‘allocation’ panel which only shows the allocation for one contract at a time Graphs can be create based on this panel
Columns When running the Optimizer, the following columns may be useful:
These columns can be added in:
Check Position Market Data This function is available in the Allocation window, Util > Check Position Market Data If the box ‘Check Allocation Position’ is checked in the Option portion of the Collateral Manager window, this gives you all the missing quotes on the security positions.
|
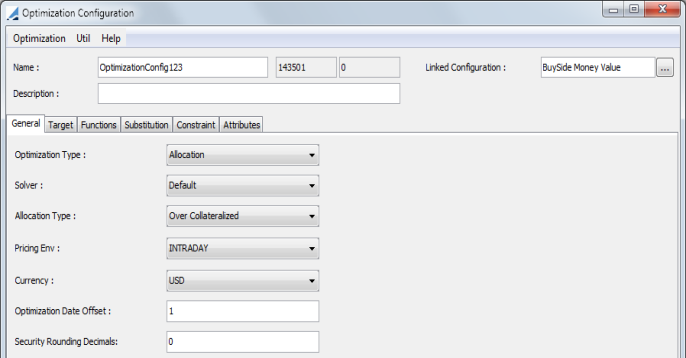
1. General Configuration
The Collateral Optimization window is available in the Margin Call contract window under Util > Optimization Configuration.
refdata.optimization.OptimizationConfigurationWindow
|
Fields |
Description |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Name |
Name of the collateral optimization configuration |
||||||||||||
|
Description |
Description of the collateral optimization configuration |
||||||||||||
|
Linked Configuration |
A Distribution Configuration can be selected in this field to link to the Optimization Configuration. With a Linked Configuration selected, the contract will be optimized for an allocation distribution automatically after the initial optimization. This functionality is used with Exposure Groups. |
||||||||||||
|
Optimization Type |
When the Optimization Configuration window is accessed through a bilateral margin call contract or Collateral Manager, the Optimization Type options are Allocation or AllocationDistribution. The AllocationDistribution is used exclusively for Buy Side Fund Distribution. When the Optimization Configuration window is accessed through a clearing member contract or Cover Distribution Manager, the Optimization Type options are CoverDistribution and FinalDistribution. |
||||||||||||
|
Solver |
Solver choices can vary depending on the Optimization Type chosen. For the Bilateral solvers:
For the Cover Distribution solvers, the options are the same regardless of the Optimization Type. The solvers available are Distribution-Rule and Asset-Distribution-Rule. These Solvers are described below. |
||||||||||||
|
Allocation Type |
Choose between:
|
||||||||||||
|
Security Rounding Decimals |
Entering a value in this field, allows you to specify the nominal precision for an allocation. Using fractional amounts for the nominal allows you to leave the price unchanged (or minimally changed) to perfectly equal the exposure amount. |
||||||||||||
|
Pricing Environment |
Pricing environment to use for the FX rate in case more than one collateral contracts are optimized at once |
||||||||||||
|
Currency |
The default currency. This is used in case more than one collateral contract is optimized and the contract currencies are different. |
||||||||||||
|
Optimization Date Offset |
The options for this field are 0 and -1. If this is set to -1, the optimizer looks at inventory as of the previous day. This can be used to offset dates for Static Data Filter, Bond, Equity, Eligibility and Inventory optimization constraints. |
2. Solvers
Calypso has eight optimizers (or solvers), Simplex and Allocation-Rule, used for the Allocation Optimization Type, Money-Value, Collateral-Quantity, Exposure-Based and Targeted-Allocation, used for the Allocation Distribution Optimization Type and Distribution-Rule and Asset-Distribution-Rule, used for the Cover Distribution & Final Distribution Optimization Types. These optimizers are described below.
2.1 Simplex Solver
The simplex solver is more complex than the default solver. It will find the best solution that respects all of the constraints.
The implementation of the Simplex algorithm has been tested for a benchmark of up to 10,000 securities, 100,000 trades, 1,000 contracts and 30,000 concentration limits. This is also dependent on the size of the inventory, the complexity of the eligibility and haircut data, the number of legal agreements being simultaneously processed and the available memory and CPU resources on the user's workstation.
Example of Simplex Solver
Assuming the following:
| • | There are two candidates, Bond A and Bond B |
| • | There are 1,000 of Bond A and 2,000 of Bond B |
| • | The concentration limit indicated that the allocation cannot be more than 60% of Bond A |
| • | The Target Limit is Minimize-Cash |
| • | Required Margin is 2,000 |
It would be translated as:
|
Target |
|
|
F = Cash (Minimize) |
|
|
Constraints |
|
|
Bond A < 1,000 |
Bond A Inventory Constraint |
|
Bond B < 2,000 |
Bond B Inventory Constraint |
|
Bond A + Bond B + Cash = 2,000 |
Required Margin Constraint |
|
Bond A ≤ 1,200 (2,000 x 60%) |
Concentration Constraint |
|
Bond A, Bond B, Cash > 0 |
Implementation for Simplex Solver
There are three implementations available for this solver:
| » | Minimize-Cash |
In this case, the target is to minimize cash. The weight will be 0 for all assets, except the cash that will be weighted at 1. It can be translated mathematically to F = Cash
| » | Collateral-Cost (minimize or maximize) |
The weight (cost) of each asset comes from a pricer that needs to be implemented.
| » | Weighted-Category (minimize or maximize) |
For each asset class, you must define a weight.
If the target is to minimize, the optimizer will first give assets with the smallest weight and keep the assets with the biggest weight.
If the target is to maximize, the optimizer will first give assets with the biggest weight and will keep the assets with the smallest weight
It can be translated mathematically to F = Wcat1.BondA + Wcat1.BondB + Wcat2.BondC + Wcat3.Cash
Goal Type - This is defined only if the optimizer is Simplex and the Target Type is Weighted-Category. You must define whether the optimizer's goal is to minimize or maximize.
Inventory - Mandatory constraint for a Simplex/Weighted Category solver.
2.2 Allocation-Rule Solver
The Allocation-Rule solver performs allocations using a set of rules that defines the steps of the collateral selection. This selection is made after every other constraint is applied. This rule is based on allocation preferences. It selects the best collateral based on the rules and allocates as much of this collateral as possible while respecting the defined constraints, such as eligibility or concentration.
The target configuration type that must be used for this optimizer is Allocation-rule.
2.3 Distribution-Rule Solver
This solver is used with Cover Distribution.
The Distribution-Rule optimizer is an order based algorithm. It finds a solution based on the target that respects all of the constraints. It first sorts the liabilities, then sorts the assets to cover within each liability. Each liability is fully processed before moving on to the next liability. The target configuration type that must be used for this solver is Distribution-rule.
2.4 Asset-Distribution-Rule Solver
This solver is used with Cover Distribution.
This also is an order based algorithm. With this rule, each asset preference is applied to the liabilities in the liability order over multiple passes, with the different asset preferences. In this model, each liability is not fully processed before moving on to the next. Instead, each asset preference is allocated before moving on to the next asset preference. The target configuration type that must be used for this solver is Asset-distribution-rule.
2.5 Exposure-Based Solver
This solver is used to distribute cash to Exposure Groups based on the ratio of each Exposure Group's Net Balance over the total Net Balance, minus the previous day's cash balance per Exposure Group.
2.6 Money-Value Solver
This solver is used for Buy Side Fund Distribution. It is used for collateral distribution for cash margin call trades.
2.7 Collateral-Quantity Solver
This solver is used for Buy Side Fund Distribution. It is used for collateral distribution for security margin call trades.
2.8 Targeted-Allocation Solver
This solver is used for Buy Side Fund Distribution. It is used for collateral distribution for security margin call trades.
3. Functions
In this panel, you are able to select various functions that will take place during an optimization. These include, Allocation, Recall, Return and Substitution.
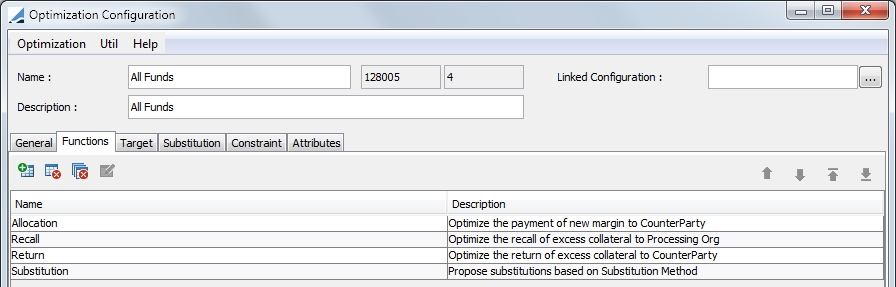
The Return function returns the cheapest excess collateral back to the Counterparty using the Target Configuration defined in the Optimization Configuration. The Recall function returns the most expensive excess collateral back to the Processing Org but does the inverse of what is set in the Target Configuration.
For example, if the Target Configuration is set to Minimize, Return will minimize and Recall will maximize. If the Target Configuration is set to Maximize, Return will maximize and Recall will minimize.
All functions (Allocation, Recall, Return and Substitution) are set by default in the Functions panel. If you do not wish to have a particular function performed, it must be deleted manually.
4. Target Configuration
The Target panel enables you to define the target for the optimization such as minimizing cash, optimizing based on a category, category weighting or based on collateral cost as well as your target allocation for cover distribution.
In the Default optimizer, the securities available for allocation are the securities that are designated in the Eligible Securities panel of the contract definition as well as in the categories selected in the target. (This is if the target contains categories which would be in the Target Types Category or Weighted Category.)
For example, if Bond A is not in the target category, it will not be included in the allocation considerations even if it is designated in the Eligible Securities panel of the contract.
For the currencies available for allocation, they do not have to be contained in a category in the target type to be available. But, if a currency is not designated in the target category but it is designated in the Eligible Currencies panel of the margin call contract, it will be last in the order of allocation. Therefore, it will be used at the end if there is a remaining margin to pay.
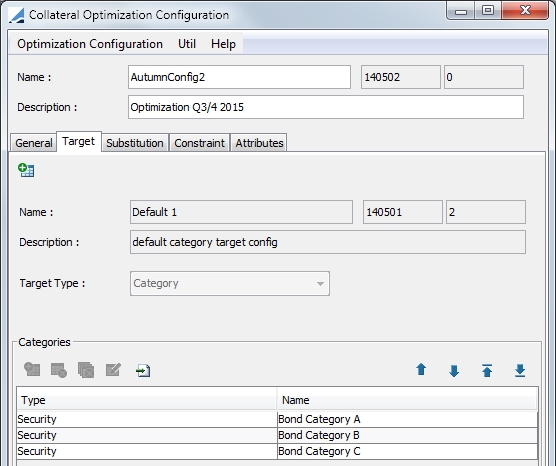
To define a target in your optimization configuration, you must first create a target configuration. Select Util > Target Configuration in the Optimization Configuration window.
|
Fields |
Description |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
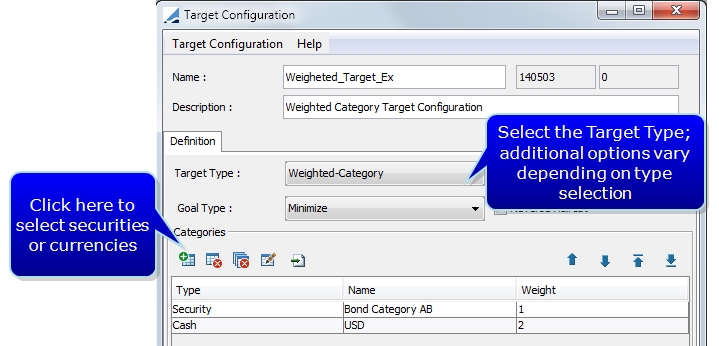
Target Type |
Select the desired target type:
The Cash Cost area is used to assign collateral cost to cash assets being allocated. As many currencies may be added as desired but any given currency can only be listed once. Each currency added is given a cost.
String name = product.getType(); String className = "tk.collateral.optimization.pricer.impl." + name + "CollateralPricer";
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Goal Type |
Only used with Weighted-Category and Collateral-Cost Target Types. The goal may be to either Minimize or Maximize the collateral in the category or inventory. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Reverse Haircut |
Selecting this checkbox makes the optimization price equal to weight * 1/haircut. |
Click  to add a category.
to add a category.
| » | For Category, you may select either a security or cash for the category. |
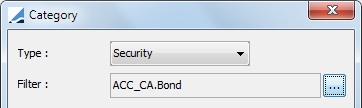
| » | For the Weighted-Category target type, you must also select a weight. |
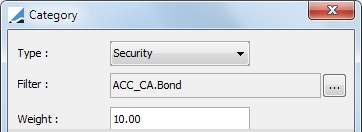
| » | For a Weighted-Category, you are able to import categories by selecting  in the Categories area at the bottom of the window. You can upload a .csv file with the following columns: in the Categories area at the bottom of the window. You can upload a .csv file with the following columns: |
| – | Security or Cash |
| – | a static data filter name |
| – | the optimization price for this category |
NOTE: When selecting a static data filter for a security, the filter should be associated with the group ANY or Margin Call.
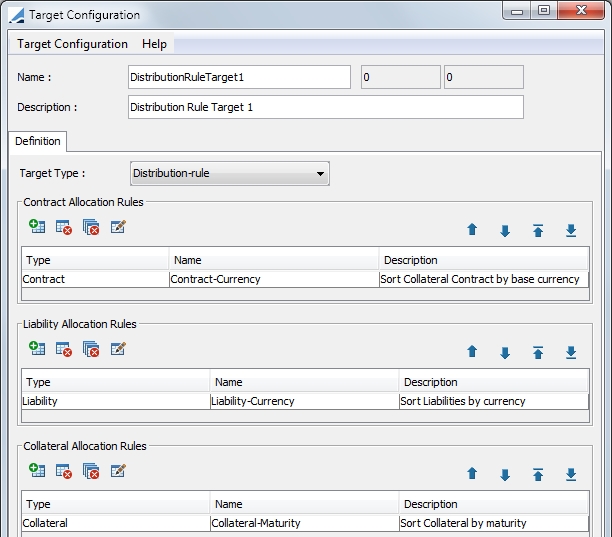
4.1 Distribution-rule Target Configuration
The target configuration for the Distribution-rule Target Type is more complex than the other target type configurations.
Ⓘ This target type is used specifically for the Distribution-Rule solver which is used specifically for Cover Distribution.
When you select the target type of Distribution-rule, there are three allocation rules that must be defined. The definition of these rules is the basis for the Distribution-Rule solver. The solver addresses these rules in order of the rule and also in order within the rule. Therefore, the priority ordering that is created for these rules is critical to the cover distribution result.
This configuration is comprised of Contract Allocation Rules, Liability Allocation Rules and Collateral Allocation Rules.
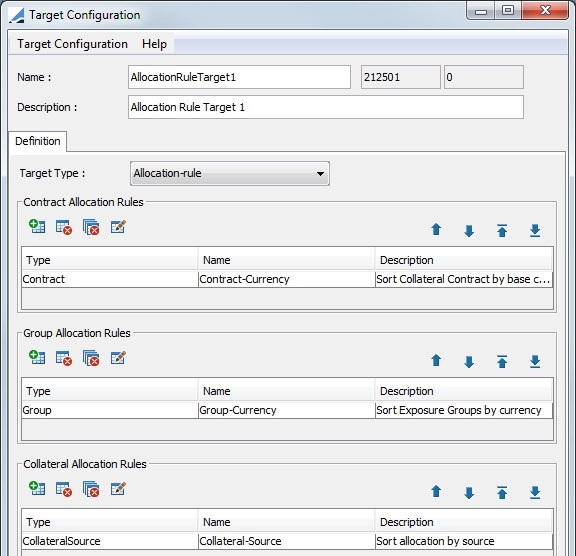
4.2 Allocation-rule Target Configuration
This target type is used specifically for the Allocation-Rule solver which is used only for bilateral collateral management.
When you select the target type of Allocation-rule, there are three allocation rules available for definition. Contract and Collateral Allocation rules should both be defined. Group Allocation Rules should be defined based on a user's needs. These rules apply to Exposure Groups.
The definition of these rules is the basis for the Allocation-Rule and Targeted Allocation Rule solvers. The solvers addresses these rules in order of the rule and also in order within the rule. Therefore, the priority ordering that is created for these rules is critical to the collateral allocation result.
This configuration is comprised of Contract Allocation Rules, Group Allocation Rules and Collateral Allocation Rules.
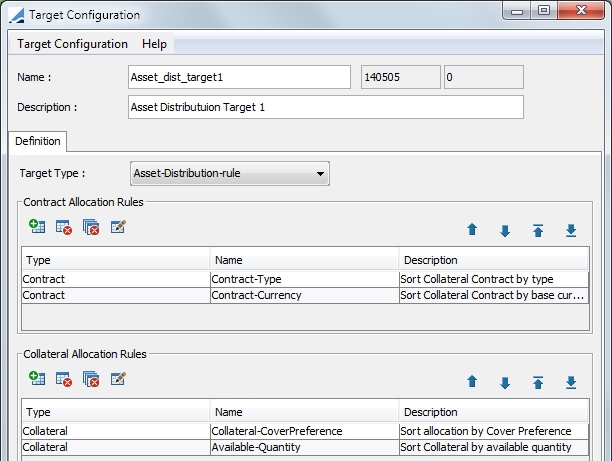
4.3 Asset-Distribution-rule Target Configuration
Ⓘ This target type is used specifically for the Asset-Distribution-Rule solver which is used for Cover distribution
When you select the Asset-Distribution-rule, there are two allocation rules that must be defined. The definition of these rules is the basis for the Asset Distribution-Rule solver. The solver addresses these rules in order of the rule and also in or within the rule. Therefore, the priority ordering that is created for these rules is critical to the cover distribution result.
This configuration is comprised of Contract Allocation Rules and Collateral Allocation Rules.
4.4 Trade-Allocation-rule Target Configuration
This target configuration is used for Money Fill Repo Allocation. For details, refer to the Repo Trading Guide.
4.5 Contract Allocation Rules
This rule allows you to specify which type of contract you would like to use first for allocation. You may specify an attribute, contract currency, subtype, type or margin requirements. (The attribute selections are taken from the Additional Info panel of the Margin Call Contract.)
It is possible to have liabilities on both a deposit and a child contract.
4.6 Group Allocation Rules
This rule applies to Exposure Groups. The Group Allocation Rules are not mandatory, but they will apply if Exposure Groups are optimizable in the scenario setup. Not all Exposure Groups can have their order of allocation optimized, this depends on other configurations.
You may specify to sort by group currency or group margin.
Select to sort either by group currency or group margin.
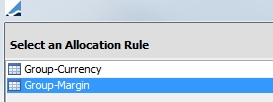
Click Next.
If Group-Currency is chosen, you are prompted to select the currency or currencies in the next window. If there are multiple currencies, they will be sorted in the order that is specified.
If Group-Margin is chosen, Exposure Groups will be sorted by required margin in either ascending or descending order.
4.7 Liability Allocation Rules
The liability allocation rules specify type of liabilities to allocate and in which order. Select  to add a new rule.
to add a new rule.
Select to either sort the liabilities by currency or by name.
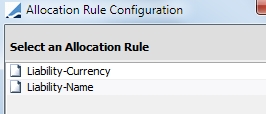
Click Next.
If you choose Liability-Currency, you are prompted to select the currency or currencies in the next window. If there are multiple currencies, they will be sorted in the order that is specified.
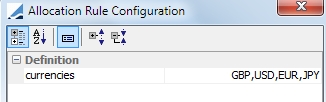
If you choose Liability-Name, you are prompted to select a liability group or groups and a direction for the sorting, ascending or descending.
Excess buffer maybe a liability group in this scenario as well. In order to have the excess buffer allocated last, add a rule with Liability-Name with only excess buffer selected as the group with descending order. Then, you may sort by Liability-Currency. After that, add another Liability-Name rule that contains the remaining groups by which you would like to sort using ascending order.
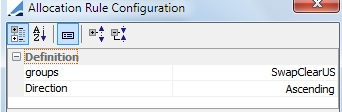
The solver will look at the first rule first, in the above example, sorting the liabilities by currency. Then, it will sort those in the designated group by name in ascending order.
4.8 Collateral Allocation Rules
This rule set, allows you to specify the collateral allocation order.
You have the ability to designate collateral based on available quantity, category and currency.
For Cover Distribution, you also may elect to use the cover preferences specified in the clearing member contract.
|
Rule Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Available-Quantity |
Specify ascending or descending order. This rule takes into account any constraint based on quantity. |
|
Collateral-Category |
Specify the liability currency for the category as well as the category target configuration used as an order preference for the categories.
|
| Collateral-Currency |
Select a currency or multiple currencies by which to sort the collateral. The collateral will be sorted by the currencies in the order specified.
|
|
Collateral-Haircut |
Sort collateral by haircut, ascending or descending. |
|
Collateral-Maturity |
Sort collateral by maturity, ascending or descending. |
|
Position Value |
Sort security by position value, ascending or descending. |
4.9 Liability Group Configuration
The creation of liability groups allows for the combining of liabilities and placing them into a group so that they may be considered as the same in terms of cover distribution.
Liability group configuration is done in the Liability Group Context window. This window can be accessed from the clearing member contract by selecting Util > Liability Group Configuration refdata.clearing.LiabilityGroupContextWindow.
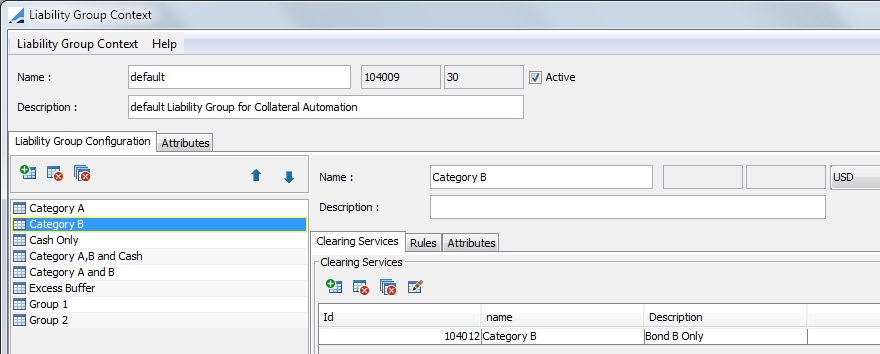
Follow the steps below to configure a liability group.
| » | Enter a liability group name and description and select a currency. |
| » | Designate the clearing services to which the liability group subscribes. |
| » | Define rules that apply specifically to the liability group. The rule types are: |
| – | Excess Buffer - When this rule is defined, it means that the excess buffer that is defined at the contract level is used as a liability group. |
| – | Liability Grouping - This rule allows you to group liabilities to match a specified static data filter. Select the static data filter to use. Select the Ccy Breakdown checkbox if you wish to group the liabilities per currency. If you do not select the Ccy Breakdown checkbox, there will be one group for all currencies. |
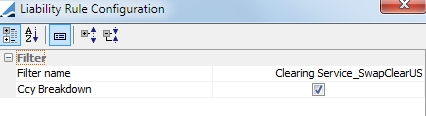
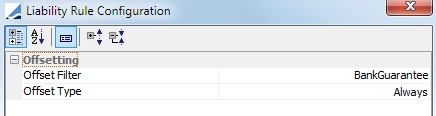
| – | Liability Offsetting - This rule allows you use positive liabilities to offset negative liabilities. This rule is always based on a static data filter. Select the offset filter and the offset type, either Always or By Filter |
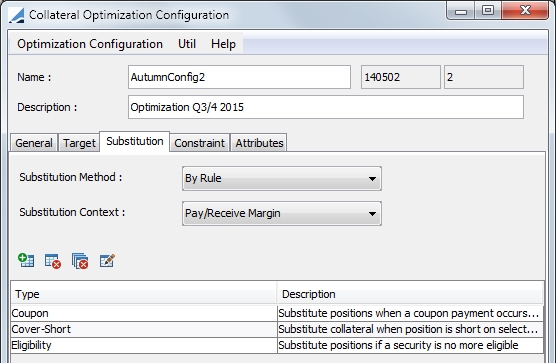
5. Substitution
The Substitution panel determines if the optimizer should proceed to substitutions and if so, under which conditions. Substitutions would occur when collateral previously part of the optimal solution is no longer part of the latest optimal solution when the optimizer is re-run.
| » | If substitution is not allowed, even if collateral previously given as collateral no longer fits the optimal solution, the collateral will not be moved back in the inventory and will not be replaced by other collateral. |
| » | If substitution is allowed, then if collateral previously given as collateral no longer fits the optimal solution, it will be replaced by other collateral. |
| » | For Cover Distribution, the Substitution Method must be Always. |
5.1 Substitution Methods
You may choose from three substitution methods:
| • | Never - The optimizer never proceeds to substitution. This limits the number of trades and therefore the cost. But, if eligibility rules change, collateral given out may no longer respect those rules. |
| • | Always - The optimizer will always proceed to substitution. Using this option always ensures the best possible allocation. But, it may create a large number of trades. Previously delivered collateral will not be reallocated to another contract. Only collateral in the inventory will be substituted. |
This is the required option to be used in cover distribution.
When Always is selected, a Substitution Delta field is displayed. A designation in this field prevents substitution of like for like collateral by reducing the weight of previously delivered collateral by the value in the Substitution Delta field.
This value should be set based on the number of decimals present in the weighting table of the weighted category Target configuration. If weights are defined to 2 decimal places, then a delta of .01 means assets of identical weight will be less preferable to the previously delivered collateral.
For example, a previously delivered asset with a weight of 10.25 will be considered as having a weight of 10.24 and therefore is preferable to another asset with the same weight in the inventory. The delta can be set to a larger value to increase the material benefit of a substitution. Setting to delta to 1 in the above example would mean that the previously delivered asset with a weight of 10.21 will only be substituted if it finds an asset in the inventory with a weight of 9.24 or less.
| • | By Rule - If this option is chosen, click  to display the Substitution Configuration window. The options in this window are described below. to display the Substitution Configuration window. The options in this window are described below. |
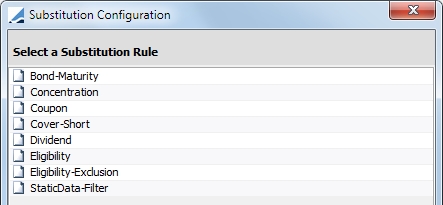
Each of the available substitution rules are detailed below.
|
Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
|
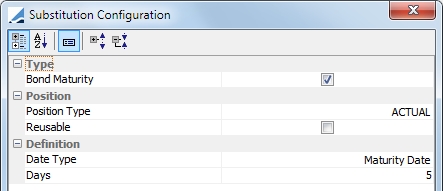
Bond-Maturity |
Substitute positions when a bond maturity date is occurring in the next n days.
Position Type: ACTUAL or THEORETICAL Reusable: not applicable (not reusable) Date Type: Maturity Date is the only option Days: Enter the number of days within which the bond maturity date should be for substitution. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
|
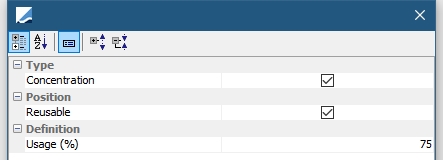
Concentration |
Substitute positions when a concentrations limit is breached.
Reusable: Select if the substituted position can be re-used for the allocation concentration rule type. Usage (%): Usage per cent of the concentration limit Cash concentration limit breaches are considered when allocating collateral using the Allocation-Rule solver with the Concentration rule set. Cash collateral substitution is automatically created. |
|
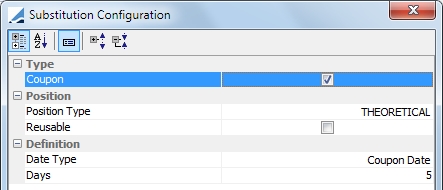
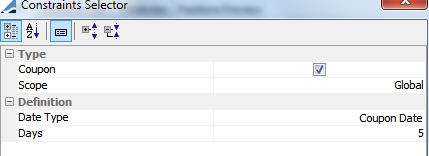
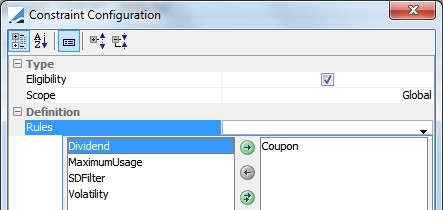
Coupon |
Substitute position if a coupon payment is to occur in the next 'x' days.
Position Type: ACTUAL or THEORETICAL Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called into another allocation. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. Date Type: Coupon Date or Record Date Days: If a coupon payment is to occur under the designated number of days, the security is not used by the optimizer as a substitution. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
|
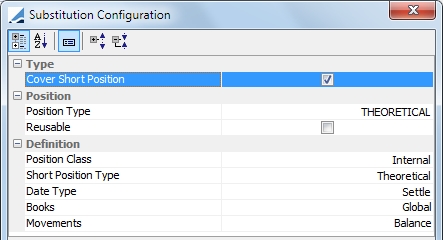
Cover Short |
Substitute position when a position is short on selected books.
Position Type: ACTUAL or THEORETICAL Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called into another allocation. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. Position Class: Position class filter. Select from Internal, External, Client Margin_Call Short Type Position: Any position defined in the Inventory Position such as Actual, Not Settled, Theoretical, Expected, Forecast, etc... Date Type: Available, Booking, Settle or Trade Date Books: Select books considered for this substitution rule. Movements: Any balance of movement type defined in the Inventory Position. |
|
Dividend |
Substitute position if a dividend payment is to occur in the next 'x' days.
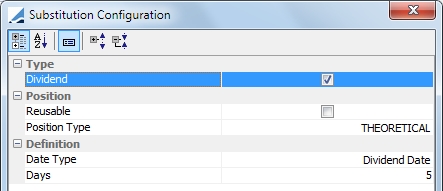
Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called into another allocation. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. Position Type: ACTUAL or THEORETICAL Date Type: Date type description, Coupon Date or Record Date Days: If a dividend payment is to occur under the designated number of days, the security is not used by the optimizer. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
|
Eligibility |
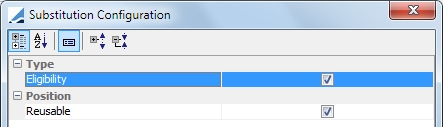
Substitute position if a security is no longer eligible.
Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. |
|
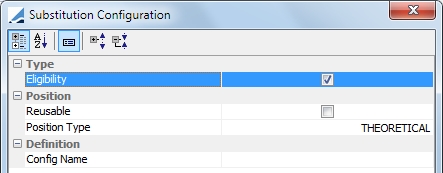
Eligibility - Exclusion |
Substitute position if a security is part of the temporary exclusion configuration.
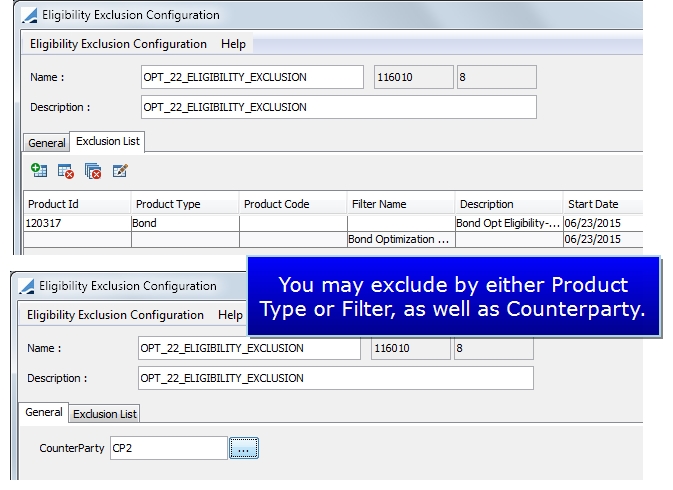
Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called into another allocation. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. Position Type: ACTUAL or THEORETICAL Config Name: Any configuration defined in the Eligibility Exclusion Configuration window. To access this window, in the Collateral Configuration Optimization window, select Util > Eligibility Exclusion.
|
|
Static Data Filter |
Substitute position if a security belongs to a designated static data filter.
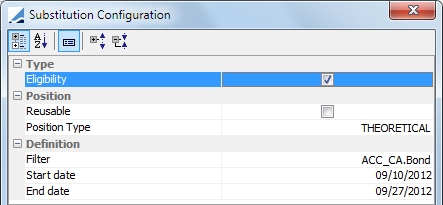
Reusable: If this is selected, the optimizer re-injects collateral that has been called into another allocation. If it is unselected, re-injection is not possible. Position Type: THEORETICAL or ACTUAL Filter: Select any defined static data filter Start date: Substitute positions if a security matches a static data filter after the start date. The start date is compared against the value date of the margin call entry. End date: Substitute positions if a security matches a static data filter before the end date. The end date is compared against the value date of the margin call entry. |
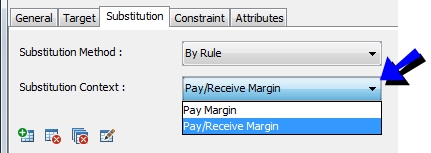
5.2 Substitution Context
You may select to optimize only contracts that are paying margin on that day by selecting Pay Margin. By selecting Pay/Receive Margin, contracts that have no call or are receiving margin will be optimized as well as contracts that are paying margin.
6. Constraints
This panel allows you to define whether the optimizer should respect certain constraints when calculating the optimal solution.
| » | Constraints may be global. Global means that the constraint applies globally to all contracts that are optimized. For example, respecting the dividends is a global constraint, but concentration is a contract specific constraint. Whether a constraint is global or not is pre-determined. This is not a selectable field. |
| » | The selection of Constraints varies depending on the Optimization Type that is chosen. |
| » | Master contract level constraints are considered when optimizing at Exposure Group level. |
Ⓘ [NOTE: There is one constraint available for the AllocationDistribution Optimization Type. This constraint is described in the Buy Side Fund Distribution documentation]
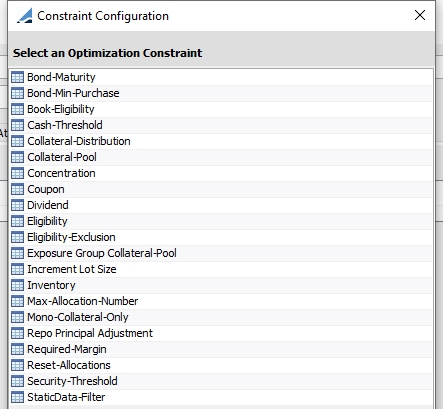
Constraint options for Bilateral Optimization
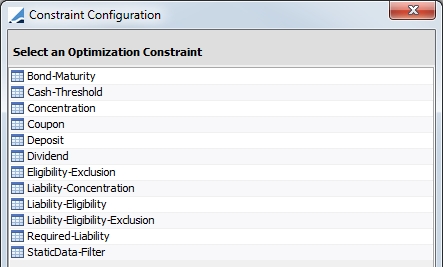
Constraint options for Cover Distribution Optimization
|
Constraint |
Description |
||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
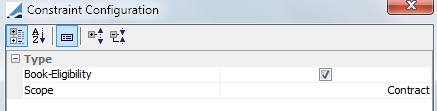
Book-Eligibility |
This constraint respects the eligible books on the contract. With this constraint, allocations are generated by book.
This is a contract specific constraint, which is indicated by the entry in the Scope field. |
||||||||||||
|
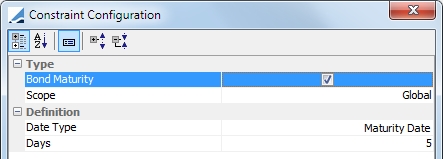
Bond-Maturity |
Using this constraint, you may exclude a security if a bond maturity date is occurring in the next n days.
Scope: This is a Global constraint which means it applies to any contract. Date Type: Maturity Date is the only option Days: Enter the number of days for the exclusion. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
||||||||||||
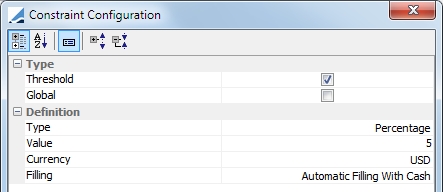
|
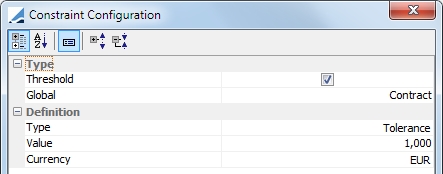
Cash Threshold |
To minimize the number of trades suggested by the optimizer, you may define a cash threshold. Because cash is the adjustment variable, any trade below the cash threshold will no be created and will result in a remaining margin. For example, if there is a cash threshold of 1,000 EUR and the optimizer found an optimal solution with a cash trade of 750 EUR, as it is less than 1,000 EUR, no cash trade will be created and there will be a remaining margin of 750 EUR.
Type:
Value: Value of the threshold Currency: Currency of the threshold |
||||||||||||
|
Collateral-Pool |
Allocate securities that are in the specified Collateral Pool. During the optimization process, the collateral positions will be generated based on the sources listed in this definition.
|
||||||||||||
|
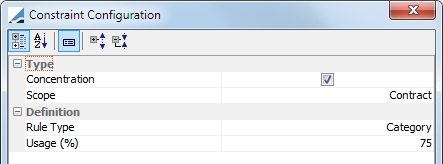
Concentration |
Securities allocated only if they fit the selected concentration rules.
Scope: This constraint is defined at the contract level Rule Type: Select concentration rule type ISSUE, ISSUER and /or CATEGORY Usage (%):
|
||||||||||||
|
Coupon |
Excludes a security if a coupon payment is to occur in the following x number of days.
Date Type: Coupon Date or Record Date Days: If a coupon payment is to occur under the designated number of days, the security is not used by the optimizer. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
||||||||||||
|
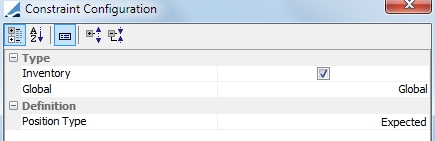
Deposit |
Indicates that you want to use a deposit account as a collateral pool. (Cover Distribution only) Ⓘ Mandatory constraint for cover distribution
Position Type: Expected should be used. This is the deposit positions based on the settle date. A deposit is not counted towards the deposit amount until the deposit is settled in the account. |
||||||||||||
|
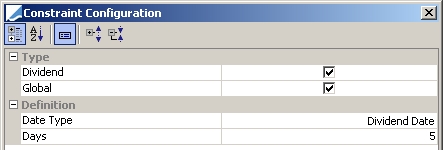
Dividend |
Excludes a security if a dividend payment is to occur in the following x number of days.
Date Type: Dividend Date or Record Date Days: If a dividend payment is to occur under the designated number of days, the security is not used by the optimizer. These days are business days, using the security holiday calendar. |
||||||||||||
|
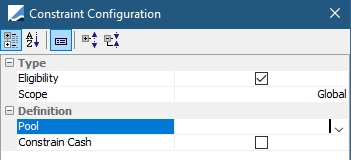
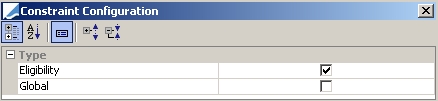
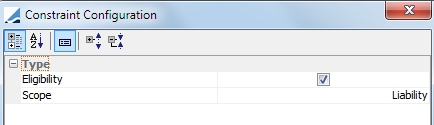
Eligibility |
Allocate only securities that are eligible per the contract definition. (Allocation only)
|
||||||||||||
|
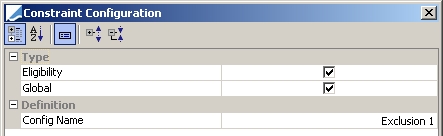
Eligibility Exclusion |
Allocate securities only if they are not part of the temporary exclusion configuration.
Config Name: Any configuration defined in the Eligibility Exclusion Configuration window. To access this window, in the Collateral Configuration Optimization window, select Util > Eligibility Exclusion.
|
||||||||||||
|
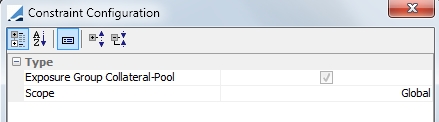
Exposure Group Collateral-Pool |
Allocate inventory from the underlying Collateral Pools.
|
||||||||||||
|
Increment Lot Size |
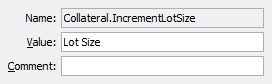
Used to designate and respect nominal lot size in the Optimizer. To use this constraint, define a product code to be used in the Collateral.IncrementLotSize domain value.
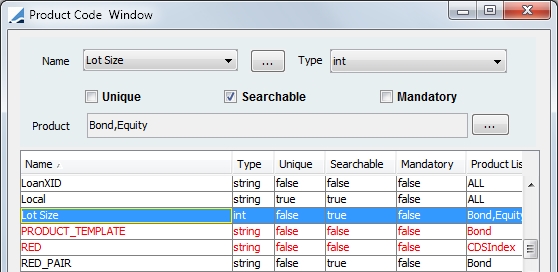
Then, define the product code in the Product Code window to be available in Bond and Equity product definition windows.
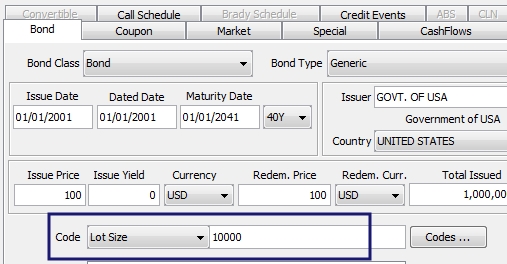
Designate the increment value in the product definition window. For example, setting it to 1000 means that allocations of the security must be in nominal quantities of 10,000.
Finally, select the constraint on the optimizer.
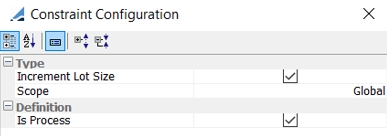
When Is Process is checked, the lot size is applied during the allocation process to the collateral candidates:
If Is Process is not checked, the lot size is applied the end of the process and may result in under allocation of collateral. |
||||||||||||
|
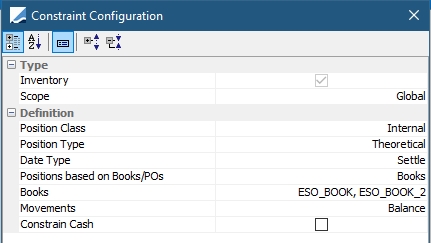
Inventory |
Allocate securities that are available on the specified inventory position on the value date defined in the collateral manager (Allocation only)
Position Class: Internal, External, Client or Margin_Call Position Type: Any position type defined in the Inventory Position such as, Actual, Not Settled, Theoretical, Expected, Forecast, etc... Date Type: Available, Booking, Settle or Trade Date Positions based on Books/POs: If Books is chosen, the Books field is visible. The positions are loaded based on the values selected in the field. If Processing Org is chosen, the Processing Org field is visible. The positions are loaded based on the selected PO's associated books. Client: Available when Position Type is Client. The list of available clients to choose from in the Client field is populated from legal entities with the role of “Client” and/or “Counterpaty”. Account: Available when Position Type is Client. The list of available Accounts depends on the Client selected. The list contains all accounts with the legal entity of the chosen Client. Books: Select books considered for this constraint rule. Movements: Any balance or movement type defined in the Inventory Position. Multiple movements may be chosen. If multiple movements are defined, they will be part of the loading criteria when the solver is building the collateral pool. The selected movements must not overlap each other as there is no check in place to prevent such a setup. Constrain Cash: Select to include cash as a constraint. |
||||||||||||
|
Liability-Eligibility |
Indicates that you must match the eligibility that you define at the clearing service level. (Cover Distribution only)
|
||||||||||||
|
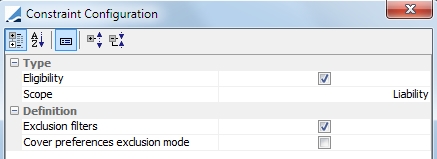
Liability-Eligibility-Exclusion |
Indicates that Eligibility Exclusions established in the contract are to be used. (Cover Distribution only) Selecting the Exclusion filters check box, means that the specific exclusions defined on the lower part of the Eligibility Exclusions panel will be respected. Selecting the Cover preferences exclusion mode checkbox, means that the choice made in the "Exclude Assets not defined as Cover Preferences" flag on the Eligibility Exclusions panel will be respected. Selecting both checkboxes respects both at the same time.
|
||||||||||||
|
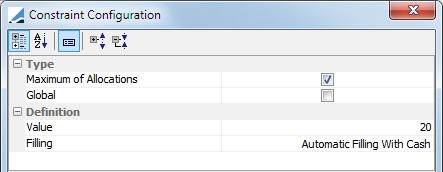
Max Allocation Number |
Limits the number of allocations per contract to the value specified in the constraint. (Allocation only)
Global: This is a global constraint Value: Maximum number of allocations permitted Filling: Filling method, Automatic Filling With Cash or No Filling
NOTE: With the Simplex solver, this constraint is a post-processing constraint. As a result, if the number of allocations suggested by the solver is above the maximum allowed, the solver replaces these additional allocations with cash. If the contract does not allow for a cash margin, the contract will not be fully allocated and this will result in the contract having a remaining margin. |
||||||||||||
|
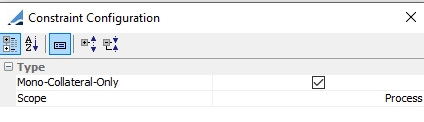
Mono-Collateral-Only |
For a given exposure, this constraint filters out any collateral asset with an available value lower than the exposure amount. This ensures that exposures will either be covered, if possible, by a single collateral asset or remain uncovered. (Used for Allocation Rule Solver)
This constraint is applied on an exposure by exposure basis an depends on each exposure amount. |
||||||||||||
|
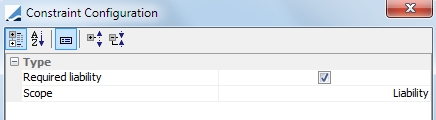
Required-Liability |
The allocation amount must be equal to the liability (Cover Distribution only) Ⓘ Mandatory constraint for cover distribution
|
||||||||||||
|
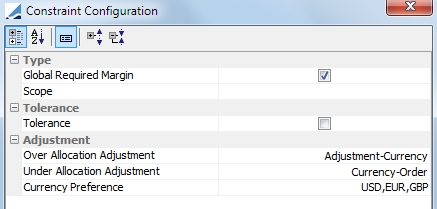
Required Margin |
Ⓘ Mandatory constraint Allocated amount must be equal to the Global Required Margin (Allocation only)
Tolerance: Select if the optimizer can use the tolerance as defined in the margin call contract Over Allocation Adjustment: Specify how to adjust when there is an over allocation Under Allocation Adjustment: Specify how to adjust when there is an under allocation Options for Over Allocation Adjustment and Under Allocation Adjustment are:
Currency Preference: Define the currency preferences for the remaining allocation when Currency-Order is selected.
NOTE: The remaining amount is not able to be adjusted with a security. It may only be adjusted with cash. |
||||||||||||
|
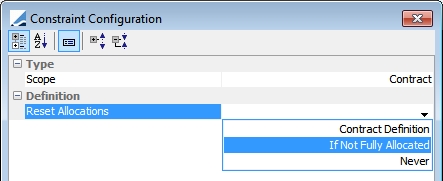
Reset Allocations |
Affects contracts that accept SECURITY only (because CASH is considered to be unlimited). This constraint can be set at the contract level.
Contract Definition: The optimizer refers to what has been defined on each contract If Not Fully Allocated: The optimizer resets allocations (does not suggest any allocations) if the contract is not fully allocated due to insufficient inventory (ie. there is an remaining margin) Never: The optimizer will be allowed to do partial allocations of contracts
NOTE: If there is remaining margin on a SECURITY only contract due to ROUNDING and not due to insufficient inventory, the allocations will not be reset. |
||||||||||||
|
Security-Threshold |
Unlike the cash-threshold, the security-threshold does not lead to a remaining margin, since the security is not an adjustment variable. (Allocation only) If the optimizer suggests an allocation with a security for an amount under the security threshold, the corresponding trade will not be suggested and the optimizer will move to find another security. The security threshold can modify the typology of the allocation but will not create a remaining margin.
Type:
Value: Value of either the percentage or value in the Type field Currency: Currency for the constraint Filling: Filling method, Automatic Filling With Cash or No Filling |
||||||||||||
|
Source |
Allocate securities based on collateral source. This rule can only be used if the optimization uses a collateral pool constraint.
|
||||||||||||
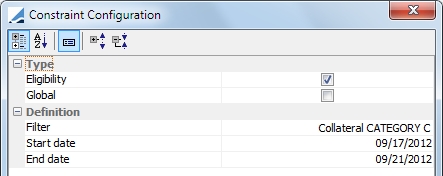
|
Static Data Filter |
Allocate securities only if they do not match the static data filter selected.
Filter: Select any static data filter available. Start Date: Excludes collateral that matches a Static Data Filter after the Start Date. The start date is compared against the value date of the margin call entry. End Date: Excludes collateral that matches a Static Data Filter before the End Date. The end date is compared against the value date of the margin call entry. |
NOTE: The Attributes tab is currently not used.
7. Optimization Process
The optimization process can be run manually from various points in Calypso.
| » | Optimization is based on the Remaining Margin. |
Remaining Margin = Global Required Margin – Booked Allocation Margin – Pending Allocation Margin where
Booked Allocation Margin = Daily Cash + Security Margin and
Pending Allocation Margin = Cash + Security Margin
| » | The Remaining Margin will be 0 if there is a margin call and the Global Required Margin if there is no call. |
| » | To designate and respect nominal lot size in the Optimizer, use the Increment Lot Size Constraint. |
7.1 Manual Optimization
In the Collateral Manager, click the Optimize button.
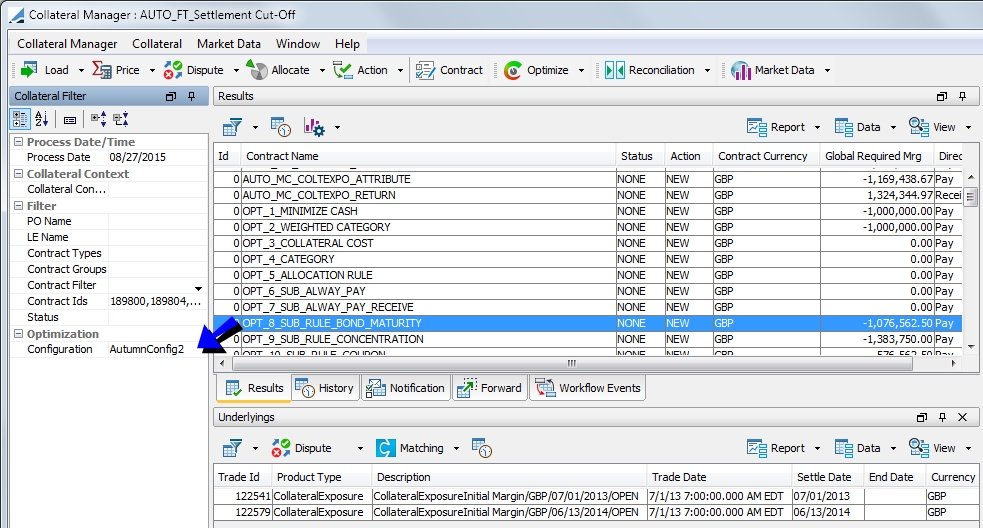
To optimize in this manner, you must set the Optimizer that you want to use in the Margin Call Filter section of the window. Once this is set, you can run the optimization through the  button.
button.
You can choose to optimize only the contracts selected (Optimize Selected) or all of the contracts loaded (Optimize All). By default, the optimization is run only on the contracts selected. From this button, you are also able to select Configuration, which will open the Collateral Optimization Configuration window.
7.2 Optimization from Collateral Allocation Window
To display the Collateral Allocation window, click the  button, or select Margin Call > Allocate from the menu.
button, or select Margin Call > Allocate from the menu.
Select the optimizer that you would like to use from the drop-down box and then click  . If the optimizer is run from this window, it is run at the contract level.
. If the optimizer is run from this window, it is run at the contract level.
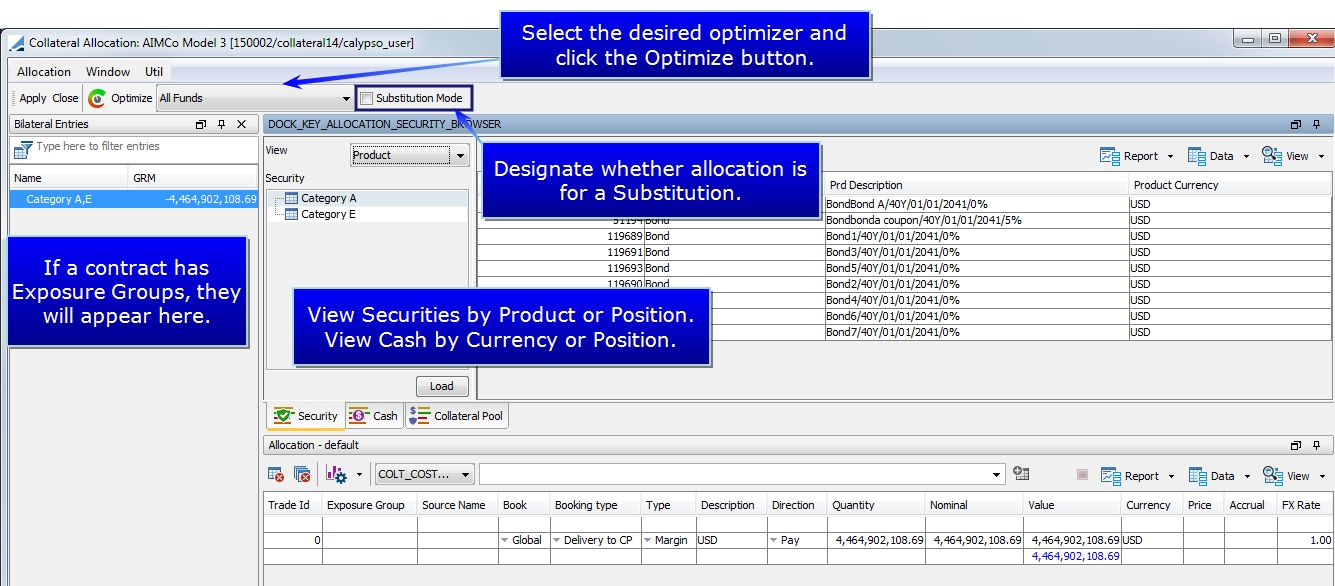
For contracts utilizing Collateral Pools, the Collateral Pool panel allows you to sort and display positions based on the pools.
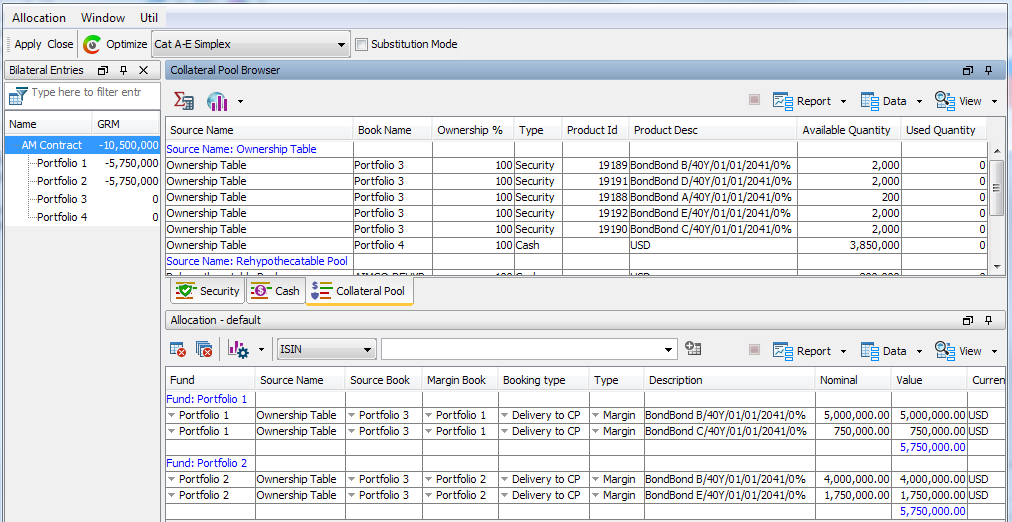
Positive, Negative and null Exposure Group positions can be filtered for display.
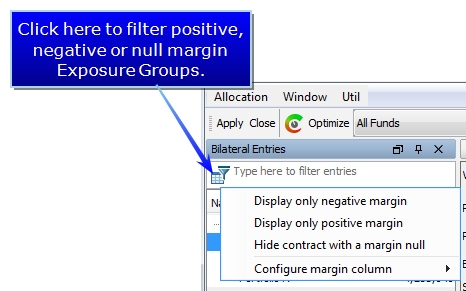
It is possible to hide the Filter using a menu option available in the Window > Show View menu. This view is also part of what is saved when a Template is created.
Ⓘ [NOTE: The Collateral Allocation search depends on product types added to the ProductSelectorTypes.Repo and bondType domains. If all of the expected bonds are not displaying in the search, make sure that the appropriate bond type is in each of these domains]
7.3 Optimization via Scheduled Task
You may run the optimization as part of an End of Day process using a scheduled task. For bilateral collateral management, see COLLATERAL_MANAGEMENT Scheduled Task. For cover distribution, see COVER_DISTRIBUTION Scheduled Task.
7.4 Optimization via Engine Server
You can elect to run the Optimizer in the Engine Server by setting the following environment properties:
UseCollateralOptimizationService = True to enable the feature - There is a “Optimization Events” tab on the Collateral Manager where you can see the status of the optimization. When it completes, you will get a popup saying optimization completed.
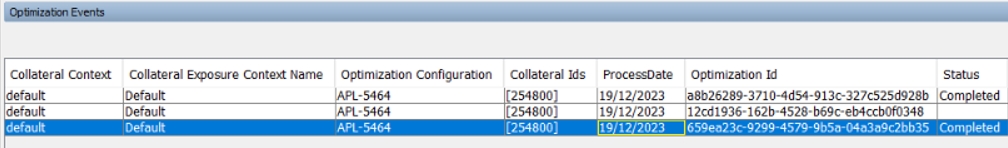
AutoSaveServerSideOptimization = True to save the optimization results to the database by automatically applying the action associated with "Allocate" (in Collateral Context > Workflow panel) to the margin call entry when the optimizer completes.
8. Lock Process
It is possible to lock a collateral position suggested by the optimizer. If you are not satisfied with the suggested allocation, you can add new collateral and input the value, or change the value of one of the collateral.
The optimizer will not consider the previously locked allocations as used Inventory. These allocations are excluded from the Optimization process.
Initial Optimization Run
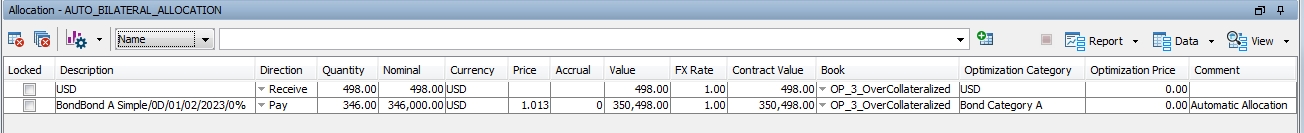
Adding a manual allocation and locking the column:
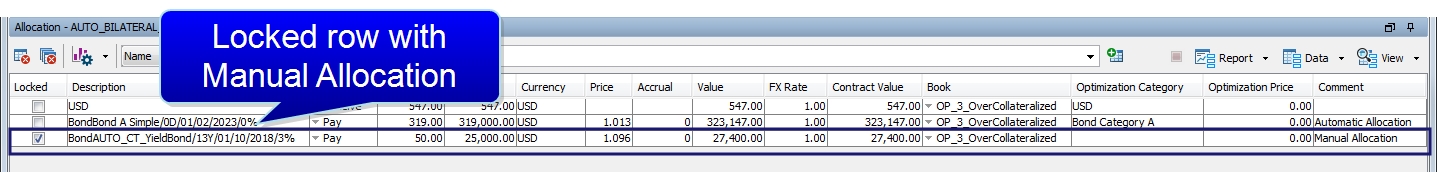
After the optimizer is rerun, the solution is now:

9. Optimization Analysis
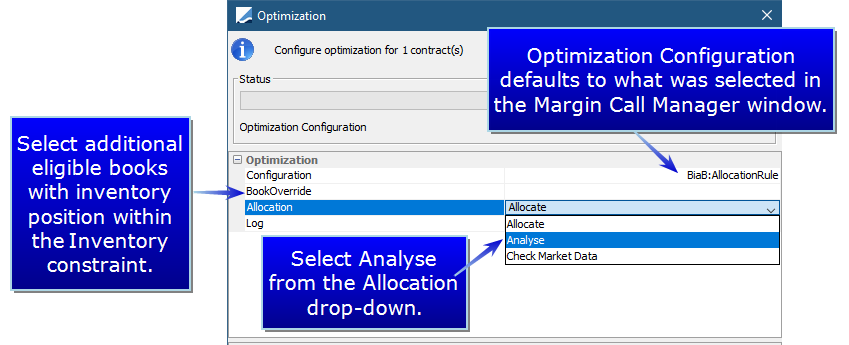
In order to understand or analyze an optimization without actually performing an allocation, the Optimization Analysis functionality is available. Using the Optimization Analysis, you are able to load, save update and delete an optimization. Optimization Analysis can be run from Collateral Manager via the Optimize button or from the COLLATERAL_MANAGEMENT scheduled task using the Optimization attribute.
9.1 Running an Optimization Analysis
To run an Optimization Analysis, Select Optimize Selected or Optimize All from the Optimize drop-down button.
After the optimization is completed, the Optimization Analysis window is displayed.
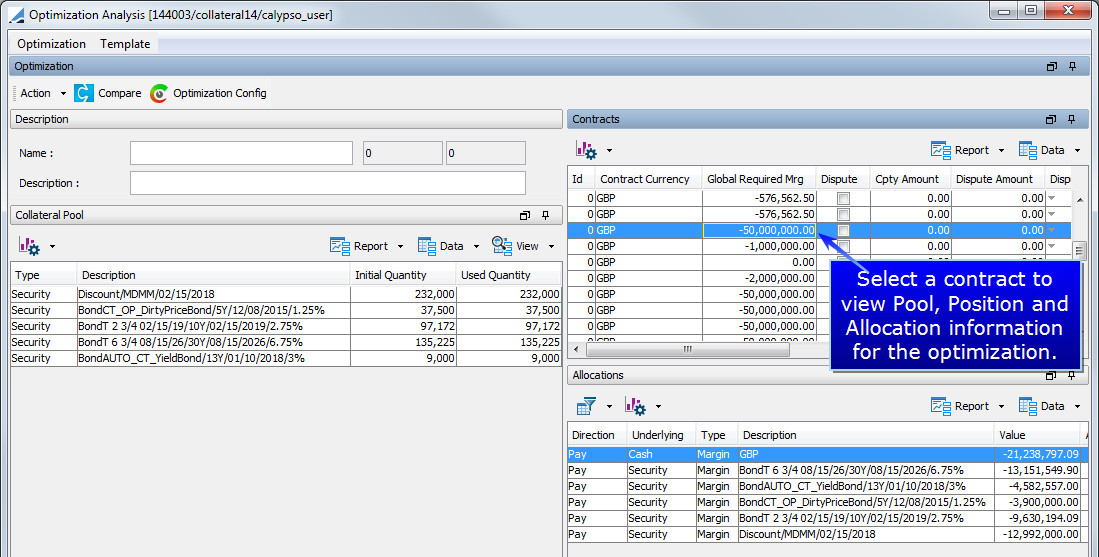
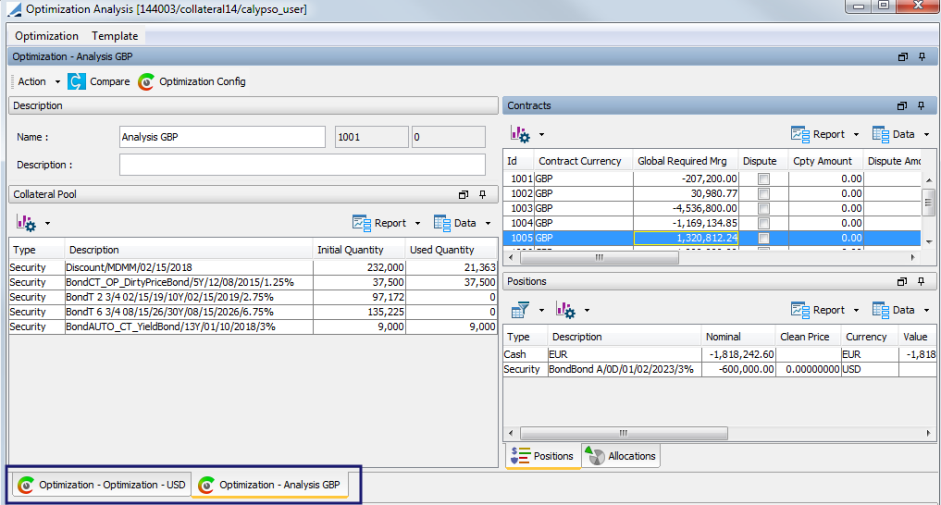
The Contracts section contains regrouped information on the contracts, which allows for navigation between them.
The five panels in the windows are:
| • | Description: This area contains the name, Id, version and description of the optimization after it has been saved. |
| • | Contracts: These area the contracts contained in the optimization. Select a contract to display details in other areas of the window. |
| • | Allocations: Allocation information for the selected contract entry |
| • | Positions: Position information (allocations from previous days) for the selected contract |
| • | Collateral Pool: This area displays the collateral pool for each contract entry. This pool contains the list of each security accepted by the contract with the initial quantity and the quantity used by the optimizer to make allocations |
9.2 Saving and Loading an Optimization
| » | You may save an optimization by selecting Save from the Action button drop-down. |
This action only saves the active optimization. If you wish to save all of the optimizations that are open, select Optimization > Save All.
Action > Delete deletes the selected optimization, while Action > Close closes the selected optimization.
| » | To load a saved optimization, select Load from the Optimization menu. |
| » | From the Collateral Manager window, choose Optimize > Optimization Analysis to display the Optimization Analysis window without executing an optimization if you wish to load an already saved optimization. |
| » | You may save, load and delete templates as well through the Template menu option. A template saves the way the window is displayed, such as the report templates and the layout of the window. |
If several optimizations are open at the same time, they are displayed in different tabs in the window.
9.3 Optimization Comparison
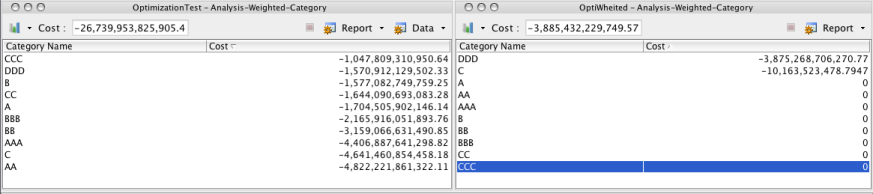
The Collateral optimization framework provides multiple solver implementations (Default, Allocation-Rule, Simplex) with different target/goal definitions. Optimizations cannot be compared without a common measure of comparison. For example, the Simplex solver requires a weighted per asset category but the default solver uses a sorted list category. To achieve the comparison, a "comparison target" is defined, which needs to be defined as a weighted category.
To run a comparison on all of the open optimizations, click the  button. A comparison configuration window is displayed containing two options, Target and Aggregation by.
button. A comparison configuration window is displayed containing two options, Target and Aggregation by.
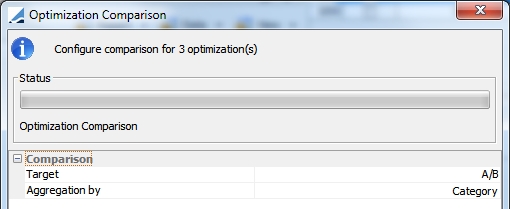
| • | Target: Choose the weighted target configuration which will be used as a reference to make the comparison |
| • | Aggregation by: This allows you to define the optimization category by which the securities will be aggregated. By default, categories aggregate by static data filter names. |
After the comparison is complete, the comparison will be displayed in the bottom part of the window.
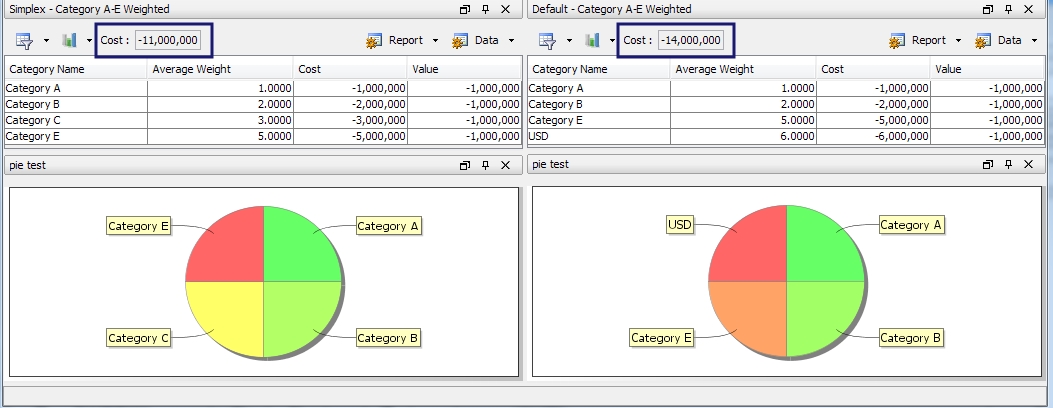
On the top of the report is a present cost, which represents the total cost of the optimization. This cost gives a quick comparison of the optimizations in the same base optimization target defined during the comparison setup. In this example, you can see that the cost of the Simplex - Category A-E Weighted optimization is less than the cost of the Default - Category A-E Weighted optimization. This comparison area also provides the options of displaying the allocations in the optimizations visually via charts and graphs. Click  and select Create. From this menu, you may select several different charts. After the chart is created, select Add from the chart menu to add it to the Optimization Analysis window.
and select Create. From this menu, you may select several different charts. After the chart is created, select Add from the chart menu to add it to the Optimization Analysis window.
9.4 Creating an Optimization Analysis Custom Attribute
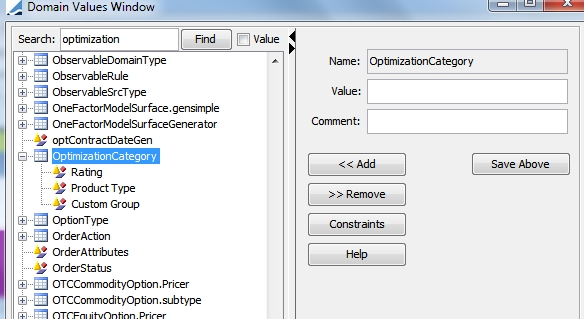
Sometimes, the number of categories used in the comparison may be too high to obtain a good high-level view. To obtain a better view, an upper-aggregation level may be defined as an Optimization Category custom attribute.
Custom attributes are defined under the domain value OptimizationCategory.
Once a custom field is defined in the domain value, it will be automatically added to the Target Configuration window. You are also able to add the attributes directly through the Target Configuration window by clicking the  .
.
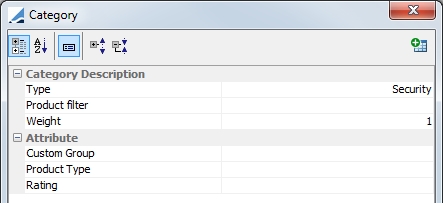
The target type should be Weighted Category. Below is an example of a completed target configuration using the custom attributes.
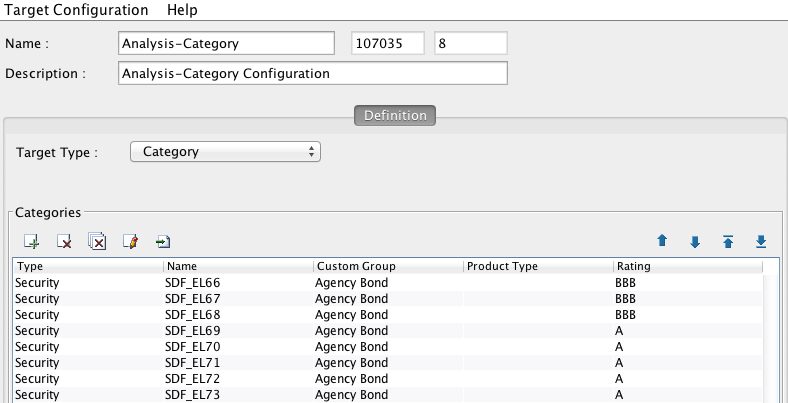
Now, using this configuration, in the Optimization Comparison, you could choose to aggregate by Rating in the Aggregation by field to display comparison that is easier to interpret.