Pricing Script Definition
![]() Download PDF - Pricing Script Reference Guide
Download PDF - Pricing Script Reference Guide
A Pricing Script can be used for exotic modeling of Equity Structured Options, Bond Exotic Notes, and various product types in the Pricing Sheet. The Pricing Script allows defining event based payoffs and features difficult to capture as generic products.
It is recommended that you involve the Customer Delivery Team in the implementation of exotic product payoffs via pricing scripts.
Ⓘ [NOTE: Only Calypso approved pricing scripts are supported]
Option Pricing Scripts
"Option" related pricing scripts must be defined in the domain “PricingScript.OPTIONS” by script name. This allows proper option accounting.
FX TARF Pricing Scripts
FX TARF pricing scripts must be defined in the domain “PricingScript.TARF” by script name. This allows proper FX TARF accounting.
Also, the STRIKE variable must be mapped to the variable defined in the pricing script using the window “Mapping for Pricing Script Report” (menu action refdata.MappingPricingScriptReportWindow).
1. Pricing Script Overview
Choose Calypso Navigator > Configuration > System > Add Pricing Script Definition (menu action product.cfcalc.PricingScriptDefinitionWindow) to open the Pricing Script Definition window.
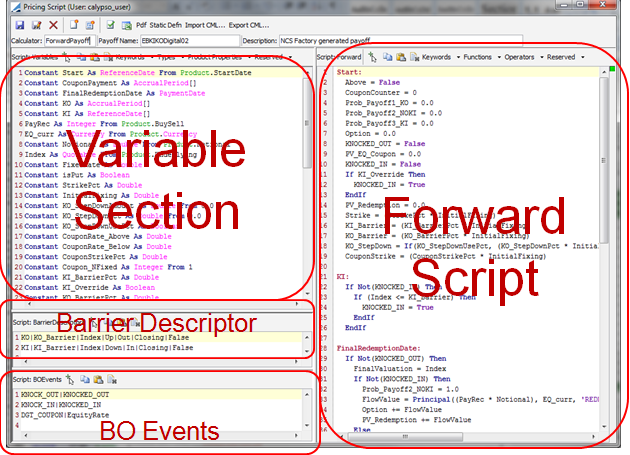
Pricing Script Definition window
The Pricing Script Definition window contains two main script sections. The left panel is the variables section, where all variables and events are defined, and the right side is the forward script.
You can choose Script: Variables > Declaration to define the variables or Script: Variables > Meta Data to view the variables in table format and set meta data as needed.
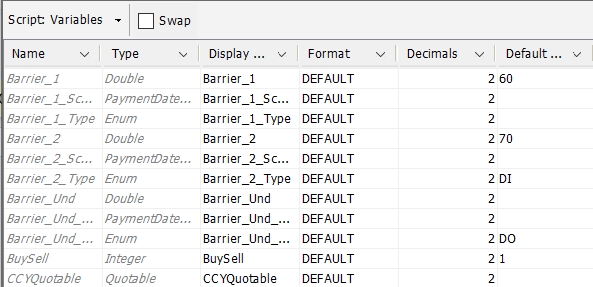
1.1 Starting Points
Defining a payoff script is essentially writing the pricer. There are two main goals:
| • | Program the product’s cashflows |
| • | Return an NPV to the product |
1.2 Basic Script Example
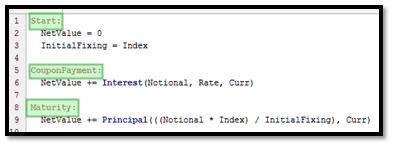
The pricing script is an event based forward script. This means, there is defining of the events of the payoff (coupons, fixings, redemptions, etc.) and the corresponding actions as blocks of code. These are then executed in the order in which they are specified.
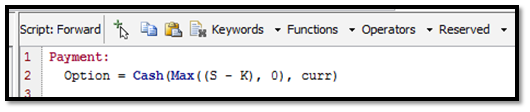
A vanilla call option can be captured as one event "Payment" where the amount Max(Spot-Strike,0) is paid out. The function call Cash() does two things:
| • | Generates the cashflows |
| • | Defines NPV by returning the forward value of the payment |
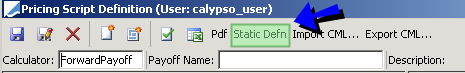
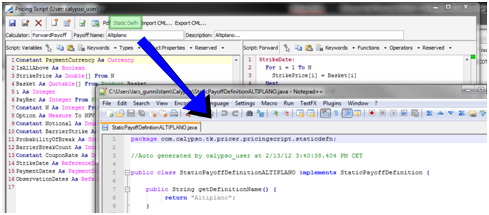
1.3 Static Definition
A payoff can also be exported as java code for jar packaging by clicking "Static Definition".
2. Setup
2.1 System Lock
In order to save pricing script definitions, the following user environment flags have to be set.
ALLOW_SAVE_PRICING_SCRIPT_VARIABLES_TABLE=true
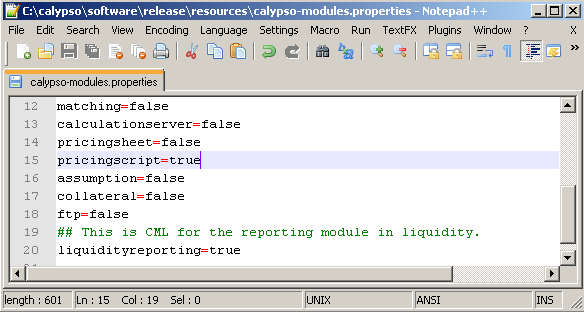
2.2 Calypso ML Activation
In order to use Calypso ML import/export, the file "calypso-module.properties" needs to contain "pricingscript=true".
The file is found under <calypso_home>/resources/.
Ⓘ [NOTE: Changes to resources have to be re-deployed to your application servers. Please refer to the Calypso Installation Guide for details]
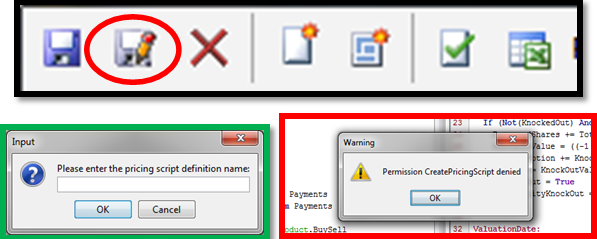
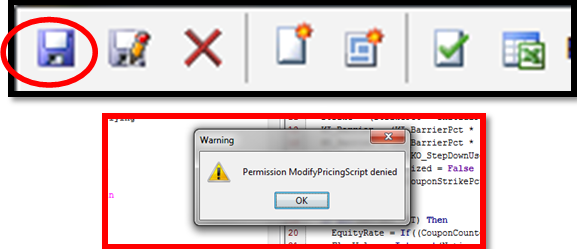
2.3 Access Permissions
Access permissions for creating, modifying and removing scripts can be configured in the Access Permissions window, panel "Group Access".
The following functions apply to the Pricing Script Definition window. If they are not available for selection, you can add them to the function domain.
CreatePricingScript
ModifyPricingScript
RemovePricingScript
3. Execution process
3.1 Introduction
To be able to write the scripts, it is crucial to understand the execution process. The following determines the execution process.
Order of Code Blocks within the Pricing Script
Trade Setup: The dates assigned by trade to schedules
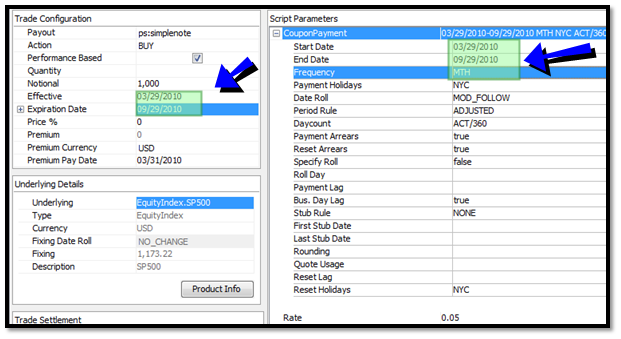
When the trade is configured, the event grid visualizes the execution pattern, and the user can verify this against the term sheet.
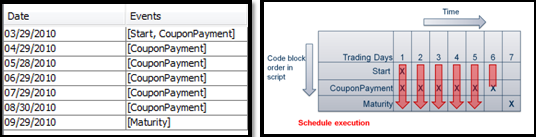
The cashflows are then generated based on the execution sequence and the event code.
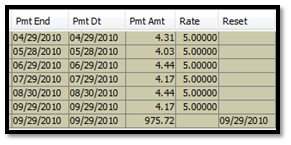
3.2 Code Example trade ShortPath
The ShortPath payoff definition is an example of a payoff with four schedules.
The code is divided into blocks, with one event per schedule. The code will be executed once per event date. The union of all events constitutes the event dates.
For each event date, the code is executed from top to bottom, and only the events that take place on the current execution date are taken into consideration.
Short Overview:
| • | Start date – Variables are set to their initial values. |
| • | IR Coupon Date – A floating rate coupon is paid, using the quotable IR_FloatRef. Payments are added to the PriceLegIR measure. |
| • | EQ Coupon Date – An equity linked payment takes place that uses the quotable array Basket. Any payments are added to the PriceLegEQ measure. |
| • | Maturity – Final redemption is calculated and paid out. The final note price is calculated by adding PriceLegEQ + PriceLegIR. |
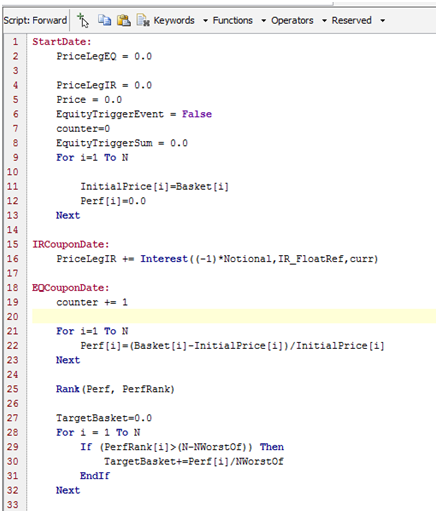
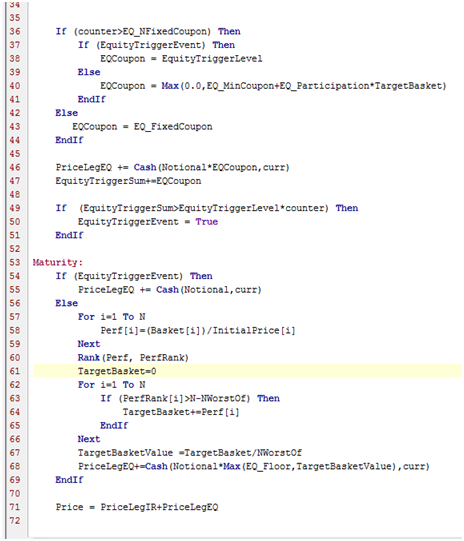
Meta Data
You can choose
3.3 Trade Capture
Pricing Script trades are captured using the Pricing Sheet - Please refer to Calypso Pricing Sheet documentation for details.