Scheduled Tasks Configuration and Execution
The Scheduled Tasks window allows monitoring scheduled tasks execution, configuring scheduled tasks and chains of scheduled tasks, and scheduling the execution of scheduled tasks.
Scheduled tasks are executed by the Calypso Scheduler.
Contents
- Tour of the Scheduled Tasks Window
- Execution Report - Task Execution Monitoring
- Task and Schedule Configuration - Configuring Scheduled Tasks
- Process Log - Viewing Execution Logs
1. Executing Scheduled Tasks
1.1 Executing Scheduled Tasks On-the-fly
You can select a task in the Scheduled Task Definitions & Scheduling window, and execute it on-the-fly using the Run button.
Using this function will not affect the task's schedule, or any chained task to which it belongs.
Ⓘ [NOTE: It requires the Calypso Scheduler to be running]
1.2 Starting the Calypso Scheduler
The Calypso Scheduler is started using "<calypso home>/deploy-local/<environment>/scheduler.bat" on Windows platforms, or "<calypso home>/deploy-local/<environment>/scheduler.sh" on *nix platforms.
With the API Gateway, you need to start the following servers BEFORE starting the Calypso Scheduler:
discoveryServer.bat\.sh
gatewayServer.bat\.sh
sharedServices.bat\.sh
scheduler.bat\.sh
You can set the following spring-boot properties in <calypso home>/client/resources/appConfig/scheduler.properties:
calypso.timezone.defaulting-strategy to select the strategy for setting the reference timezone of the server:
None - No strategy
DataBase - (Default) The strategy sets the timezone of the Calypso Scheduler to the data server timezone
UserDefaults - The strategy sets the timezone of the Calypso Scheduler to the User Defaults timezone of CLIENTUSER
skip execution timeout to set the skip execution timeout - Default is 1 minute.
You can set it to a number of ms if the unit is not specified (example 120000 for 2 minutes) or specify the duration unit like 2m (for 2 minutes), 1h (for 1 hour).
In case the Data Server is not up and running, connection retry upon first attempt is based on environment properties MAX_NUMBER_OF_RECONNECTION and TIMEOUT_RECONNECT.
Two log files are generated on the server where the Calypso Scheduler is running, under <user home>/Calypso:
| • | CalypsoScheduler_<environment>_<version>.log – Log file for scheduled tasks executed on-the-fly. |
| • | CalypsoScheduler_ScheduledTask_<environment>_<version>.log – Log file for scheduled tasks executed using a schedule. |
You can also view the log files for the Calypso Scheduler from the Calypso DevOps Center.
You can view log files for individual scheduled tasks from the Execution Report panel in the Scheduled Tasks window.
If one of the scheduled tasks in a chain is stopped, or finishes with errors, or is not triggered (due to insufficient memory), the chain will be finished with errors (no other scheduled task is executed). To view the failed scheduled tasks ids, you have to turn on the log category "com.calypso.apps.scheduling.BaseCalypsoJobListener" to INFO level.
When stopping a chain, all scheduled tasks inside the chain are stopped.
By default, the Scheduler starts with a fresh index folder when there is a CorruptIndexException. An error message is logged and the corrupted index folder is backed up.
You can set environment property SCHEDULER_AUTOFIX_CORRUPTED_INDEX = false to turn off that feature. In this case, the Scheduler does not start when there is a CorruptIndexException.
Arguments
| • | -memory – Max allowable memory in gigabyte. Default is 5GB. |
This is not the memory allocated to the Calypso Scheduler process to run, this defines how many scheduled tasks can be run in parallel.
For example, if you have 10 scheduled tasks with -Xmx512m and Calypso Scheduler -memory argument defaulting to 5GB, then you will not be able to run the 10th scheduled task unless one of the 9 scheduled tasks running in parallel finishes execution.
| • | -clean-misfires – Should only be used after migration to version 15.0 (from before version 14.0) if you are not running the Calypso Scheduler right away. This will avoid having dozens of misfires (all the triggers will be marked as no misfire). This should be used only once after the migration. The scheduled tasks should be executed manually in this case. |
1.3 Executing Scheduled Tasks at the Command Line
You can execute scheduled tasks at the command line using the Quartz task runner.
Note that command-line execution requires setting the CLASSPATH variable.
Example on Windows:
setlocal
set CALYPSO_HOME=<calypso home>
Example: set CALYPSO_HOME=C:\calypso\calypso-16.1.0.72
set CLASSPATH=%CALYPSO_HOME%\client\lib\*;%CALYPSO_HOME%\client\resources;%CLASSPATH%
echo %CLASSPATH%
Sample command (this is a one-line command):
java -classpath %CLASSPATH% -Xms512m -Xmx1024m -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=1GB com.calypso.apps.startup.StartQuartzTaskRunner -log -env CAL1610 -user calypso_user -password calypso -taskExtRef "Position snapshot bk USD" -currDate 07/17/20 -valTime 1507
Arguments Details
| • | -currDate – Valuation date. Format: mm/dd/yy |
| • | –env – Environment properties file to be run with |
| • | –log – To write to the log file |
| • | –password – Password of the user |
| • | –task – Scheduled task ask ID given by the system when the scheduled task is configured. You can view the scheduled task IDs in the Scheduled Task Definition and Scheduling window |
| • | -taskExtRef – Scheduled task external reference given by the user. It is the recommended approach as it is a business key that is consistent across systems |
| • | -scheduledTaskType - Scheduled task type - This is not required except for the MARGIN_INPUT scheduled task (from the Margins module) |
| • | –user – User name who runs the scheduled task |
| • | -valuationTime – Valuation time. Format: HHMM (HH is in 24 hour format) |
| • | -Xms512m – Minimum memory for running the scheduled task (optional) |
| • | -Xmx1024m – Maximum memory for running the scheduled task (optional) |
| • | -skipTo - Task ID of a task you want to skip to - When executing a chain, in the case of failure of some scheduled tasks, you can restart the chain by skipping the initially executed scheduled tasks |
You can monitor the execution of the scheduled task from the Execution Report panel in the Scheduled Tasks window.
1.4 Executing Chains at the Command Line
You can execute chains at the command line using the Chain Quartz task runner. It runs each scheduled task in the chain in a separate JVM process.
Sample command (this is a one-line command):
java -Xms512m -Xmx1024m com.calypso.apps.startup.StartChainQuartzTaskRunner -log -env CAL1800 -user calypso_user -password calypso -taskExtRef "EOD reports" -currDate 07/17/20 -valTime 1507
Arguments Details
| • | -currDate – Valuation date. Format: mm/dd/yy. |
| • | –env – Environment properties file to be run with. |
| • | –log – To write to the log file. |
| • | –password – Password of the user. |
| • | –task – Chain ID given by the system when the chain is configured. You can view the chain IDs in the Scheduled Task Definition and Scheduling window. |
| • | -taskExtRef – Chain external reference given by the user. It is the recommended approach as it is a business key that is consistent across systems. |
| • | –user – User name who runs the chain. |
| • | -valuationTime – Valuation time. Format: HHMM (HH is in 24 hour format). |
| • | -Xms512m – Minimum memory for running the chain (optional). |
| • | -Xmx1024m – Maximum memory for running the chain (optional). |
| • | -skipTo - Task ID of a task you want to skip to - In the case of failure of some scheduled tasks, you can restart the chain by skipping the initially executed scheduled tasks. |
You can monitor the execution of the chain from the Execution Report panel in the Scheduled Tasks window.
2. Tour of the Scheduled Tasks Window
From the Calypso Navigator, navigate to Configuration > Scheduled Tasks (menu action scheduling.ScheduledTaskListWindow).
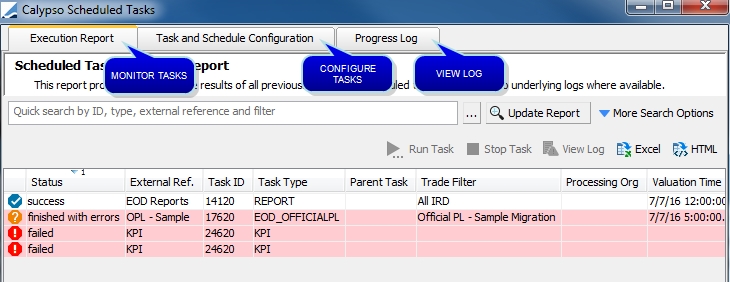
Scheduled Tasks window
| • | You can monitor scheduled tasks execution in the Execution Report panel. |
| • | You can configure scheduled tasks and schedule their execution in the Task and Schedule Configuration panel. |
| • | You can view tasks under processing and completed tasks in the Process Log panel. |
These panels are described below.
Ⓘ [NOTE: If the Calypso Scheduler is not running, the error message shown below will be displayed]
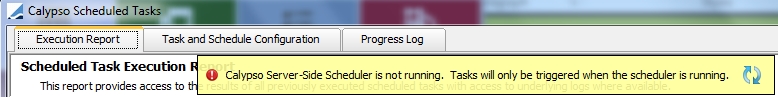
Calypso Scheduler not running error message
3. Execution Report - Task Execution Monitoring
The Execution Report panel allows monitoring the execution of the scheduled tasks. It also allows starting and stopping tasks.
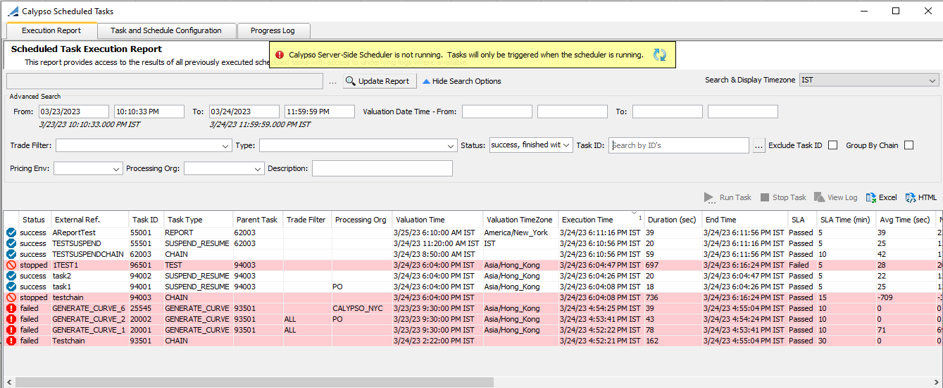
Execution Report panel
| » | Click More Search Options to view and select search criteria as needed. You can also select the timezone next to "More Search Options". |
| – | Exclude Task ID- When checked, the Task IDs provided in the field “Task ID” are excluded from the search. They are included otherwise. |
| – | Group By Chain: |
When checked, if the Task ID is a chain Task ID, all the Child Task IDs are part of the Execution Report. If the Task ID is NOT a chain Task ID, only the Task ID provided in the Task ID field is part of the Execution Report.
When NOT checked, irrespective of whether the Task ID is a chain Task ID or not, only the Task IDs provided in the Task ID field is part of the Execution Report.
| » | Click Update Report to load the corresponding tasks and chains of tasks. |
Once the tasks are loaded, you can perform additional functions as described below.
When a scheduled task does not have a valuation time, and environment property DEFAULT_SCHEDULED_TASK_VALUATION_TIME is not set, the valuation time shows the execution time. If the scheduled task is executed within a chain, the valuation time shows the chain trigger time.
When a scheduled task is executed by a trigger, the valuation date is the trigger date. Otherwise, it is the execution date.
Running a Task
You can select a task or a chain of tasks, and click Run Task to run it again on-the-fly.
Stopping a Task
You can select a task or a chain of tasks currently running, and click Stop Task to stop its execution.
If you stop a scheduled task within a chain, it will stop the chain as well.
View Log
You can select a task or a chain of tasks, and click View Log to view its execution log.
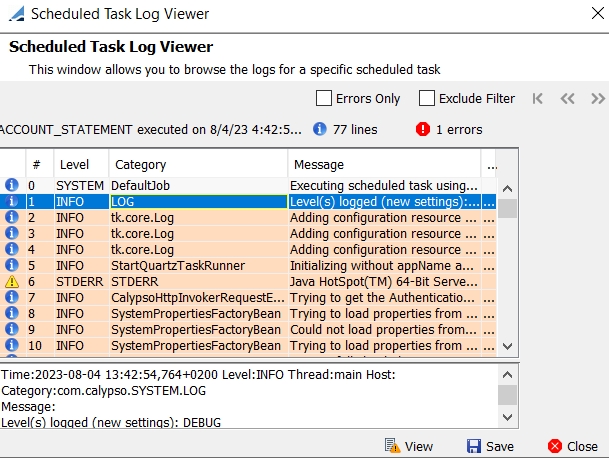
Sample execution log
By default, you can view 20000 rows per page. You can modify the display using environment property VIEW_LOG_PAGE_SIZE.
| » | You can check Errors Only to only view error logs. |
| » | You an check Exclude Filter to exclude messages with repeated patterns. Click ... to defined the patterns to be excluded. |
Example:
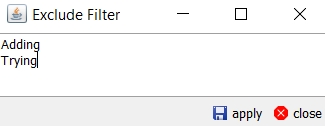
Once you click apply, the rows with the selected patterns are no longer displayed.
[NOTE: Special characters might cause issue while performing filtration on the Scheduled Task Log Viewer as there is a limitation from Lucene’s side]
| » | You can click View to get the full log for a given row in the Filtered Log View window and use Ctrl-F to search the log. |
| » | You can click Save to save the log to a file. |
Log files are stored in a local file based database. By default, log files older than 100 days are purged. You can configure the number of days to keep log files using the environment property SCHEDULED_TASK_LOGS_DAYS_TO_KEEP.
Link schedule task ID to SQL executed on database side
Added new column "CLIENTREQUESTID" in "ServerRequest", "IncomingServerRequest", "SQL" and "ClientRequest" in the log Appender. This will be only visible when log category "Monitoring.ClientRequestId" is enabled for any app or all apps.
This new column will have value as: <User Name>/<App Name>/<Instance_Name>/<Moddule Name>/<pid>/<ST123>/<Unique_GeneratedIdClientSide>
Instance_Name,Module Name, ST id is optional as it will be available based on APP setup.
Exporting the Report
You can click Excel to export the report to an XLSX Worksheet.
You can click HTML to export the report to HTML.
Enhanced Reporting
You can set environment property CalypsoScheduler.Enhanced.Reporting=true to display the following reserved exit codes and status codes:
| • | [0] - Success |
The following exit codes are reserved by Calypso for Windows:
| • | [501] - Not triggered InsufficientMemory |
| • | [502] - Finished with errors |
| • | [503] - Stopped |
| • | [511] - Not triggered TimeElapsed |
| • | [512] - Not triggered DateRule |
| • | All other exit codes are seen as "failed". |
The following exit codes are reserved by Calypso for Linux/MAC OS:
| • | 201 - Not triggered InsufficientMemory |
| • | 202 - Finished with errors |
| • | 203 – Stopped |
| • | 211 - Not triggered TimeElapsed |
| • | 212 - Not triggered DateRule |
| • | All other exit codes are seen as "failed". |
Otherwise (CalypsoScheduler.Enhanced.Reporting=false), [0] is used for Success and "finished with errors", and all other exit codes are seen as "failed".
4. Task and Schedule Configuration - Configuring Scheduled Tasks
The Task and Schedule Configuration panel allows configuring scheduled tasks and scheduling their execution.
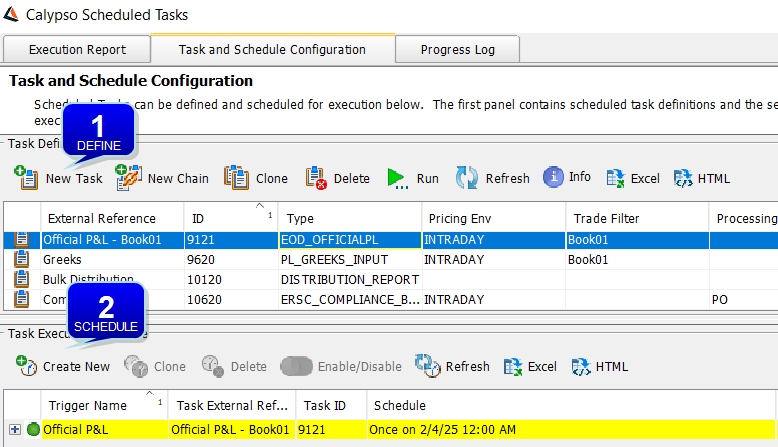
Task and Schedule Configuration panel
Step 1 – Define Tasks and Chains of Tasks
The upper portion of the window displays scheduled tasks that have been configured. It allows configuring new tasks and chains of tasks.
| » | Click New Task to create a new task. It brings up the Scheduled Task Definition window. |
 See Scheduled Task Definition Window for details.
See Scheduled Task Definition Window for details.
| » | You can click New Chain to create a new chain of tasks. It brings up the Task Chain Definition window. |
 See Task Chain Definition Window for details.
See Task Chain Definition Window for details.
| » | You can select a task and delete its configuration using the Delete button. |
| » | You can select a task and execute it on-the-fly using the Run button. |
Using this function will not affect the task's schedule, or any chained task to which it belongs.
It requires the Calypso Scheduler to be running.
| » | You can refresh the window with newly configured tasks using the Refresh button. |
Step 2 – Scheduled Tasks Execution
The lower portion of the window allows scheduling tasks execution. An execution schedule is referred to as a trigger.
| » | Click Create New to create a trigger. |
 See Trigger Definition Window for details.
See Trigger Definition Window for details.
The corresponding task will be executed according to the trigger details.
| » | You can double-click a trigger to view its details and modify it. |
| » | You can click Disable at any time to stop the execution schedule. |
When a trigger is disabled, it will not execute until it is re-enabled. Click Enable to re-enable a disabled trigger.
| » | You can refresh the window with newly configured triggers using the Refresh button. |
| » | You can select a trigger and delete its configuration using the Delete button. |
Ⓘ In the 'Task and Schedule Configuration' window, when a task/chain is selected, any triggers referencing that task/chain are highlighted. Likewise, when a trigger is selected, the associated task/chain is highlighted. Also, when a user selects a task, any chains containing that task or any trigger referencing those chains are highlighted.
Tip - If you want to override trigger information while re-importing trigger details from Config Workbench, you need to set environment property ALLOW_TRIGGER_REIMPORT = true. Default is false, the trigger information is not overwritten.
Exporting the Configurations
You can click Excel to export the configuration list or schedule list to an XLSX Worksheet.
You can click HTML to export the configuration list or schedule list to HTML.
4.1 Scheduled Task Definition Window
This window allows configuring scheduled tasks.
Click New Task in the Task and Schedule Configuration panel.
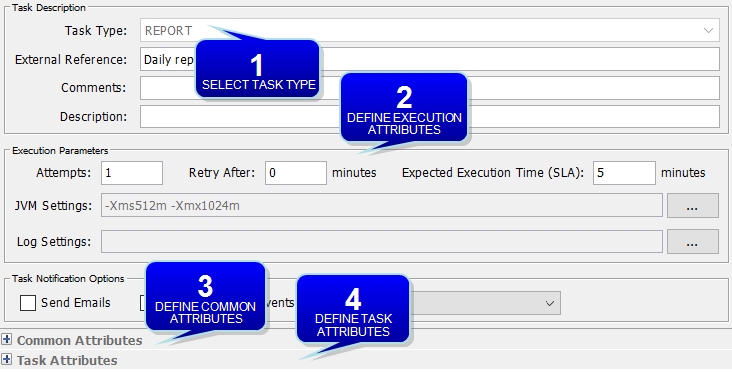
Scheduled Task Definition window
| » | Enter the fields described below then click Save to save the configuration. |
Upon saving, the scheduled task is given a unique id by the system, and it appears in the Task Definitions area.
Definition Details
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Task Type |
Select the task type. The task type selection will display attributes specific to the selected task in the Task Attributes area. Task types are defined in the domain "scheduledTask". |
| External Reference |
Enter an external reference. The external reference is mandatory. It is needed to define an execution schedule for this task. |
| Comments |
Enter comments as needed related to this task. |
| Description |
Enter a description as needed. |
| Attempts |
Enter the number of attempts to retry the task if its execution fails. |
| Retry After |
Enter the number of minutes after which to retry the task execution. |
| Expected Execution Time (SLA) |
Enter the number of minutes that the task should take to complete its execution. You can set 0 for no SLA. The expected execution time is mandatory. An alert will be generated if the execution time is exceeded.
|
| JVM Settings |
Each execution schedule is kicked off in its own JVM, providing the ability to ensure that tasks do not impact other running tasks. It also allows sizing specific tasks with large memory settings using the JVM Settings per task as well as killing tasks executions on-the-fly. As a result, the Calypso Scheduler can execute with limited memory and most tasks that are not memory intensive can do the same. Only tasks with a high-memory requirement can be configured to use a large memory setting using -Xms and -Xmx. It can be selected from a list defined in domain "SCHEDULED_TASK_JVM_SETTINGS". User can select multiple required JVM args from multi select dropdown, which will be concatenated by space. Default JVM setting value will be -Xms512m -Xmx1024m. By default, Calypso has provided -Xmx value from 1g to 10g in "SCHEDULED_TASK_JVM_SETTINGS" domain values.
|
| Send Emails |
Check to send an email to the user selected in the "To user" field upon completion of the scheduled task. The user's email address should be set in the User Defaults. To use the email function, you need to specify your Mail server in a file named The Content of the file should be: HOST= <HostName or IP address of MailServer> PORT= <Port Usually 25> FROM= <from address>
|
| Publish Business Events |
Check to publish a scheduled task event upon completion of the scheduled task. This allows triggering other processes. For example, for the RATE_RESET, OPTION_EXERCISE, and CORPORATE_ACTION scheduled tasks, the corresponding windows will open in the environment of the user selected in the "To user" field. |
Common Attributes
Some of these attributes do not apply to all types of scheduled tasks. The documentation for the individual scheduled tasks specifies the common attributes requirements.
The Timezone, Valuation Time and Valuation Date Offset apply to all scheduled tasks to determine the valuation date.
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| Task ID |
Scheduled task ID given by the system upon saving. |
| Processing Org |
Select a processing organization as needed to limit the scope of the scheduled task. |
| Trade Filter |
Select a trade filter as needed to limit the scope of the scheduled task. |
| Filter Set |
Select a filter set as needed to limit the scope of the scheduled task. |
| Pricing Environment |
Select a pricing environment to retrieve market data. |
| Timezone |
Select the timezone to determine the valuation time. |
|
Valuation Time Hour Valuation Time Minute |
Enter the valuation time at which data will be retrieved on the valuation date in the selected timezone. You can specify hour "24" and minute "00" - It will be interpreted as 23:59:59:999. You can set the default valuation time (24 hour format HHMM) in the environment property DEFAULT_SCHEDULED_TASK_VALUATION_TIME. If not set on the scheduled task or in the environment property, the default valuation time is the scheduled task’s execution time. |
|
Undo Time Hour Undo Time Minute |
Enter an undo time as applicable. It determines the time of the trade version that should be used. This only applies if the Audit mode is enabled. You can specify hour "24" and minute "00" - It will be interpreted as 23:59:59:999. Can be mandatory based on the type of scheduled task, and is specified in the documentation for the individual scheduled tasks. |
| Valuation Date Offset |
Enter a number of days to adjust the valuation date from the current date. The valuation date is used to retrieve data. Valuation date = current date - offset. For example, an offset of 2 indicates that the scheduled task will use data from 2 days ago. |
|
From Days To Days |
Enter a number of days in the From Days field to compute the start date from the valuation date. Start date = valuation date - abs(from days). Enter a number of days in the To Days field to compute the end date from the valuation date. End date = valuation date + abs(to days). For example, today is April 21. Val Date Offset is 1 and From Days/To Days is 5/2. The valuation date is Apr 20, start date is April 15, and end date is April 22. They are adjusted based on the selected business holiday calendars. Ⓘ [NOTE: This is the default behavior - Some scheduled tasks may have a different behavior, which is explained with the scheduled task] |
| Pricer Measures |
Select a list of pricer measures that should be computed by the scheduled task as applicable. Can be mandatory based on the type of scheduled task, and is specified in the documentation for the individual scheduled tasks. |
| Business Holidays | Select holiday calendar to compute the start date and end date. |
Task Attributes
Set the attributes of the scheduled task based on its type.
The task attributes are described in the documentation for the individual scheduled tasks.
The following notifications can be sent to the user running the scheduled task (through the Calypso Scheduler or at the command line) regardless of the "Send Emails" setting.
The user's email address should be set in the User Defaults.
To use the email function, you need to specify your Mail server in a file named calypso_mail_config.properties that should be deployed on your application servers.
The content of the file should be:
HOST= <HostName or IP address of MailServer>
PORT= <Port Usually 25>
FROM= <from address>
You can set the following environment properties:
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications=true or false - Provides global control over whether emails are sent or not (must be true for the other notifications to be sent) |
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications.FinishedWithErrors=true or false - Provides ability to choose whether email is sent when scheduled task finishes with errors |
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications.NotTriggeredInsufficientMemory=true or false - Provides ability to choose whether email is sent when scheduled task is not triggered due to insufficient memory |
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications.OnFailure=true or false - Provides ability to choose whether or not failure emails are sent |
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications.OnImmediateMissedSLA=true or false - Provides ability to choose whether email is sent when the SLA is missed even as the task is still running |
| • | CalypsoScheduler.Notifications.OnMissedSLA=true or false - Provides ability to choose whether email is sent when the SLA is missed after the task is finished |
4.2 Task Chain Definition Window
This window allows defining chains of tasks that will be executed based on their order in the chain.
Click New Chain in the Task and Schedule Configuration panel.
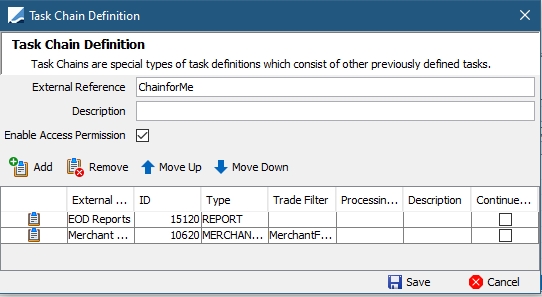
Task Chain Definition window
| » | Enter an external reference for the chain. The external reference is mandatory. It is needed to define an execution schedule for this chain of tasks. |
| » | Enter a free form comment as needed. |
| » | Click Add to add tasks to the chain. You will be prompted to select the tasks you want to chain from the list of configured tasks. |
Note that only tasks that do not already belong to that chain will appear for selection.
You can move the scheduled tasks up or down. They will be executed in the order in which they are displayed.
You can now double-click a scheduled task to view its definition.
| » | You can check the "Continue on Error" checkbox to allow the system to continue running a chain of tasks even if the corresponding task fails or has an error. Otherwise, the execution of the chain will be interrupted. |
| » | Click Save to save the chain. |
The task type of a chain is set to CHAIN. A chain appears with the following icon.
![]()
You can double-click a chain to view its content.
Chain Access Permissions
Access permissions can be used at individual chain level as well as being assigned with Group Access.
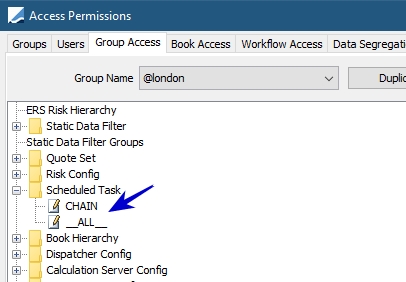
Chain access permission designation at Group level
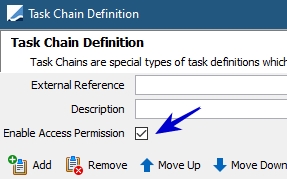
Chain access permission designation at individual level
Users can see a particular chain only if:
| • | the user is given permission to run the chain (Group Access in access permissions) |
| • | the user is allowed to run the chain (Group Access in access permissions) and all the tasks present inside the chain |
| • | the user is allowed to run the chain, may not have permission to execute all the tasks present inside the chain and the access permission at (individual) chain level is disabled (though in the report section or Task Chain definition, only the task which the logged user could execute could will be visible) |
In short, if the user has access to run the chain (Group Access in Access Permissions), and the access permission at (individual) chain level is enabled, that chain will be visible to the user only if the logged in user has access to run all the tasks inside that chain.
The access permission is disabled by default for all chains. Only the users who have access to create or update the chain can enable/disable the access permission.
Additionally, a check has been added to allow users to run the chain/scheduled task only if they have permission. By default this is disabled. To enable it, define the domain value STPermissioningEnabled in the function domain.
4.3 Trigger Definition Window
This window allows defining execution schedules for the tasks and chains.
Click Create New in the Task and Schedule Configuration panel.
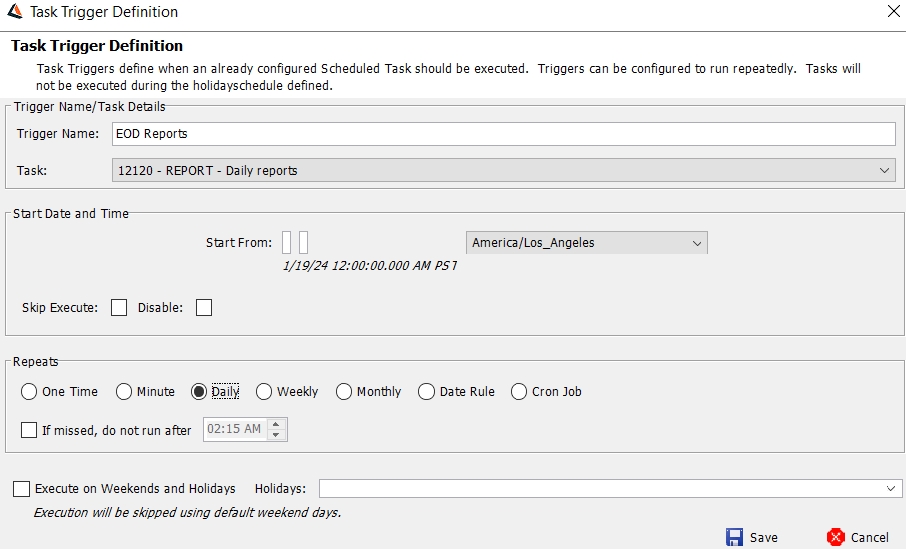
Trigger Definition Window
| » | Enter a trigger name. It will be used to start the execution. |
| » | Select a task or a chain of tasks from the Task Name field. |
| » | Enter the start date and time, and select the execution timezone. |
| » | You can check"Skip Execute" to skip the execution of a scheduled task if its execution was missed because the Calypso Scheduler was not running. It will be executed the next time it is due. |
Otherwise a missed scheduled task will be executed as soon as the Calypso Scheduler is started.
| » | You can check the "Disable" checkbox to disable the trigger. |
| » | Select the execution frequency: |
| – | One Time. |
| – | Minute: Select the interval in minutes. |
| – | Daily: You can specify a time after which the trigger will not be executed if it missed the start time. |
| – | Weekly: Cycles weekly based on the "Start From" date and time. |
| – | Monthly: Cycles monthly based on the "Start From" date and time. |
| – | Date Rule: Select a date rule. |
| – | Cron Job: Enter a Cron expression. |
| » | Select the "Execute on Weekends and Holidays" checkbox to allow the trigger to be executed on weekends and holidays. |
| – | Checking this box will cause the system to ignore non-business days and holidays defined in the holiday calendar. |
 See “Defining Holiday Calendars” for details.
See “Defining Holiday Calendars” for details.
| » | Select one or more holiday calendars in the "Holidays" list to determine the days on which the trigger will not be executed, provided "Execute on Weekends and Holidays" is not checked. |
| – | When multiple holiday calendars are selected, those non-business days and holidays are combined and, together, are skipped by the scheduled task. |
| – | When left blank, the system uses the holiday calendar specified in User Defaults. |
 See “Defining User Defaults” for details.
See “Defining User Defaults” for details.
| » | Click Save to save the trigger. |
5. Process Log - Viewing Execution Logs
The Process Log panel allows viewing tasks under processing, and completed tasks.
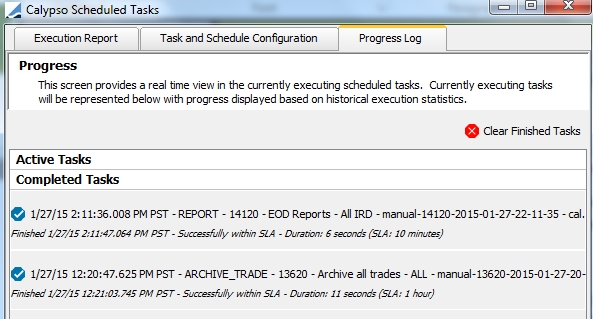
Process Log panel
6. Limitations
There are special scenarios that may impede the functionality of the Calypso Scheduler. These scenarios should be avoided. If an error occurs, check the log for full details.
Case 1
Only one particular task type, defined by task ID, can run in the Scheduler at any given time.
Example: A task with ID_123 cannot run if there is another trigger running task with ID_123 configured to run concurrently. Running concurrent tasks will cause and error. Concurrent runs happen in the future when 2 triggers are configured for the same task run almost identically. Check the log for details.
Case 2
Each task has a specific amount of memory assigned. They might run in parallel or not depending on the overall allotted memory of the Calypso Scheduler.
Example: TASK_123 and TASK_567 use 300MB of memory each. If both are triggered to run at the same time, and the Calypso Scheduler is run with -memory = 512MB, TASK_567 will not start until TASK_123 is finished. Check the log for details.
Case 3
Defining scheduled tasks to run with an attempt/retry designation could cause an error if there has been a trigger to run the same task.
Example: TASK_123 is set to run at 1800 hours with 3 retries every ten minutes. If the task fails, it will retry in 11 minutes, i.e. run for 1 minute, fail, then wait 10 minutes to retry. This would set the task to run at 1800hrs, 1811hrs, and 1822hrs. If the same task has a trigger set on it to run every 10 minutes if a failure occurs, the task could restart during the time lag, i.e. start, fail, and retry at 1810hrs, 1820hrs and 1830hrs. Because of the time lag, TASK_123 would run against itself at 1811hrs (fail/retry), overlapping the 1810hrs (trigger definition). This would cause an error. Check the log for details.
Case 4
You can set multiple triggers for the same task. If the trigger sets the task to run against another trigger on the same task, the task could run with another instance of itself, causing an error.
Example: TASK_123 has a trigger to run if a filter detects a certain date rule. TASK_123 will also run if a filter detects a certain book. If the book and the date rule filters trigger the task in the same time period, there will be a error.